kube-apiserver 权限控制
kube-apiserver( Kubernetes API Server)作为Kubernetes集群的请求入口,接收集群中组件与客户端的访问请求,kube-apiserver对接口请求访问,提供了3种安全权限控制,每个请求都需要经过认证、授权及准入控制器才有权限操作资源对象。
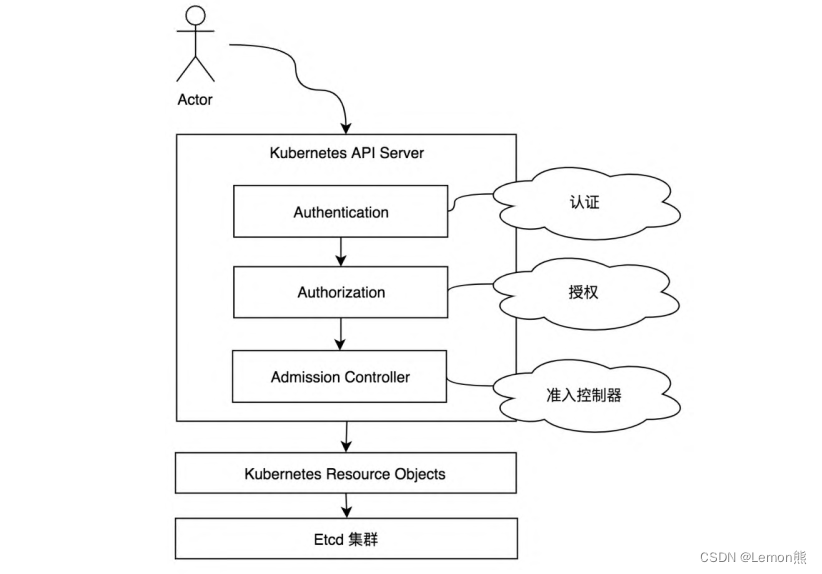
- 认证:确认是否具有访问Kubernetes集群的权限,针对请求的认证。
- 授权:确认是否对资源具有相关权限,针对资源的授权。
- 准入控制器:在认证和授权之后,对象被持久化之前,拦截kube-apiserver的请求,拦截后的请求进入准入控制器中处理,对请求的资源对象进行自定义( 校验、 修改或拒绝)等操作。
认证
? kube-apiserver目前提供了9种认证机制,分别是BasicAuth、ClientCA、TokenAuth、BootstrapToken、RequestHeader、WebhookTokenAuth、Anonymous、OIDC、ServiceAccountAuth。每一种认证机制被实例化后会成为认证器(Authenticator) 。每一个认证器都被封装在http.Handler请求处理函数中,它们接收组件或客户端的请求并认证请求。
Authenticator 实例化
Authenticator 的实例化是在apiserver启动时设置通用配置时完成。通过Authentication.ApplyTo()创建认证配置,ApplyTo()中执行 authenticatorConfig.New()方法将9种不同的认证机制实例化成 Authenticator(认证器)并将所有的合并到合并成authenticator对象。实例化的authenticator对象会保存在genericConfig.Authentication.Authenticator。
authenticator为 unionAuthRequestHandler结构体,unionAuthRequestHandler中的Handlers数组中保存着所有的认证器。unionAuthRequestHandler 的 AuthenticateRequest()方法为认证处理函数,改函数中会遍历所有的认证器,调用每个认证器对应的 AuthenticateRequest()方法对请求进行认证,如果有一个认证器认证成功就返回ok。
func (authHandler *unionAuthRequestHandler) AuthenticateRequest(req *http.Request) (*authenticator.Response, bool, error) {
var errlist []error
// 遍历 Handlers数组
for _, currAuthRequestHandler := range authHandler.Handlers {
// 执行每个每个认证器对应的 AuthenticateRequest()方法对请求进行认证
resp, ok, err := currAuthRequestHandler.AuthenticateRequest(req)
if err != nil {
if authHandler.FailOnError {
return resp, ok, err
}
errlist = append(errlist, err)
continue
}
if ok {
returnresp, ok, err
}
}
return nil, false, utilerrors.NewAggregate(errlist)
}
Authenticator 的执行
认证器处理函数由 WithAuthentication() 函数定义并返回, WithAuthentication()函数会被函数 DefaultBuildHandlerChain()函数调用将认证处理函数封装到http.Handler请求处理函数中。
func WithAuthentication(handler http.Handler, auth authenticator.Request, failed http.Handler, apiAuds authenticator.Audiences, requestHeaderConfig *authenticatorfactory.RequestHeaderConfig) http.Handler {
return withAuthentication(handler, auth, failed, apiAuds, requestHeaderConfig, recordAuthenticationMetrics)
}
func withAuthentication(handler http.Handler, auth authenticator.Request, failed http.Handler, apiAuds authenticator.Audiences, requestHeaderConfig *authenticatorfactory.RequestHeaderConfig, metricsauthenticationRecordMetricsFunc) http.Handler {
if auth == nil {
klog.Warning("Authenticationisdisabled")
return handler
}
...
// 定义并返回认证处理函数
return http.HandlerFunc(func(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
authenticationStart := time.Now()
if len(apiAuds) > 0 {
req = req.WithContext(authenticator.WithAudiences(req.Context(), apiAuds))
}
// 执行认证器处理函数,认证器的实例化在上面有过分析
resp, ok, err := auth.AuthenticateRequest(req)
authenticationFinish := time.Now()
defer func() {
metrics(req.Context(), resp, ok, err, apiAuds, authenticationStart, authenticationFinish)
}()
// 认证失败,返回错误
if err != nil || !ok {
if err != nil {
klog.ErrorS(err, "Unabletoauthenticatetherequest")
}
failed.ServeHTTP(w, req)
return
}
...
req = req.WithContext(genericapirequest.WithUser(req.Context(), resp.User))
handler.ServeHTTP(w, req)
})
}DefaultBuildHandlerChain()函数中会调用认证、授权等功能相应的函数对http.Handler请求处理函数进行封装,对认证处理器的封装由调用WithAuthentication()函数完成。
func DefaultBuildHandlerChain(apiHandler http.Handler, c *Config) http.Handler {
handler := apiHandler
...
// 调用 WithAuthorization()函数获取授权器处理函数,授权器 c.Authorization.Authorizer作为参数
handler = genericapifilters.WithAuthorization(handler, c.Authorization.Authorizer, c.Serializer)
...
// 调用 WithAuthentication()函数获取认证器处理函数,认证器 c.Authentication.Authenticator作为参数
handler = genericapifilters.WithAuthentication(handler, c.Authentication.Authenticator, failedHandler, c.Authentication.APIAudiences, c.Authentication.RequestHeaderConfig)
}
创建通用配置流程为NewConfig()->CreateKubeAPIServerConfig()->BuildGenericConfig()->genericapiserver.NewConfig()。
其中genericapiserver.NewConfig()函数中,实例化config时指定Config.BuildHandlerChainFunc为DefaultBuildHandlerChain()。
Config.BuildHandlerChainFunc()函数在创建服务时被执行。
// 函数调用过程:NewConfig()->CreateKubeAPIServerConfig()->BuildGenericConfig()->genericapiserver.NewConfig()
func NewConfig(codecs serializer.CodecFactory) *Config {
...
// 实例化 Config
return &Config{
...
BuildHandlerChainFunc: DefaultBuildHandlerChain, // 指定Config.BuildHandlerChainFunc为DefaultBuildHandlerChain
...
}
}
在创建APIExtensionsSerer、KubeAPIServer、AggregatorServer 3个服务时都首先会调用GenericConfig.New()创建通用服务GenericAPIServer。
GenericConfig.New()中会先调用c.BuildHandlerChainFunc()函数获取handlerChainBuilder对象。
然后调用函数NewAPIServerHandler()实例化apiServerHandler,NewAPIServerHandler()函数中会设置 apiServerHandler.FullHandlerChain 为 Config.BuildHandlerChainFunc。
最后将 apiServerHandler 赋值给 GenericAPIServer.Handler。
func (c completedConfig) New(name string, delegationTarget DelegationTarget) (*GenericAPIServer, error) {
...
// 调用 c.BuildHandlerChainFunc()返回认证器处理函数
handlerChainBuilder := func(handler http.Handler)http.Handler {
return c.BuildHandlerChainFunc(handler, c.Config)
}
...
// 实例化 apiServerHandler,设置 apiServerHandler.FullHandlerChain为 Config.BuildHandlerChainFunc
apiServerHandler := NewAPIServerHandler(name, c.Serializer, handlerChainBuilder, delegationTarget.UnprotectedHandler())
// 将 GenericAPIServer.Handler赋值为 apiServerHandler
s := &GenericAPIServer {
...
Handler: apiServerHandler,
...
}
}
这时我们知道apiServerHandler.FullHandlerChain包含着认证器的处理函数,下面我们来分析的apiServerHandler.FullHandlerChain执行过程。
因为apiServerHandler实现了ServeHTTP(ResponseWriter, *Request)方法,所以是一个http.Handler实例。
启动http服务的流程为prepared.Run()->preparedGenericAPIServer.Run()->NonBlockingRun()->SecureServingInfo.Serve()。
在SecureServingInfo.Serve()函数中,实例化http.Server时,指定 server.Handler为 apiServerHandler。
func (s preparedGenericAPIServer) NonBlockingRun(stopCh <-chan struct{}, shutdownTimeout time.Duration) (<-chanstruct{}, <-chan struct{}, error) {
...
// 执行 Serve函数,apiServerHandler被为参数
stoppedCh, listenerStoppedCh, err = s.SecureServingInfo.Serve(s.Handler, shutdownTimeout, internalStopCh)
if err != nil {
close(internalStopCh)
return nil, nil, err
}
...
}
func (s *SecureServingInfo) Serve(handler http.Handler, shutdownTimeout time.Duration, stopCh <-chan struct{}) (<-chan struct{}, <-chanstruct{}, error) {
...
secureServer := &http.Server {
Addr: s.Listener.Addr().String(),
Handler: handler, // 指定 server.Handler为 apiServerHandler
MaxHeaderBytes: 1 << 20,
TLSConfig: tlsConfig,
IdleTimeout: 90 * time.Second,
ReadHeaderTimeout: 32 * time.Second,
}
}
server.Handler.ServeHTTP()会在处理客户端请求时执行,也就是执行了APIServerHandler.ServeHTTP方法,而APIServerHandler.ServeHTTP方法中会执行apiServerHandler.FullHandlerChain函数,即执行了认证器的处理函数。
// 函数调用过程:prepared.Run()->preparedGenericAPIServer.Run()->NonBlockingRun()->SecureServingInfo.Serve()->RunServer()->server.Serve()
func (srv *Server) Serve(l net.Listener) error {
...
// 循环处理客户端请求
for{
rw, err := l.Accept()
c := srv.newConn(rw)
c.setState(c.rwc, StateNew, runHooks) // before Serve can return
// 为每一个连接开启一个goroutines
go c.serve(connCtx)
}
}
func(c *conn) serve(ctx context.Context) {
// 读取数据和其他的流程忽略
...
// 执行 APIServerHandler.ServeHTTP
serverHandler{c.server}.ServeHTTP(w,w.req)
}
授权
? 在客户端请求通过认证之后,会来到授权阶段。kube-apiserver同样也支持多种授权机制,并支持同时开启多个授权功能, 客户端请求在授权阶段,只要有一个授权器通过则授权成功。
? kube-apiserver目前提供了6种授权机制,分别是AlwaysAllow、AlwaysDeny、ABAC、Webhook、RBAC、Node,可通过指定--authorization-mode参数设置授权机制。
???每一种授权机制被实例化后会成为授权器(Authorizer) ,每一个授权器都被封装在http.Handler函数中,它们接收组件或客户端的请求并授权请求。
? 在kube-apiserver中,授权有3个概念,分别是Decision决策状态、授权器接口、RuleResolver规则解析器。
- Decision决策状:用于决定是否授权成功,如下。
const(
// 表示授权器拒绝该操作。
DecisionDeny Decision=iota
// 表示授权器允许该操作。
DecisionAllow
// 表示授权器对是否允许或拒绝某个操作没有意见,会继续执行下一个授权器。
DecisionNoOpinion
)
- 授权器接口:每一种授权机制都需要实现Authorize()授权器接口方法,该方法会接收一个Attributes参数。Attributes是决定授权器从HTTP请求中获取授权信息方法的参数,例如GetUser、GetVerb、GetNamespace、GetResource等获取授权信息方法。如果授权成功,Decision决策状态变为DecisionAllow;如果授权失败,Decision决策状态变为DecisionDeny,并返回授权失败的原因。
- RuleResolver规则解析器:每个授权器都需要实现RulesFor方法,RulesFor方法通过接收的user用户信息及namespace命名空间参数,解析出规则列表并返回。规则列表分为如下两种。
- ResourceRuleInfo: 资源类型的规则列表,例如/api/v1/pods的资源接口。
- NonResourceRuleInfo: 非资源类型的规则列表,例如/api或/health的资源接口。
授权器实例化
? 授权器的实例化也是在apiserver启动时设置通用配置时完成,调用BuildAuthorizer()函数创建授权器和RuleResolver规则解析器。所有的授权器会被合并成unionAuthzHandler类型对象,该类型是一个[]authorizer.Authorizer切片,unionAuthzHandler的Authorize()方法中会遍历已启用的授权器列表并执行授权器。
type unionAuthzHandler []authorizer.Authorizer
//Authorizesagainstachainofauthorizer.Authorizerobjectsandreturnsnilifsuccessfulandreturnserrorifunsuccessful
func (authzHandler unionAuthzHandler) Authorize(ctx context.Context, a authorizer.Attributes)(authorizer.Decision, string, error) {
var(
errlist []error
reasonlist []string
)
// 遍历授权器列表
for _, currAuthzHandler := range authzHandler {
// 执行授权器
decision, reason, err := currAuthzHandler.Authorize(ctx, a)
if err != nil {
errlist = append(errlist, err)
}
if len(reason) != 0 {
reasonlist = append(reasonlist, reason)
}
switch decision {
case authorizer.DecisionAllow, authorizer.DecisionDeny:
// 只要有一个授权器通过,则返回授权成功
return decision, reason, err
case authorizer.DecisionNoOpinion:
// continue to the next authorizer
}
}
return authorizer.DecisionNoOpinion, strings.Join(reasonlist, "\n"), utilerrors.NewAggregate(errlist)
}授权器的执行
? WithAuthorization()函数会返回kube-apiserver的授权Handler方法。和认证器的配置相同,WithAuthorization函数会在DefaultBuildHandlerChain()中被调用。其他的处理流程认证器相同。
???授权器处理函数的执行和认证器相同,都会被封装在http.Handler函数中,在处理客户端请求时执行。
func WithAuthorization(hhandler http.Handler,auth authorizer.Authorizer,s runtime.NegotiatedSerializer) http.Handler {
return withAuthorization(hhandler, auth, s, recordAuthorizationMetrics)
}
func withAuthorization(handler http.Handler,a authorizer.Authorizer, sruntime.NegotiatedSerializer, metrics recordAuthorizationMetricsFunc) http.Handler {
// 如果a授权器为空, 则说明kubeapiserver未启用任何授权功能
if a == nil {
klog.Warning("Authorization is disabled")
return handler
}
return http.HandlerFunc(func (w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
ctx := req.Context()
authorizationStart := time.Now()
// 从HTTP请求中获取客户端信息
attributes, err := GetAuthorizerAttributes(ctx)
if err != nil {
responsewriters.InternalError(w,req,err)
return
}
// 对请求进行授权
authorized, reason, err := a.Authorize(ctx, attributes)
authorizationFinish := time.Now()
defer func() {
metrics(ctx, authorized, err, authorizationStart, authorizationFinish)
}()
//an authorizer like RBAC could encounter evaluation errors and still allow the request, so authorizer decision is checked befor eerror here.
if authorized == authorizer.DecisionAllow {
audit.AddAuditAnnotations(ctx,
decisionAnnotationKey, decisionAllow,
reasonAnnotationKey, reason)
handler.ServeHTTP(w, req)
return
}
if err != nil {
// 返回 HTTP 401 Unauthorized
audit.AddAuditAnnotation(ctx, reasonAnnotationKey, reasonError)
responsewriters.InternalError(w, req, err)
return
}
klog.V(4).InfoS("Forbidden", "URI", req.RequestURI, "reason", reason)
audit.AddAuditAnnotations(ctx,
decisionAnnotationKey, decisionForbid,
reasonAnnotationKey, reason)
responsewriters.Forbidden(ctx, attributes, w, req, reason, s)
})
}
准入控制器
准入控制器会在验证和授权请求之后,对象被持久化之前,拦截kube-apiserver的请求,拦截后的请求进入准入控制器中处理,对请求的资源对象执行自定义(校验、修改或拒绝等)操作。准入控制器以插件的形式运行在kube-apiserver进程中,也可以将每个准入控制器称为准入控制器插件。
kube-apiserver支持多种准入控制器机制,并支持同时开启多个准入控制器功能,如果开启了多个准入控制器,则按照顺序执行准入控制器。
客户端发起一个请求,在请求经过准入控制器列表时,只要有一个准入控制器拒绝了该请求,则整个请求被拒绝(HTTP 403 Forbidden)并返回一个错误给客户端。
kube-apiserver目前支持如下两种准入控制器。
- 变更准入控制器(Mutating Admission Controller):用于变更信息,能够修改用户提交的资源对象信息。
- 验证准入控制器(Validating Admission Controller):用于身份验证,能够验证用户提交的资源对象信息。
提示:变更准入控制器运行在验证准入控制器之前。
变更准入控制器和验证准入控制器接口在文件vendor/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/admission/interfaces.go中定义,分别是MutationInterface和ValidationInterface。有些准入控制器可能同时实现了Admit和Validate方法,能够执行变更操作,也能够执行验证操作,例如AlwaysPullImages准入控制器。
type Interface interface {
Handles(operation Operation) bool
}
type MutationInterface interface{
Interface
Admit(ctx context.Context, a Attributes, o ObjectInterfaces) (err error)
}
type ValidationInterface interface {
Interface
Validate(ctx context.Context, a Attributes, o ObjectInterfaces) (err error)
}
kube-apiserver中的所有已启用的准入控制器(Admit方法及Validate方法)由 vendor/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/admission/chain.go下的chainAdmissionHandler []Interface数据结构管理。
准入控制器配置
在函数CreateKubeAPIServerConfig()中,创建通用配置后,执行opts.Admission.ApplyTo()完成准入控制器插件的注册。Admission.ApplyTo()->a.GenericAdmission.ApplyTo()。
func (a*AdmissionOptions) ApplyTo(
c *server.Config,
informers informers.SharedInformerFactory,
kubeClient kubernetes.Interface,
dynamicClient dynamic.Interface,
features featuregate.FeatureGate,
pluginInitializers ...admission.PluginInitializer,
)error {
if a == nil {
return nil
}
...
// 所有插件名称
pluginNames := a.enabledPluginNames()
...
// 注册插件
admissionChain, err := a.Plugins.NewFromPlugins(pluginNames, pluginsConfigProvider, initializersChain, a.Decorators)
if err != nil {
return err
}
c.AdmissionControl = admissionmetrics.WithStepMetrics(admissionChain)
return nil
}
所有的准入控制器会被合并成pluginHandlerWithMetrics类型对象记录到c.AdmissionControl中。pluginHandlerWithMetrics类型实现了Admit()和Validate()方法。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 使用Dependency Walker和Process Explorer排查瑞芯微工具软件RKPQTool.exe启动报错问题
- procise纯PL流程点灯记录
- Servlet技术j详解1
- NVMe over Fabrics:概念、应用和实现
- 力扣题目-JAVA解法
- 飞天使-k8s知识点10-kubernetes资源对象3-controller
- 前端性能优化三十一:花裤衩模板webpack DllPlugin
- 机器学习——特征提取
- Linux———groupadd,groupdel,groupmod命令联合总结(狠狠爱住)
- Java面试题126-135