【Java】面向对象程序设计 期末复习总结
发布时间:2024年01月04日
语法基础
数组自带长度属性 length,可以在遍历的时候使用:
int []ages = new int[10];
for (int i = 0; i < ages.length; i++)
System.out.println(ages[i]);数组可以使用增强式for语句进行只读式遍历:
int[] years = new int[10];
for (int year : years) // 这里的冒号可以看作python里的in,表示取数组里的每个元素
System.out.println(year);随机数生成有两种方法:
- 法一:使用Random类,在前面加载好,然后定义一个 rand 来使用 nextInt 或 nextDouble 方法:
import java.util.Random;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random rand = new Random();
int a = rand.nextInt(100) + 10; // 从10开始,范围为100,因此a的取值范围为[10, 100]
double b = rand.nextDouble(); // 小数的范围为[0,1]
}
}- 法二:使用Math.random()生成取值范围为 [0.0, 1.0) 的浮点数:
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = (int)(Math.random() * 100);
}
}数字和字符串的相互转换:
- 将字符串转换为数字:
String s = "123";
int a = Integer.parseInt(s);- 将数字转换为字符串:
int a = 123;
String s = String.valueOf(a);输入的初始化和关闭
import java.util.Scanner;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 0;
double b = 1.0;
String s = "";
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
a = scanner.nextInt();
b = scanner.nextDouble();
s = scanner.nextLine();
scanner.close();
}
}样卷第一题:设计一个类,产生100个随机数,计算能背3整除的和,要求存入数组中。
package final_review;
public class Text_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = new int[110];
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
a[i] = (int)(Math.random() * 100);
if (a[i] % 3 == 0)
sum += a[i];
}
a[0] = sum;
}
}简单面向对象
涉及到类的定义,成员变量、构造方法、方法定义,get、set方法,这些都很简单;
要着重掌握toString方法和equals方法:
@Override
public String toString() {
return employeeId + " " + wage + " " + tax + " " + realWage;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (this.getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Salary other = (Salary) obj;
if (employeeId == null) {
if (other.employeeId != null)
return false;
}
else if (!employeeId.equals(other.employeeId))
return false;
return true;
}另外,组合不同的类,要将一个副类作为主类的一个成员变量,但是不能直接赋值,而是用set方法,最后在main方法里定义好副类,主类调用set方法赋值。
面向对象进阶
这里主要注意一下抽象类和接口:
抽象类 abstruct 用 extends 继承
接口 interface 用 implements 使用
有两个Object的接口 Comparable<>和Cloneable,
Comparable<>要覆盖 compareTo方法,比较大小,大的返回1,小的返回-1,一样大返回0;
这样就可以用 java.util.Arrays.sort 来根据某一成员变量对其中元素进行从小到大的排序。
Cloneable要覆盖返回值为 Object 的 Clone()方法,还得在这个和main方法后面抛出异常 throws ClonesNotSupportedException。
异常处理
知道使用try catch语句就行,在有可能出现异常的类后面都加上 throws Exception
记得catch 语句的括号里有标识符 e ,如果没有具体错误提示,就写 e.printStackTrace();
IO
掌握这道真题就好了,主要考的是数据写入和读出文档:
package Test;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test_6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
writeToFile("data.txt", "dog", 2, "yellow");
readFromFile("data.txt");
}
public static void writeToFile(String fileName, Object... data) throws Exception {
PrintWriter writer = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter(fileName));
for (Object obj : data) {
writer.println(obj.toString());
}
writer.close();
}
public static void readFromFile(String fileName) throws Exception {
try {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(new FileReader(fileName));
String line = "";
while ((line = scanner.nextLine()) != null)
System.out.println(line);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}JavaFx
第一题:
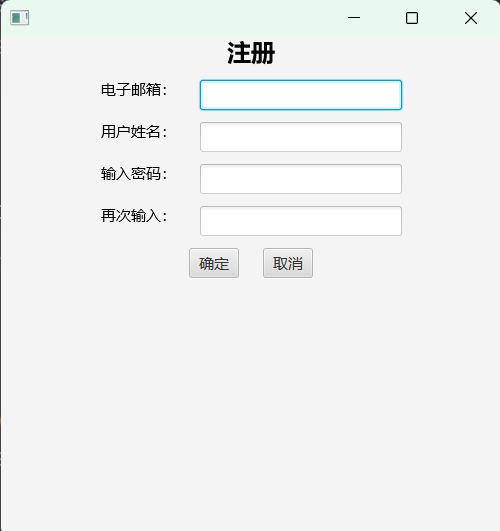
package ch05;
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.geometry.Insets;
import javafx.geometry.Pos;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Button;
import javafx.scene.layout.Pane;
import javafx.scene.control.Label;
import javafx.scene.control.TextField;
import javafx.scene.control.PasswordField;
import javafx.scene.text.Font;
import javafx.scene.text.FontWeight;
import javafx.scene.text.FontPosture;
import javafx.scene.layout.*;
import javafx.scene.text.Text;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
public class RegisterFX extends Application {
Stage primaryStage;
private Text result = new Text();
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception {
this.primaryStage = primaryStage;
VBox pane = new VBox(12);
pane.setAlignment(Pos.TOP_CENTER);
HBox pane1 = new HBox(24);
pane1.setAlignment(Pos.TOP_CENTER);
HBox pane2 = new HBox(24);
pane2.setAlignment(Pos.TOP_CENTER);
HBox pane3 = new HBox(24);
pane3.setAlignment(Pos.TOP_CENTER);
HBox pane4 = new HBox(24);
pane4.setAlignment(Pos.TOP_CENTER);
HBox pane5 = new HBox(24);
pane5.setAlignment(Pos.TOP_CENTER);
HBox pane6 = new HBox(24);
pane6.setAlignment(Pos.CENTER);
pane6.getChildren().add(result);
Text title = new Text("注册");
title.setFont(Font.font(null, FontWeight.BLACK, 24));
Text text1 = new Text("电子邮箱:");
Text text2 = new Text("用户姓名:");
Text text3 = new Text("输入密码:");
Text text4 = new Text("再次输入:");
TextField answer1 = new TextField();
TextField answer2 = new TextField();
PasswordField answer3 = new PasswordField();
PasswordField answer4 = new PasswordField();
Button b1 = new Button("确定");
Button b2 = new Button("取消");
pane5.getChildren().add(b1);
pane5.getChildren().add(b2);
pane1.getChildren().add(text1);
pane1.getChildren().add(answer1);
pane2.getChildren().add(text2);
pane2.getChildren().add(answer2);
pane3.getChildren().add(text3);
pane3.getChildren().add(answer3);
pane4.getChildren().add(text4);
pane4.getChildren().add(answer4);
pane.getChildren().addAll(title, pane1, pane2, pane3, pane4, pane5);
Scene scene = new Scene(pane, 500, 500);
primaryStage.setScene(scene);
primaryStage.show();
b1.setOnAction(e->{
if(text3.getText().equals(text4.getText()))
result.setText("注册成功");
else {
result.setText("两次输入密码不一致");
result.setFill(Color.RED);
}
});
b2.setOnAction(e->{
System.exit(0);
});
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}第二题:
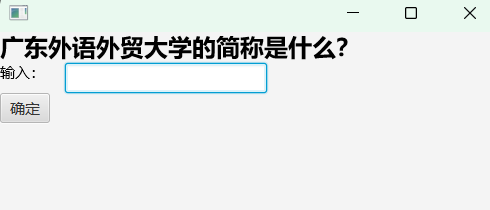
package Test;
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.geometry.Insets;
import javafx.geometry.Pos;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Button;
import javafx.scene.layout.Pane;
import javafx.scene.control.Label;
import javafx.scene.control.TextField;
import javafx.scene.text.Font;
import javafx.scene.text.FontWeight;
import javafx.scene.text.FontPosture;
import javafx.scene.layout.*;
import javafx.scene.text.Text;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class Test_4_2 extends Application {
TextField answer;
Stage primaryStage;
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception {
this.primaryStage = primaryStage;
VBox pane1 = new VBox();
pane1.setAlignment(Pos.TOP_LEFT);
HBox pane2 = new HBox(20);
pane2.setAlignment(Pos.TOP_LEFT);
Text question = new Text("广东外语外贸大学的简称是什么?");
question.setFont(Font.font(null, FontWeight.BLACK, 24));
Text text = new Text("输入:");
answer = new TextField();
Button b = new Button("确定");
pane2.getChildren().add(text);
pane2.getChildren().add(answer);
pane1.getChildren().add(question);
pane1.getChildren().add(pane2);
pane1.getChildren().add(b);
b.setOnAction(e->{
if (answer.getText().equals("广外"))
answer.setText("回答正确");
else
answer.setText("回答错误");
});
Scene scene = new Scene(pane1, 500, 200);
primaryStage.setScene(scene);
primaryStage.show();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}
多线程
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/Summerison/article/details/135376382
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!