SpringBoot启动流程
SpringBoot的启动都需要如下的启动类
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootDemo3Application.class, args);
}
}
分析启动类, 可以看出核心是:
- 注解@SpringBootApplication
- 方法SpringApplication.run(SpringBootDemoApplication.class, args)
其中@SpringBootApplication之前已经了解过,如果想要了解可以查看SpringBoot自动装配原理及分析
一、方法SpringApplication.run(SpringBootDemoApplication.class, args)
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {
return run(new Class<?>[] { primarySource }, args);
}
//继续点进下一层run方法
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
-
首先new了一个SpringApplication对象
-
然后调用SpringApplication对象的run方法
二、实例化SpringApplication对象
调用SpringApplication的1个参数的构造函数,将启动类信息传入
public SpringApplication(Class<?>... primarySources) {
this(null, primarySources);
}
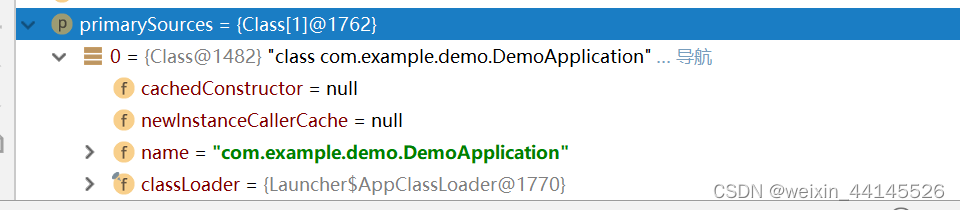
继续调用2个参数的构造方法,传入2个参数
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
//断言有主配置类, 否则抛出异常
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
//保存主配置类信息
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
//根据加载的处理器确定web应用的类型
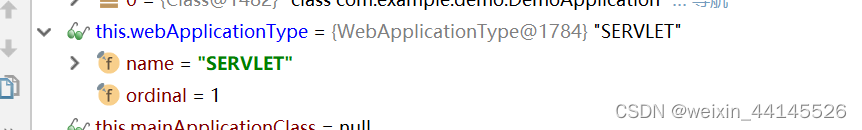
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
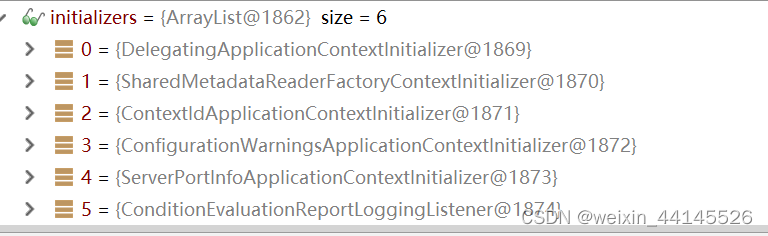
//获取所有的初始化器, 从spring.factories寻找
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
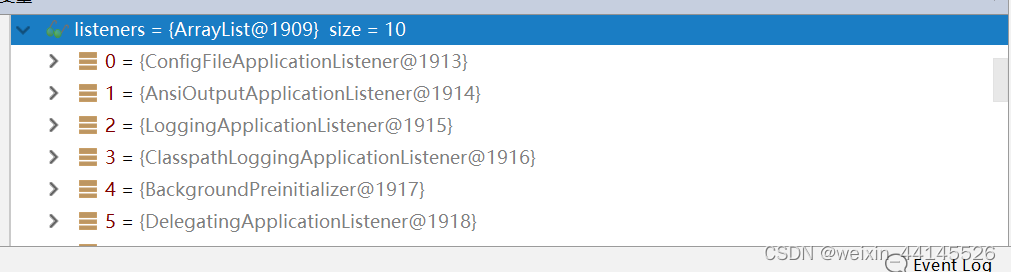
//获取所有的应用监听器, 从spring.factories寻找
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
//推断main方法所在类
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
- 当前web应用类型
- 所有的初始化器
- 所有的应用监听器
- 在项目依赖所有的spring.factories文件中可以找到以上初始化器和监听器
#路径springframework\boot\spring-boot\2.3.4.RELEASE\spring-boot-2.3.4.RELEASE.jar!\META-INF\spring.factories
# PropertySource Loaders
org.springframework.boot.env.PropertySourceLoader=\
org.springframework.boot.env.PropertiesPropertySourceLoader,\
org.springframework.boot.env.YamlPropertySourceLoader
# Run Listeners
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=\
org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener
# Error Reporters
org.springframework.boot.SpringBootExceptionReporter=\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzers
# Application Context Initializers
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\
org.springframework.boot.context.ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.context.ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.rsocket.context.RSocketPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.web.context.ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer
# Application Listeners
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\
org.springframework.boot.ClearCachesApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.builder.ParentContextCloserApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.cloud.CloudFoundryVcapEnvironmentPostProcessor,\
org.springframework.boot.context.FileEncodingApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.AnsiOutputApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigFileApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.logging.ClasspathLoggingApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.logging.LoggingApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.liquibase.LiquibaseServiceLocatorApplicationListener
# Environment Post Processors
org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor=\
org.springframework.boot.cloud.CloudFoundryVcapEnvironmentPostProcessor,\
org.springframework.boot.env.SpringApplicationJsonEnvironmentPostProcessor,\
org.springframework.boot.env.SystemEnvironmentPropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor,\
org.springframework.boot.reactor.DebugAgentEnvironmentPostProcessor
# Failure Analyzers
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzer=\
org.springframework.boot.context.properties.NotConstructorBoundInjectionFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BeanCurrentlyInCreationFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BeanDefinitionOverrideFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BeanNotOfRequiredTypeFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BindFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BindValidationFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.UnboundConfigurationPropertyFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.ConnectorStartFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.NoSuchMethodFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.PortInUseFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.ValidationExceptionFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.InvalidConfigurationPropertyNameFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.InvalidConfigurationPropertyValueFailureAnalyzer
# FailureAnalysisReporters
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalysisReporter=\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.LoggingFailureAnalysisReporter
三、调用SpringApplication对象的run方法
将main方法中的args参数传入, 分析源码
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
//实例化1个程序停止运行监听器
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
//记录启动时间
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
//让当前应用进入headless模式(自力更生模式)。java.awt.headless
configureHeadlessProperty();
//获取所有的运行监听器(这个监听器和普通的Spring监听器不同,它只用于Spring容器的启动过程中)
//默认会拿到一个EventPublishiingRunListener,它会在启动过程中的各个阶段发布对应的ApplicationEvent事件
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
//遍历 SpringApplicationRunListener 调用 starting 方法;相当于通知所有感兴趣系统正在启动过程的人,项目正在 starting
listeners.starting();
try {
//保存命令行参数(args)
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
//准备环境, 返回或者创建基础环境信息对象 : StandardServletEnvironment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
//根据环境配置需要忽略的bean信息
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
//打印banner
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
//创建IOC容器(createApplicationContext())
context = createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
//准备IOC容器的基本信息
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
//刷新IOC容器。refreshContext ---> 创建容器中的所有组件(Spring注解)
refreshContext(context);
//容器刷新完成后 ---> 这是一个空方法,(目前无内容, 预留)
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
//停止运行监听器停止运行, 记录容器启动完成花费的时间
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
//所有监听器调用 listeners.started(context); 通知所有的监听器容器已创建完成
listeners.started(context);
//调用所有runners, 遍历执行runner的run方法
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}catch (Throwable ex) {
//IOC容器创建失败,监听器会发布一个创建失败的事件
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
//通知所有的监听器, 项目进入运行状态
listeners.running(context);
}catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
四、总结
Springboot启动时,第一件重要事件就是构造SpringApplication对象,并主要完成如下事情。
- 设置源。实际就是设置Spring容器启动时依赖的初始配置类,也就是Springboot中的启动类;
- 设置WEB应用程序类型。例如可以是SERVLET,REACTIVE等;
- 加载并设置Bootstrapper,ApplicationContextInitializer和ApplicationListener;
- 设置应用程序主类的Class对象
然后调用run(),具体步骤如下:
1.创建并初始化DefaultBootstrapContext(即引导启动的容器,在创建IOC容器前需要用到的公共对象就放在该容器中)
2.从spring.factories中获取SpringApplicationRunListener(启动监听器,用于在特定场合发布特定的事件)
3.调用SpringApplicationRunListener的starting(),发布ApplicationStartingEvent事件
4.将启动参数args封装为ApplicationArguments对象
5.准备Environment
6.打印Banner
7.创建Spring容器(ApplicationContext)
8.预处理Spring容器
9.刷新Spring容器
10.Spring容器刷新后处理(空方法,扩展点,模板方法)
11.调用SpringApplicationRunListener的started(),发布ApplicationStartedEvent事件
12.调用ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner
13.调用SpringApplicationRunListener的ready(),发布ApplicationReadyEvent事件
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 微信小程序使用--如何生成二维码
- 4人遇难,北京突发火情 富维烟火识别防止悲剧再次发生
- 数据库系列文章之 ClickHouse入门
- 7-1 单身狗(PTA - 数据结构)
- QUV紫外光老化加速试验机
- Asp.Net Core 项目中常见中间件调用顺序
- 实现linux与windows进行文件共享
- 3.Java设计模式-创建型模式-单例模式-饿汉式
- 设计接口时,为其添加签名鉴权---详细教程
- Java 不同excel 版本poi如何给单元格设置背景颜色