1.2LeetCode两个链表相加,两数之和(map映射),滑动窗口,链表相交,前K个出现的数,三数之和,对链表进行排序(插入,归并)
两个链表相加?
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode *head = nullptr, *tail = nullptr;
int carry = 0;
while (l1 || l2) {
int n1 = l1 ? l1->val: 0;
int n2 = l2 ? l2->val: 0;
int sum = n1 + n2 + carry;
if (!head) {
head = tail = new ListNode(sum % 10);
} else {
tail->next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
tail = tail->next;
}
carry = sum / 10;
if (l1) {
l1 = l1->next;
}
if (l2) {
l2 = l2->next;
}
}
if (carry > 0) {
tail->next = new ListNode(carry);
}
return head;
}
};
两数之和
auto返回map,返回的是一个键值对,要用下标还要指定first以及second
m[nums[i]]=i构建映射关系
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
map<int,int>m;
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){
auto it=m.find(target-nums[i]);
if(it!=m.end())return{it->second,i};
m[nums[i]]=i;
}
return{};
}
};滑动窗口 (队列)
这道题主要用到思路是:滑动窗口
什么是滑动窗口?
其实就是一个队列,比如例题中的 abcabcbb,进入这个队列(窗口)为 abc 满足题目要求,当再进入 a,队列变成了 abca,这时候不满足要求。所以,我们要移动这个队列!
如何移动?
我们只要把队列的左边的元素移出就行了,直到满足题目要求!
一直维持这样的队列,找出队列出现最长的长度时候,求出解!
时间复杂度:O(n)
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
if(s.size() == 0) return 0;
unordered_set<char> lookup;
int maxStr = 0;
int left = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++){
while (lookup.find(s[i]) != lookup.end()){
lookup.erase(s[left]);
left ++;
}
maxStr = max(maxStr,i-left+1);
lookup.insert(s[i]);
}
return maxStr;
}
};
之所以用set而不用queue,是因为来了新元素后,queue无法第一时间确定队列窗口里是否有这个元素,必须要遍历完队列才能直到有没有,所以就用哈希表,就可以直接查询到到底有没有
链表相交
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
if(headA==nullptr||headB==nullptr)return nullptr;
ListNode* pa=headA,*pb=headB;
while(pa!=pb){
pa=pa==nullptr?headB:pa->next;
pb=pb==nullptr?headA:pb->next;
}
return pa;
}
};前K个出现的数
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> topKFrequent(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
map<int,int>m;
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++)m[nums[i]]++;
struct cmp{
bool operator()(pair<int,int>&p1,pair<int,int>&p2){
return p1.second>p2.second;
}
};
priority_queue<pair<int,int>,vector<pair<int,int>>,cmp>q;
for(auto a:m){
q.push(a);
if(q.size()>k){q.pop();}
}
vector<int>res;
while(!q.empty()){
res.push_back(q.top().first);
q.pop();
}
return res;
}
};三数之和
特判,对于数组长度 nnn,如果数组为 nullnullnull 或者数组长度小于 333,返回 [][][]。
对数组进行排序。
遍历排序后数组:
若 nums[i]>0nums[i]>0nums[i]>0:因为已经排序好,所以后面不可能有三个数加和等于 000,直接返回结果。
对于重复元素:跳过,避免出现重复解
令左指针 L=i+1L=i+1L=i+1,右指针 R=n?1R=n-1R=n?1,当 L<RL<RL<R 时,执行循环:
当 nums[i]+nums[L]+nums[R]==0nums[i]+nums[L]+nums[R]==0nums[i]+nums[L]+nums[R]==0,执行循环,判断左界和右界是否和下一位置重复,去除重复解。并同时将 L,RL,RL,R 移到下一位置,寻找新的解
若和大于 000,说明 nums[R]nums[R]nums[R] 太大,RRR 左移
若和小于 000,说明 nums[L]nums[L]nums[L] 太小,LLL 右移
三指针,一个指针确定一个数,先动一个指针,由那个指针确定一个区间(在右边),然后左右指针分别在那个区间的两侧,开始扫描
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> threeSum(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
vector<vector<int>> ans;
// 枚举 a
for (int first = 0; first < n; ++first) {
// 需要和上一次枚举的数不相同
if (first > 0 && nums[first] == nums[first - 1]) {
continue;
}
// c 对应的指针初始指向数组的最右端
int third = n - 1;
int target = -nums[first];
// 枚举 b
for (int second = first + 1; second < n; ++second) {
// 需要和上一次枚举的数不相同
if (second > first + 1 && nums[second] == nums[second - 1]) {
continue;
}
// 需要保证 b 的指针在 c 的指针的左侧
while (second < third && nums[second] + nums[third] > target) {
--third;
}
// 如果指针重合,随着 b 后续的增加
// 就不会有满足 a+b+c=0 并且 b<c 的 c 了,可以退出循环
if (second == third) {
break;
}
if (nums[second] + nums[third] == target) {
ans.push_back({nums[first], nums[second], nums[third]});
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};
class Solution:
def threeSum(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
n=len(nums)
res=[]
if(not nums or n<3):
return []
nums.sort()
res=[]
for i in range(n):
if(nums[i]>0):
return res
if(i>0 and nums[i]==nums[i-1]):
continue
L=i+1
R=n-1
while(L<R):
if(nums[i]+nums[L]+nums[R]==0):
res.append([nums[i],nums[L],nums[R]])
while(L<R and nums[L]==nums[L+1]):
L=L+1
while(L<R and nums[R]==nums[R-1]):
R=R-1
L=L+1
R=R-1
elif(nums[i]+nums[L]+nums[R]>0):
R=R-1
else:
L=L+1
return res
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> threeSum(vector<int>& nums) {
int n=nums.size();
sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());
vector<vector<int>>ans;
for(int first=0;first<n;first++){
if(nums[first]>0)break;
if(first>0&&nums[first]==nums[first-1])continue;
int third=n-1,target=-nums[first];
for(int second=first+1;second<n;second++){
if(second>first+1&&nums[second]==nums[second-1])continue;
while(second<third&&nums[second]+nums[third]>target){
third--;
}
if(nums[second]+nums[third]==target){
ans.push_back({nums[first],nums[second],nums[third]});
}
if(second==third)break;
}
}
return ans;
}
};对联表进行插入排序
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* insertionSortList(ListNode* head) {
if (head == nullptr) {
return head;
}
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
dummyHead->next = head;
ListNode* lastSorted = head;
ListNode* curr = head->next;
while (curr != nullptr) {
if (lastSorted->val <= curr->val) {
lastSorted = lastSorted->next;
} else {
ListNode *prev = dummyHead;
while (prev->next->val <= curr->val) {
prev = prev->next;
}
lastSorted->next = curr->next;
curr->next = prev->next;
prev->next = curr;
}
curr = lastSorted->next;
}
return dummyHead->next;
}
};
对链表进行插入排序的具体过程如下。
首先判断给定的链表是否为空,若为空,则不需要进行排序,直接返回。
创建哑节点 dummyHead,令 dummyHead.next = head。引入哑节点是为了便于在 head 节点之前插入节点。
维护 lastSorted 为链表的已排序部分的最后一个节点,初始时 lastSorted = head。
维护 curr 为待插入的元素,初始时 curr = head.next。
比较 lastSorted 和 curr 的节点值。
若 lastSorted.val <= curr.val,说明 curr 应该位于 lastSorted 之后,将 lastSorted 后移一位,curr 变成新的 lastSorted。
否则,从链表的头节点开始往后遍历链表中的节点,寻找插入 curr 的位置。令 prev 为插入 curr 的位置的前一个节点,进行如下操作,完成对 curr 的插入:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* insertionSortList(ListNode* head) {
if(head==nullptr){return nullptr;}
ListNode*phead=new ListNode(0);
phead->next=head;//phead的目的是能够在链表的最前面插入元素
ListNode*last=head;
ListNode*curr=head->next;
while(curr!=nullptr){
if(last->val<=curr->val){
last=last->next;//原本在逻辑以及物理上就是连续的,所以可以直接移位
}else{
ListNode*prev=phead;
while(prev->next->val<=curr->val){
prev=prev->next;
}//循环条件是p->next,这样停止时,p是小于的,p->next是大于的,那么中间就是应该在的位置
last->next=curr->next;
curr->next=prev->next;
prev->next=curr;
}
curr=last->next;//curr逻辑上就应该是Last的下一个位置,即未排序的下一个位置
}
return phead->next;
}
};/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* insertionSortList(ListNode* head) {
if(!head)return head;
ListNode*phead=new ListNode(0);
phead->next=head;
ListNode*last=head;
ListNode*curr=head->next;
while(curr){
if(last->val<=curr->val){
last=last->next;
}else{
ListNode*prev=phead;
while(prev->next->val<=curr->val){
prev=prev->next;
}
last->next=curr->next;//last在物理上是没动的,只是在逻辑上动了,即因为此时的curr前移了,所以last在逻辑上后退了
curr->next=prev->next;
prev->next=curr;
}
curr=last->next;//curr就是last逻辑上的后一个
}
return phead->next;
}
};last指向的,应该是已排序序列当中最大的那个元素
排序链表
用插入排序的结果:
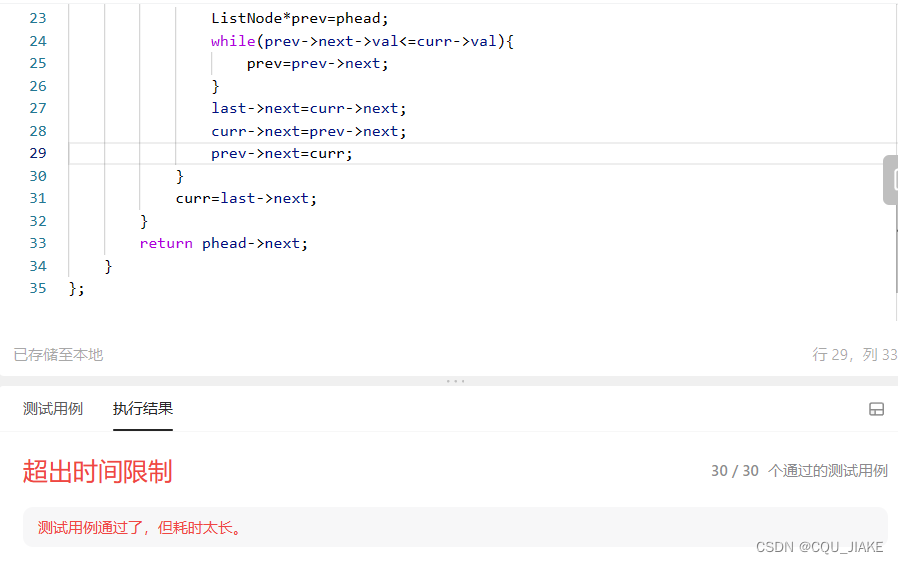
?用归并排序
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
return sortList(head, nullptr);
}
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head, ListNode* tail) {
if (head == nullptr) {
return head;
}
if (head->next == tail) {
head->next = nullptr;
return head;
}
ListNode* slow = head, *fast = head;
while (fast != tail) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
if (fast != tail) {
fast = fast->next;
}
}
ListNode* mid = slow;
return merge(sortList(head, mid), sortList(mid, tail));
}
ListNode* merge(ListNode* head1, ListNode* head2) {
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* temp = dummyHead, *temp1 = head1, *temp2 = head2;
while (temp1 != nullptr && temp2 != nullptr) {
if (temp1->val <= temp2->val) {
temp->next = temp1;
temp1 = temp1->next;
} else {
temp->next = temp2;
temp2 = temp2->next;
}
temp = temp->next;
}
if (temp1 != nullptr) {
temp->next = temp1;
} else if (temp2 != nullptr) {
temp->next = temp2;
}
return dummyHead->next;
}
};
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Python字符串处理全攻略(合集篇):常用内置方法轻松掌握
- DevC++ 用C语言的多线程 实现简单的客户端和服务器
- Excel 读写
- Html+three.js+webgl的vtk/ply/obj/三维图形显示实例
- 腾讯云微服务11月产品月报 | TSE 云原生 API 网关支持 WAF 对象接入
- JAVA实现ZIP压缩下载文件+ZIP添加多文件
- 51单片机(STC8) -- 开发环境搭建(Keil C51)
- 第十九章总结
- Nice Water Shader
- Redis面试大全