MySQL 系列:注意 ORDER 和 LIMIT 联合使用的陷阱
发布时间:2023年12月17日
文章目录
前言
- 不知道大家在在分页查询中有没有遇到过这个问题,分页查询中不同的页中出现了同一条数据,出现了分页错乱的问题:
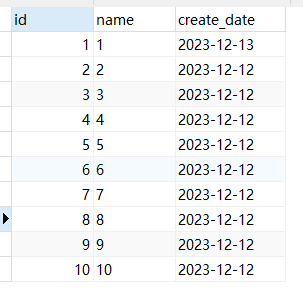
- 整体排序:
SELECT * from test_1 ORDER BY create_date;
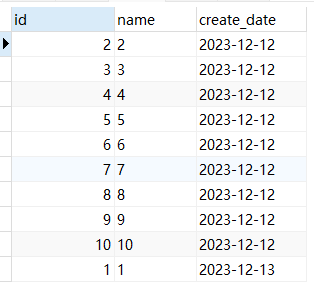
- 提取排序后的前两条:
SELECT * from test_1 ORDER BY create_date LIMIT 0,2;
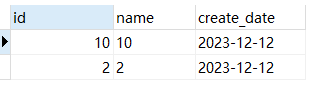
- 提取排序后的最后两条:
SELECT * from test_1 ORDER BY create_date LIMIT 8,2;
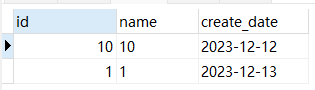
- 上面的结果是不是很奇怪,按照大家正常的思考,
MySQL对我们查询的数据进行整体排序,我们按页取出,理论上不应该在不同的页中有相同的数据,下面我们一起来看看隐藏在背后的原因。
背后的原因
- https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/limit-optimization.html
- 官网的说明内容比较多,我主要摘抄了以下几点比较相关的内容,下面我们一起来看看吧。
ORDER BY 排序列存在相同值时返回顺序是不固定的
If multiple rows have identical values in the ORDER BY columns, the server is free to return those rows in any order, and may do so differently depending on the overall execution plan. In other words, the sort order of those rows is nondeterministic with respect to the nonordered columns.- 如果多个行在ORDER BY列中具有相同的值,则服务器可以自由地以任何顺序返回这些行,并且可以根据总体执行计划以不同的方式返回。换句话说,相对于无序列,这些行的排序顺序是不确定的。
LIMIT 和 ORDER BY 联合使用时的行为
If you combine LIMIT row_count with ORDER BY, MySQL stops sorting as soon as it has found the first row_count rows of the sorted result, rather than sorting the entire result. If ordering is done by using an index, this is very fast. If a filesort must be done, all rows that match the query without the LIMIT clause are selected, and most or all of them are sorted, before the first row_count are found. After the initial rows have been found, MySQL does not sort any remainder of the result set.- 如果你联合使用 LIMIT 和 ORDER BY ,MySQL 会找到所需要的行后尽可能快的返回,而不是对所有满足查询条件的行进行排序。如果使用索引排序,那么速度会非常快;如果使用文件排序,所有满足条件都会被选中(不包括 Limit 条件),这些行的大多数,或全部都会被排序直到满足 Limit 的行数。满足的行数一旦找到,则不会对剩余的数据进行排序。
- 我们看一下官网的例子:
// 全表排序时
mysql> SELECT * FROM ratings ORDER BY category;
+----+----------+--------+
| id | category | rating |
+----+----------+--------+
| 1 | 1 | 4.5 |
| 5 | 1 | 3.2 |
| 3 | 2 | 3.7 |
| 4 | 2 | 3.5 |
| 6 | 2 | 3.5 |
| 2 | 3 | 5.0 |
| 7 | 3 | 2.7 |
+----+----------+--------+
// 部分排序时
mysql> SELECT * FROM ratings ORDER BY category LIMIT 5;
+----+----------+--------+
| id | category | rating |
+----+----------+--------+
| 1 | 1 | 4.5 |
| 5 | 1 | 3.2 |
| 4 | 2 | 3.5 |
| 3 | 2 | 3.7 |
| 6 | 2 | 3.5 |
+----+----------+--------+
// 可以看到 MySQL 并没有对所有数据整体排序之后再取数据
ORDER BY 或 GROUP BY 和 LIMIT 联合使用优化器默认使用有序索引
For a query with an ORDER BY or GROUP BY and a LIMIT clause, the optimizer tries to choose an ordered index by default when it appears doing so would speed up query execution. Prior to MySQL 5.7.33, there was no way to override this behavior, even in cases where using some other optimization might be faster. Beginning with MySQL 5.7.33, it is possible to turn off this optimization by setting the optimizer_switch system variable's prefer_ordering_index flag to off.- 简单来说,5.7.33 以前会默认会选择排序字段的索引,即使存在更快的查询计划;5.7.33 开始我们可以关闭这种优化行为。我们来看一下官网提供的例子:
mysql> CREATE TABLE t (
-> id1 BIGINT NOT NULL,
-> id2 BIGINT NOT NULL,
-> c1 VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
-> c2 VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
-> PRIMARY KEY (id1),
-> INDEX i (id2, c1)
-> );
// prefer_ordering_index 开启(默认开启)
mysql> SELECT @@optimizer_switch LIKE '%prefer_ordering_index=on%';
+------------------------------------------------------+
| @@optimizer_switch LIKE '%prefer_ordering_index=on%' |
+------------------------------------------------------+
| 1 |
+------------------------------------------------------+
mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT c2 FROM t
-> WHERE id2 > 3
-> ORDER BY id1 ASC LIMIT 2\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: t
partitions: NULL
type: index
possible_keys: i
key: PRIMARY
key_len: 8
ref: NULL
rows: 2
filtered: 70.00
Extra: Using where
// prefer_ordering_index 关闭
mysql> SET optimizer_switch = "prefer_ordering_index=off";
mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT c2 FROM t
-> WHERE id2 > 3
-> ORDER BY id1 ASC LIMIT 2\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: t
partitions: NULL
type: range
possible_keys: i
key: i
key_len: 8
ref: NULL
rows: 14
filtered: 100.00
Extra: Using index condition; Using filesort
如何解决
- 从上面我们可以知道,ORDER 列存在相同字段返回的顺序是不确定,且 LIMIT 和 ORDER BY 联合使用时可能不会对所有行进行排序,我们可以在排序字段中加入一个不存在重复值的列进行辅助排序,那么则不会存在这个问题。
- 比如在文章开头的案例中我们可以加入 ID 字段进行辅助排序:
SELECT * from test_1 ORDER BY create_date,id;
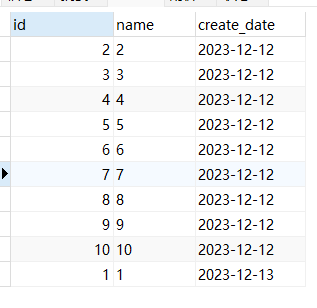
SELECT * from test_1 ORDER BY create_date,id LIMIT 0,2;
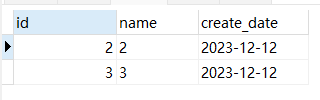
SELECT * from test_1 ORDER BY create_date,id LIMIT 8,2;
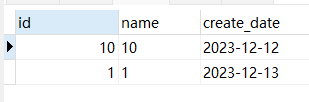
- 可以看到,分页的顺序和我们整体排序的顺序一致,不会出现分页错乱的问题。
其它说明
- MySQL 版本:
SELECT VERSION();
5.7.36-log
个人简介
👋 你好,我是 Lorin 洛林,一位 Java 后端技术开发者!座右铭:Technology has the power to make the world a better place.
🚀 我对技术的热情是我不断学习和分享的动力。我的博客是一个关于Java生态系统、后端开发和最新技术趋势的地方。
🧠 作为一个 Java 后端技术爱好者,我不仅热衷于探索语言的新特性和技术的深度,还热衷于分享我的见解和最佳实践。我相信知识的分享和社区合作可以帮助我们共同成长。
💡 在我的博客上,你将找到关于Java核心概念、JVM 底层技术、常用框架如Spring和Mybatis 、MySQL等数据库管理、RabbitMQ、Rocketmq等消息中间件、性能优化等内容的深入文章。我也将分享一些编程技巧和解决问题的方法,以帮助你更好地掌握Java编程。
🌐 我鼓励互动和建立社区,因此请留下你的问题、建议或主题请求,让我知道你感兴趣的内容。此外,我将分享最新的互联网和技术资讯,以确保你与技术世界的最新发展保持联系。我期待与你一起在技术之路上前进,一起探讨技术世界的无限可能性。
📖 保持关注我的博客,让我们共同追求技术卓越。
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35578171/article/details/134982661
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Java基础-----Date类(二)
- 深度学习在人体动作识别领域的应用:开源工具、数据集资源及趋动云GPU算力不可或缺
- 浅析js中的闭包
- 数组去重的多种方法
- 【HHO三维路径规划】哈里斯鹰算法无人机避障三维航迹规划【含Matlab源码 3780期】
- List详解,线性表
- 普通人做VR全景创业,优势表现在哪里?
- py11-python之正则-re
- 物联网开发点对点通信模式NFC和蓝牙如何无缝结合
- 消息队列-RockMQ-过滤发送消息实践