hack_back_ckpt.rcs 教程:gem5 从检查点恢复并使用和检查点不同的script
简介
gem5 检查点可以作为加速,跳过不需要的部分。但是每次restore恢复的时候,因为disk fixed,使用的仍然是创建检查点时的脚本。这样每一次运行不同的脚本的时候就需要创建不同的检查点,失去了用检查点从而跳过系统启动时间的意义。hack_back_ckpt.rcs可以实现这个过程但是并没有具体的介绍如何使用依旧如何更改。实际上,在2023 gem523的版本,这个文件不能直接使用而是需要更改。我更改的全部代码在文后,并且提供了讲解。
关键点
分别是read两次,echo/cat 显示来确认新脚本加载成功,然后用bash而不是原文的exec避免报错
read 两次
原hack_back_ckpt.rcs文件只用了一次,这样还是老脚本,新制定的–script 不起作用。
/sbin/m5 readfile > /tmp/runscript
改动:m5readfile 两次
/sbin/m5 readfile > /tmp/runscript
/sbin/m5 readfile > /tmp/runscript
echo cat 确认
cat /tmp/runscript
echo "yzzzzzz54oading second new script..."
/sbin/m5 readfile > /tmp/runscript
cat /tmp/runscript
echo "yzzzzz59runing second new script..."
这样会显示两次的脚本,第一次依旧是老脚本,第二次就会显示成restore恢复时制定的新脚本。
用 bash 而不是exec
原文是exec /tmp/runscript
我用的是 bash /tmp/runscript 。我的script是:
cd /home/gem5/parsec-benchmark; source env.sh; parsecmgmt -a run -p blackscholes -c gcc-hooks -i simsmall -n 2; sleep 5; m5 exit;
restore时运行的bash命令
在host上:
./build/X86/gem5.opt -d m5out/onlyoneCPUkvmCheckPointDifferRCS20231218restore configs/deprecated/example/fs.py --script=configs/yz2023Nov/small_n2/yzfs_canneal.script --kernel=/home/yz/.cache/gem5/x86-linux-kernel-4.19.83 --disk=/home/yz/.cache/gem5/x86-parsec --checkpoint-dir=m5out/onlyoneCPUkvmCheckPointDifferRCS20231218 -r 1 --restore-with-cpu=X86KvmCPU --cpu-type=TimingSimpleCPU --num-cpus=1 --script=configs/yz2023Nov/yzfs_parsec.script
结果
restore 成功
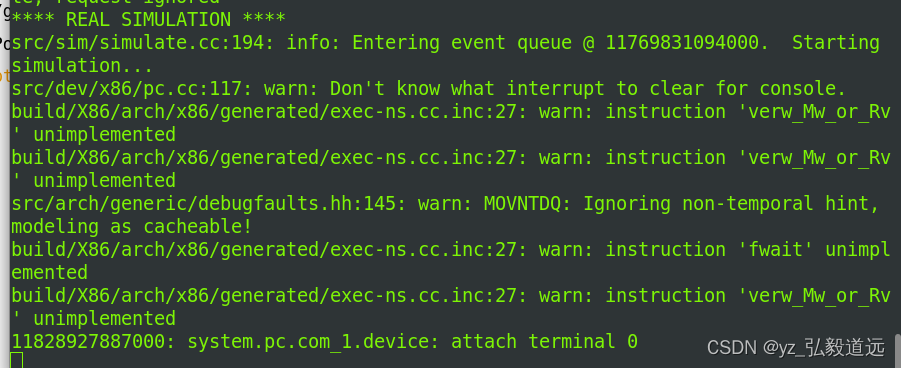
老脚本继续运行,m5 readfile第一次读的还是老脚本
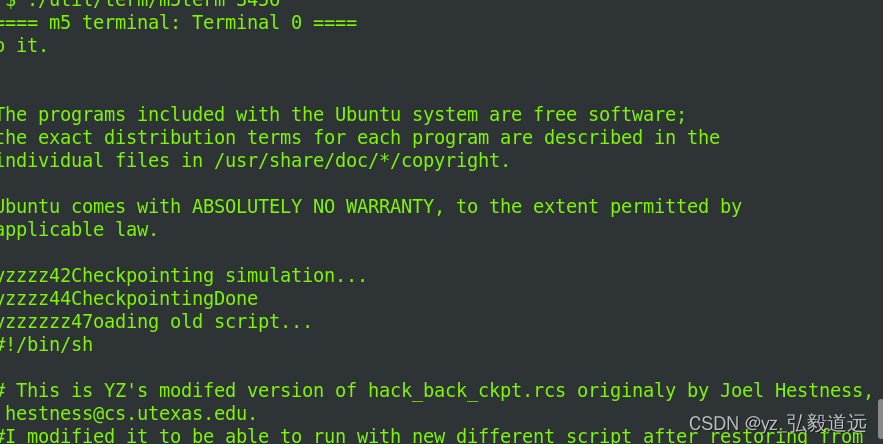
老脚本预判需要读新脚本并执行:
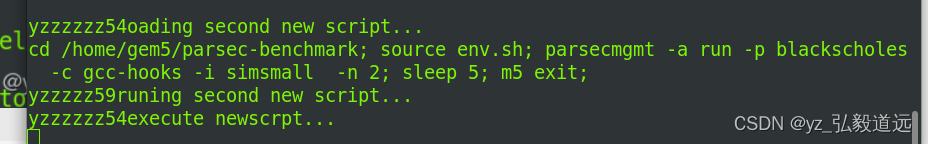
这里的命令来自于:–script=configs/yz2023Nov/yzfs_parsec.script。

时间消耗: 10s 左右生成checkpoint 10s左右恢复成功开始输出脚本内容。这个和cpu num有关,更和使用的kvmcpu有关,在无关紧要的部分可以使用kvm很快的加速。
一些技巧:
–cpu-type=X86KvmCPU使用 X86KvmCPU来快速检查 bash script是否成功
./build/X86/gem5.opt -d m5out/onlyoneCPUkvmCheckPointDifferRCS20231218restore configs/deprecated/example/fs.py --script=configs/yz2023Nov/small_n2/yzfs_canneal.script --kernel=/home/yz/.cache/gem5/x86-linux-kernel-4.19.83 --disk=/home/yz/.cache/gem5/x86-parsec --checkpoint-dir=m5out/onlyoneCPUkvmCheckPointDifferRCS20231218 -r 1 --restore-with-cpu=X86KvmCPU --cpu-type=X86KvmCPU --num-cpus=1 --script=configs/yz2023Nov/yzfs_parsec.script
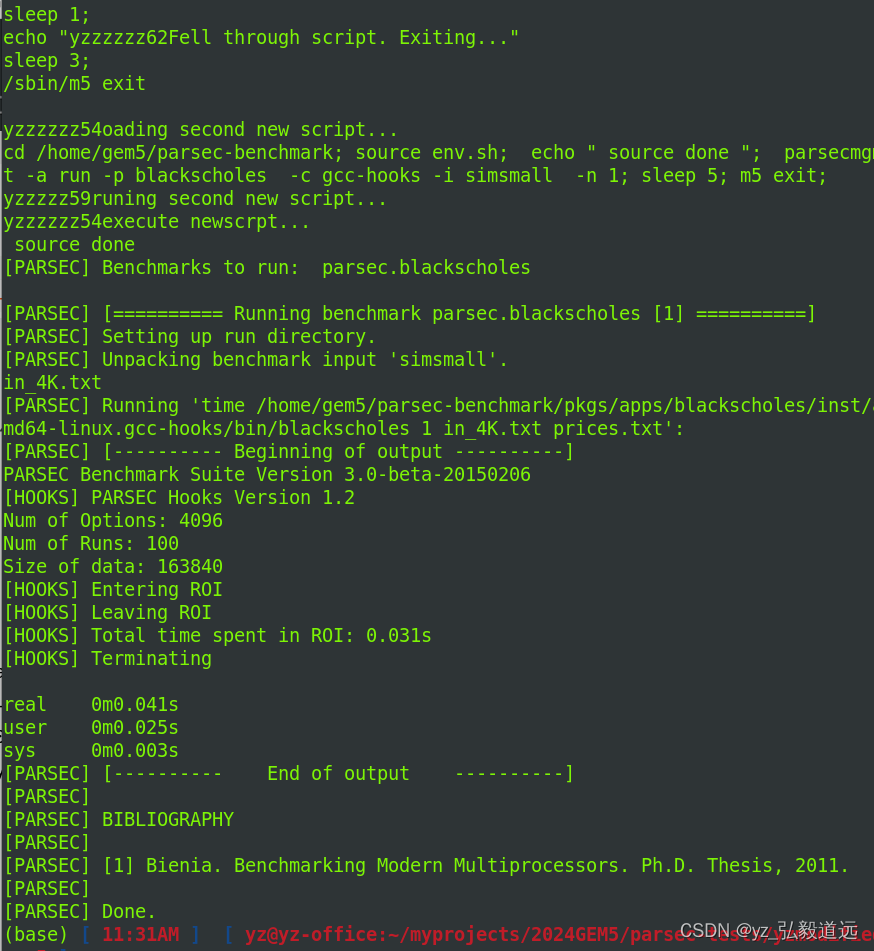
只需要几秒中,就可以完成,甚至有时候来不及m5term 。 m5term结果显示:
附录,全部代码
这就是yzhack_back_ckpt.rcs全部的内容:
#!/bin/sh
# This is YZ's modifed version of hack_back_ckpt.rcs originaly by Joel Hestness, hestness@cs.utexas.edu.
#I modified it to be able to run with new different script after restoring from a checkpoint.
#The key idea is to "m5read file" twice and "bash" rather than “exec” the script
# Demo econd new script: cd /home/gem5/parsec-benchmark; source env.sh; parsecmgmt -a run -p blackscholes -c gcc-hooks -i simsmall -n 2; sleep 5; m5 exit;
# You should observe via m5term 3456: First: old script, showing the content of this scipt. Second: new script, show the contents of cd /home/gem5/parsec-benchmark; source env.sh; parsecmgmt -a run -p blackscholes -c gcc-hooks -i simsmall -n 2; sleep 5; m5 exit;
#author: Yizhi Chen: yizhic@kth.se 2023-Dec-18th
# Test if the RUNSCRIPT_VAR environment variable is already set
if [ "${RUNSCRIPT_VAR+set}" != set ]
then
# Signal our future self that it's safe to continue
export RUNSCRIPT_VAR=1
else
# We've already executed once, so we should exit
echo "yzzzWe've already executed once, so we should exit"
sleep 2
/sbin/m5 exit
fi
# Checkpoint the first execution
echo "yzzzz42Checkpointing simulation..."
/sbin/m5 checkpoint
echo "yzzzz44CheckpointingDone"
# Test if we previously okayed ourselves to run this script
if [ "$RUNSCRIPT_VAR" -eq 1 ]
then
# Signal our future self not to recurse infinitely
export RUNSCRIPT_VAR=2
# Read the script for the checkpoint restored execution
echo "yzzzzzz47oading old script..."
/sbin/m5 readfile > /tmp/runscript
cat /tmp/runscript
echo "yzzzzzz54oading second new script..."
/sbin/m5 readfile > /tmp/runscript
cat /tmp/runscript
echo "yzzzzz59runing second new script..."
chmod 755 /tmp/runscript
# Execute the new runscript
if [ -s /tmp/runscript ]
then
echo "yzzzzzz54execute newscrpt..."
#exec /tmp/runscript
bash /tmp/runscript
else
echo "yzzzzz56Script not specified. Dropping into shell..."
/bin/bash
fi
fi
sleep 1;
echo "yzzzzzz62Fell through script. Exiting..."
sleep 3;
/sbin/m5 exit
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- SQL delete不走索引
- 腾讯云对象存储COS计算文件的大小
- 四大攻击类型并存,NIST 警告人工智能系统带来的安全和隐私风险
- 【教学类-35-19】20240117 中4班描字帖(学号+姓名 A4竖版2份 横面)
- 【无标题】
- 抖店需要缴纳保证金吗?后期如何更换类目?实操详解!
- 轻量应用服务器与云服务器CVM对比——腾讯云
- ssm基于Java Web的怀旧唱片售卖系统论文
- java 版本企业招标投标管理系统源码+多个行业+tbms+及时准确+全程电子化
- SSL证书中RSA算法跟ECC算法的区别