深入理解memtester
发布时间:2024年01月23日
??团队博客: 汽车电子社区
一、概述
??A userspace utility for testing the memory subsystem for faults. It’s portable and should compile and work on any 32- or 64-bit Unix-like system. (Yes, even weird, proprietary Unices, and even Mac OS X.) For hardware developers, memtester can be told to test memory starting at a particular physical address as of memtester version 4.1.0.
memtester官网:https://pyropus.ca./software/memtester/
二、安装
2.1、源码编译安装
??源码编译安装请参考如下命令:
// 1.下载源码
wget http://pyropus.ca/software/memtester/old-versions/memtester-4.3.0.tar.gz

// 2. 解压缩
tar xzvf memtester-4.3.0.tar.gz
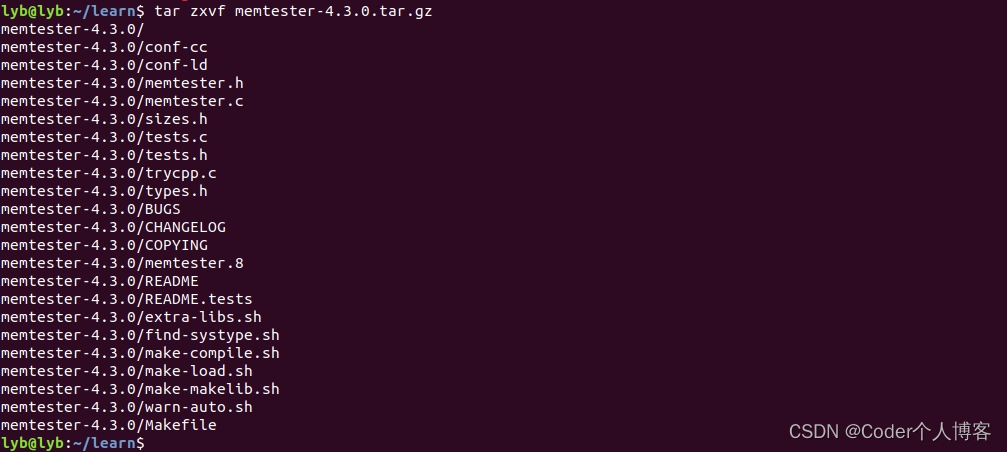
// 3. 编译
sudo make
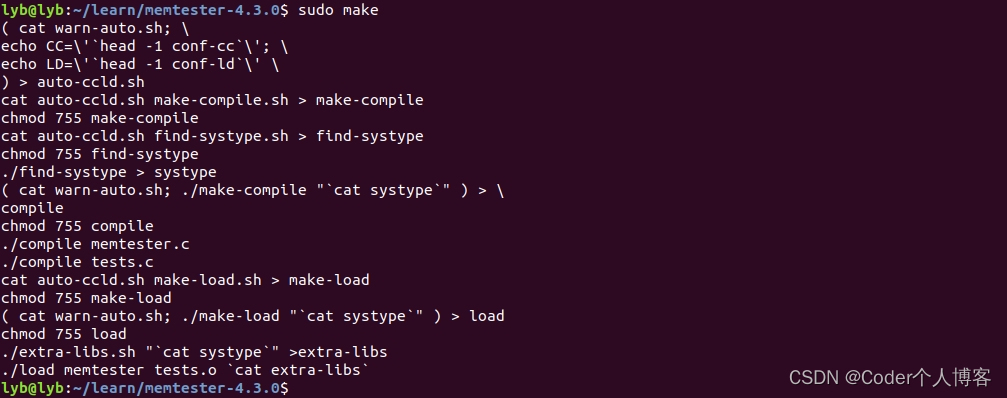
// 4. 安装
sudo make install

2.2、命令行安装
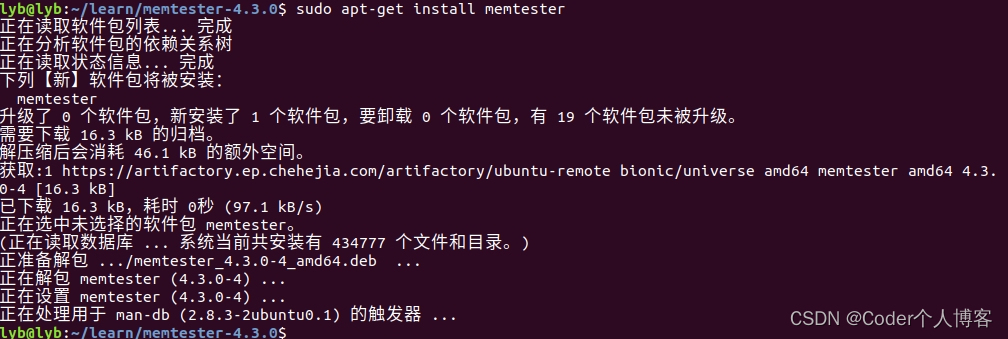
??Ubuntu下执行如下命令进行安装:
sudo apt-get install memtester
3.2、安装确认
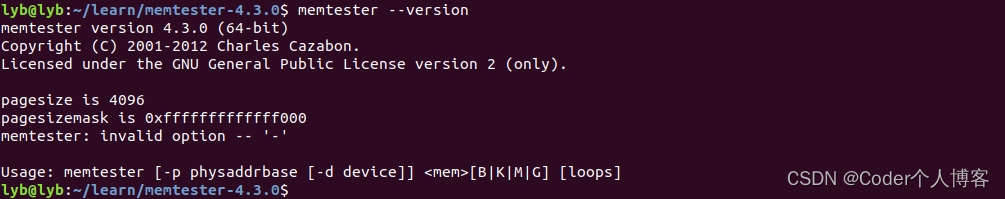
??执行如下命令来确认memtester是否安装成功:
memtester --version
三、重要参数详解
3.1、查询支持的参数
??执行如下命令可以确认memtester支持的参数:
man memtester
memtester(8) Maintenance Commands memtester(8)
NAME
memtester - stress test to find memory subsystem faults.
SYNOPSIS
memtester [-p PHYSADDR [-d DEVICE]] <MEMORY> [ITERATIONS]
DESCRIPTION
memtester is an effective userspace tester for stress-testing the memory subsystem. It is very
effective at finding intermittent and non-deterministic faults. Note that problems in other hardware
areas (overheating CPU, out-of-specification power supply, etc.) can cause intermittent memory
faults, so it is still up to you to determine where the fault lies through normal hardware diagnostic
procedures; memtester just helps you determine whether a problem exists.
memtester will malloc(3) the amount of memory specified, if possible. If this fails, it will
decrease the amount of memory requested until it succeeds. It will then attempt to mlock(3) this
memory; if it cannot do so, testing will be slower and much less effective. Run memtester as root so
that it can mlock the memory it tests.
Note that the maximum amount of memory that memtester can test will be less than the total amount of
memory installed in the system; the operating system, libraries, and other system limits take some of
the available memory. memtester is also limited to the amount of memory available to a single
process; for example, on 32-bit machines with more than 4GB of memory, memtester is still limited to
less than 4GB.
Note that it is up to you to know how much memory you can safely allocate for testing. If you
attempt to allocate more memory than is available, memtester should figure that out, reduce the
amount slightly, and try again. However, this can lead to memtester successfully allocating and
mlocking essentially all free memory on the system -- if other programs are running, this can lead to
excessive swapping and slowing the system down to the point that it is difficult to use. If the sys‐
tem allows allocation of more memory than is actually available (overcommit), it may lead to a dead‐
lock, where the system halts. If the system has an out-of-memory process killer (like Linux),
memtester or another process may be killed by the OOM killer.
So choose wisely.
OPTIONS
-p PHYSADDR
tells memtester to test a specific region of memory starting at physical address PHYSADDR
(given in hex), by mmap(2)ing a device specified by the -d option (below, or /dev/mem by
default). This is mostly of use to hardware developers, for testing memory-mapped I/O devices
and similar. Note that the memory region will be overwritten during testing, so it is not
safe to specify memory which is allocated for the system or for other applications; doing so
will cause them to crash. If you absolutely must test a particular region of actual physical
memory, arrange to have that memory allocated by your test software, and hold it in this allo‐
cated state, then run memtester on it with this option.
MEMORY the amount of memory to allocate and test, in megabytes by default. You can include a suffix
of B, K, M, or G to indicate bytes, kilobytes, megabytes, or gigabytes respectively.
ITERATIONS
(optional) number of loops to iterate through. Default is infinite.
ENVIRONMENT
If the environment variable MEMTESTER_TEST_MASK is set, memtester treats the value as a bitmask of
which tests (other than the stuck address test) to run. The value can be specified in decimal, in
octal (with a leading 0), or in hexadecimal (with a leading 0x). The specific bit values correspond‐
ing to particular tests may change from release to release; consult the list of tests in the source
for the appropriate index values for the version of memtester you are running. Note that skipping
some tests will reduce the time it takes for memtester to run, but also reduce memtester's effective‐
ness.
NOTE
memtester must be run with root privileges to mlock(3) its pages. Testing memory without locking the
pages in place is mostly pointless and slow.
EXIT CODE
memtester's exit code is 0 when everything works properly. Otherwise, it is the logical OR of the
following values:
x01 error allocating or locking memory, or invocation error
x02 error during stuck address test
x04 error during one of the other tests
AUTHOR
Written by Charles Cazabon.
REPORTING BUGS
Report bugs to <charlesc-memtester-bugs@pyropus.ca>.
COPYRIGHT
Copyright ? 2001-2012 Charles Cazabon
This is free software; see the file COPYING for copying conditions. There is NO warranty; not even
for MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
memtester 4 June 2012 memtester(8)
3.2、参数说明
- -p physaddrbase:从XX物理地址开始遍历检查。
- -d device: 制定要检查的设备名。
- mem: :默认使用M(MB),可以指定B, K, M, or G(分别代表 bytes, kilobytes, megabytes, or gigabytes)。
- loops:测试的次数,默认是无限。
四、实例
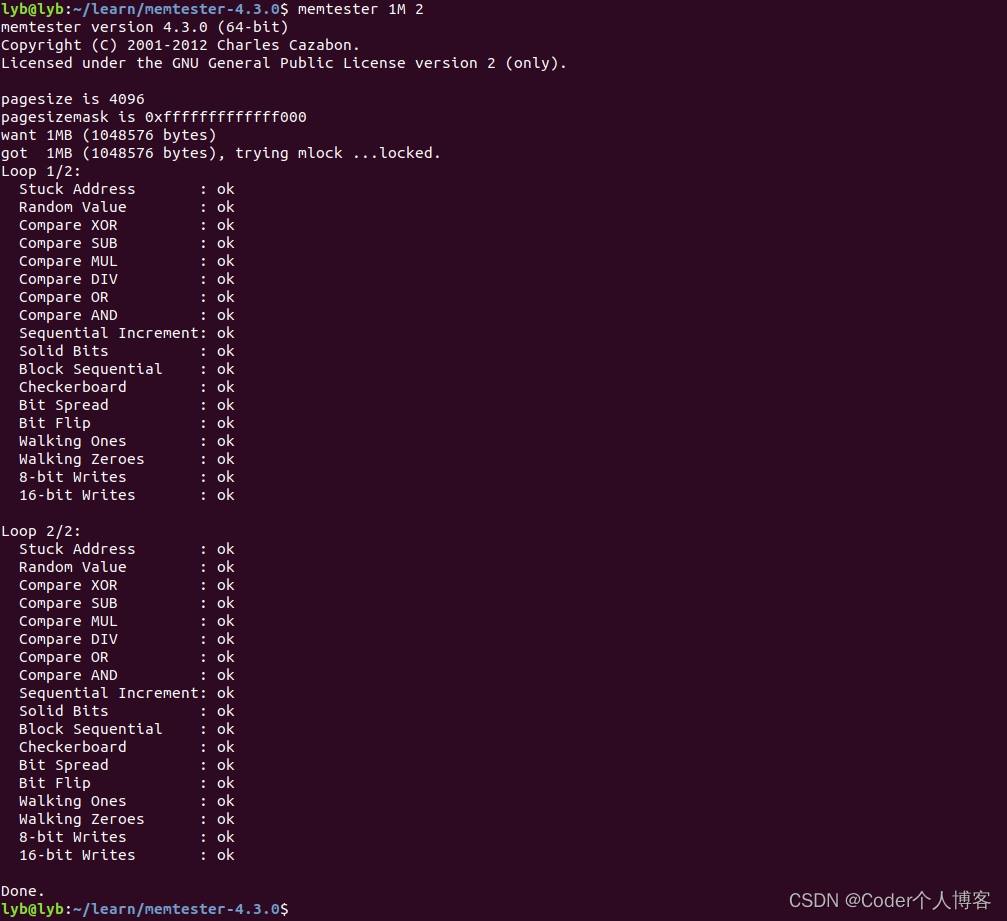
4.1、不指定设备检查
??分配1M内存用于memtest,循环两次
memtester 1M 2
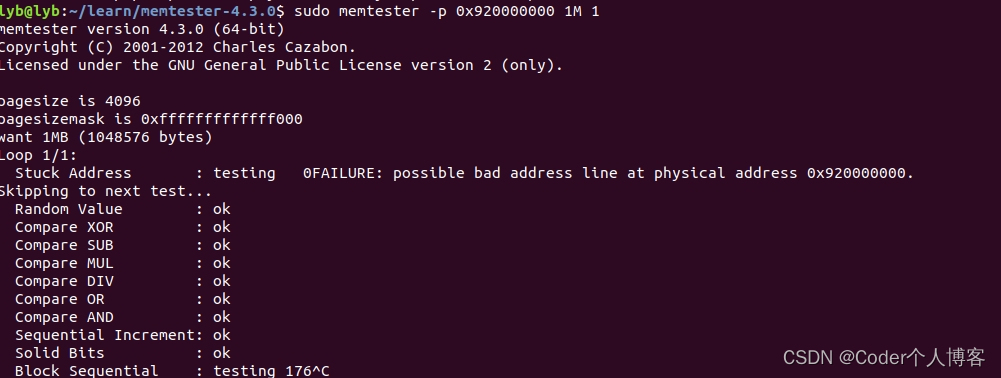
4.2、指定起始地址检测
??分配1M内存用于memtest,循环两次
memtester -p 0x120000000 1M 1
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/code_lyb/article/details/135777406
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Element ui 改变el-transfer 穿梭框的大小
- 详解HTTPS加密工作过程
- 【MyBatis-Plus】进阶之乐观锁、悲观锁&逻辑删除&分页和查询构造器的使用
- 嵌入式科普(9)vscode无法跳转和恢复默认配置
- 用通俗易懂的方式讲解:万字长文带你入门大模型
- 保护数据库数据安全就用行云管家!全方位保障!
- 计算机毕业设计SSM基于Java的题库管理系统的设计与实现9516x9【附源码】
- 01 ZigBee开发环境IAR搭建
- 自动驾驶多传感器融合学习笔记
- 2024年做为程序员的我们面临生成式人工智能所需要的新思维