数据结构实验4:链表的基本操作
目录
一、实验目的
1、 熟练掌握链表结构体的实现。
2、 熟练掌握链表的存储结构上实现基本操 作:查找、插入和删除算法
二、实验原理
链表(Linked List)是一种基本的数据结构,它用于存储和组织数据元素。链表中的元素被称为节点(Node),每个节点包含两部分:数据域和指针域。
1. 节点
每个节点包含两个部分:数据域和指针域。
-
数据域(Data Field): 存储节点的数据元素。这可以是任何数据类型,例如整数、字符、对象等。
-
指针域(Pointer Field): 存储指向下一个节点的引用(地址)。对于双向链表,可能还有指向前一个节点的引用。
2. 指针
链表的节点通过指针相互连接。指针存储了节点的地址,使得可以按顺序遍历链表。
3.链表的类型
3.1 单向链表
每个节点只有一个指针,指向下一个节点。
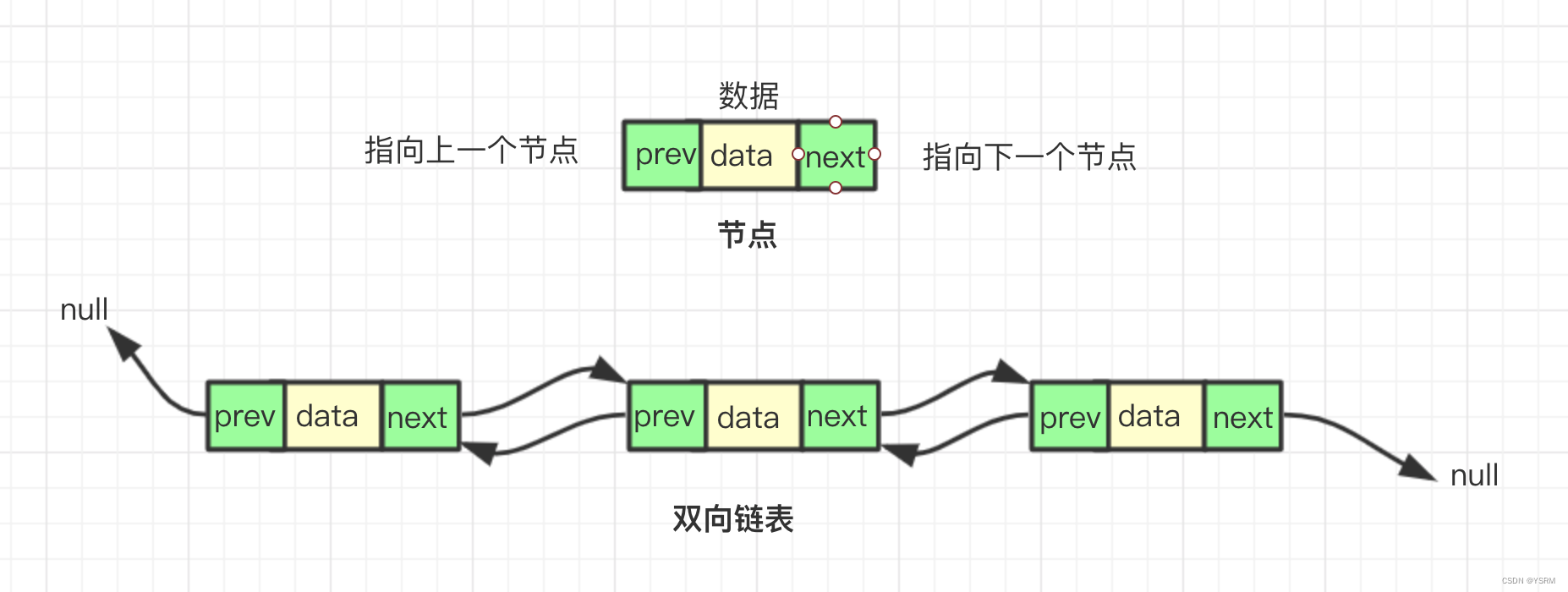
最后一个节点指向空节点(NULL)。
struct ListNode {
int data;// 数据域,存储节点的数据
struct ListNode* next;// 指针域,指向下一个节点的地址
};对于头节点的定义
struct LinkedList {
struct ListNode* head;
};3.2 双向链表
每个节点有两个指针,一个指向前一个节点,另一个指向下一个节点。?
第一个节点的prev指向NULL,最后一个节点的next指向NULL
struct ListNode {
int data;// 数据域,存储节点的数据
struct ListNode* next;// 指针域,指向下一个节点的地址
struct ListNode* prev;// 指针域,指向前一个节点的地址
};对于头节点的定义
struct DoublyLinkedList {
struct ListNode* head;
};
?3.3 单向循环链表
尾节点的指针指向头节点,形成一个闭环。
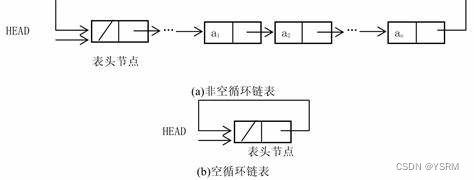
struct ListNode {
int data;// 数据域,存储节点的数据
struct ListNode* next;// 指针域,指向下一个节点的地址
};对于头节点的定义
struct CircularLinkedList {
struct ListNode* head;
};?3.4 双向循环链表
带头结点的循环双向链表在链表尾部连接到头结点,同时每个节点都有一个指向前一个节点的指针。
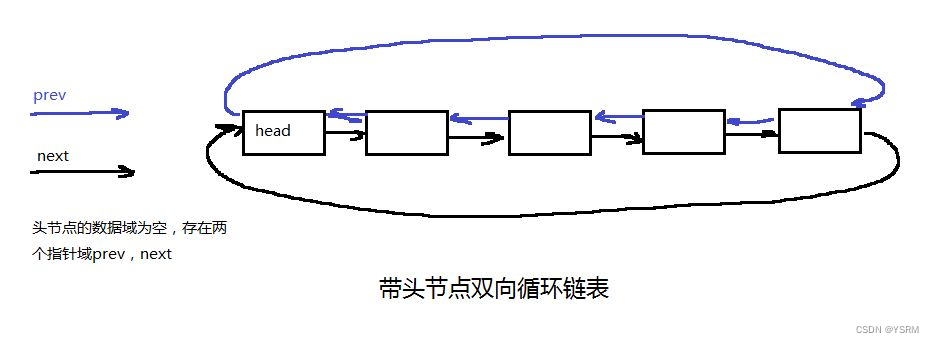
struct ListNode {
int data;// 数据域,存储节点的数据
struct ListNode* next;// 指针域,指向下一个节点的地址
struct ListNode* prev;// 指针域,指向前一个节点的地址
};对于头节点的定义
struct CircularDoublyLinkedList {
struct ListNode* head;
};?4. 单链表的插入
4.1 头插法
头插法是一种在单链表中插入节点的方法,它将新节点插入到链表的头部,成为新的头结点。
- 创建一个新的节点。
- 将新节点的
next指针指向当前链表的头结点。- 更新链表的头结点,使其指向新节点。
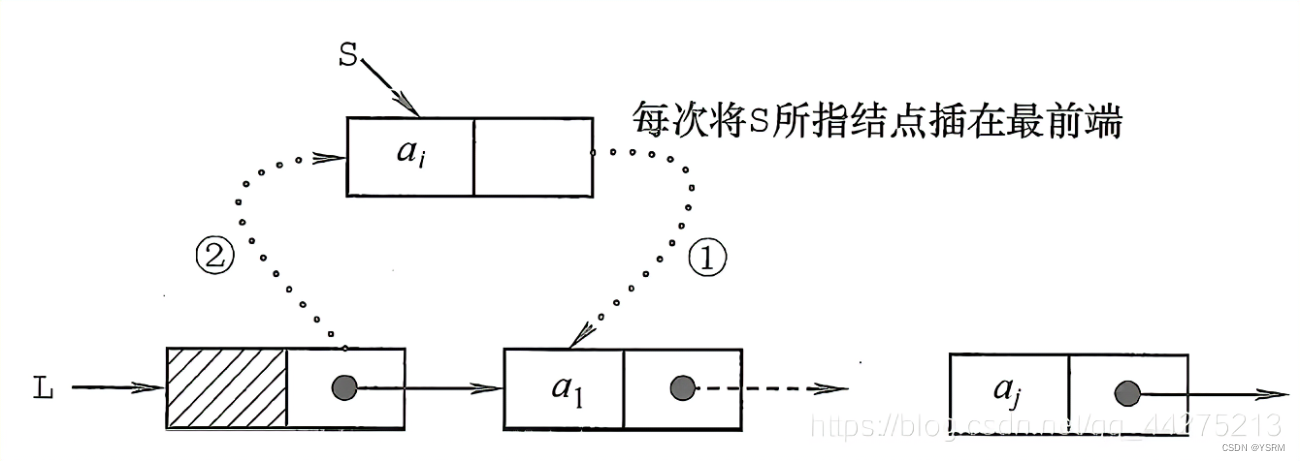
struct ListNode* insertAtBeginning(struct ListNode* head, int elem) {
//创建新节点
struct ListNode* newNode = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
if (newNode == NULL) {
cout << "内存分配失败" << endl;
return;
}
newNode->data = elem;//赋值
newNode->next = head;//newNode的指针指向head
head = newNode;//newNode成为新的头节点
return head;
}?示例
依次插入4 3 2 1
int main() {
//初始化单链表
struct ListNode* head = NULL;
for (int i = 4; i > 0; i--) {
head = insertAtBeginning(head, i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
cout << head->data << " ";
head = head->next;
}
return 0;
}结果为
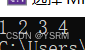
正好与输入顺序相反,这就是头插法的特色
4.2 尾插法
?尾插法是一种在单链表中插入节点的方法,它将新节点插入到链表的尾部。相对于头插法,尾插法需要遍历整个链表找到尾节点,然后在尾节点之后插入新节点。
- 创建一个新的节点。
- 若链表为空,将新节点设置为头结点。
- 若链表不为空,遍历链表找到尾节点。
- 将尾节点的
next指针指向新节点。
struct ListNode* insertAtEnd(struct ListNode* head, int elem) {
struct ListNode* newNode = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
if (newNode == NULL) {
cout << "内存分配失败" << endl;
return head;
}
//设置新节点的数据和指针
newNode->data = elem;
newNode->next = NULL;
//查找尾节点
if (head == NULL) {//如果该链表为空链表,头节点指向该新节点
head = newNode;
}
else {
struct ListNode* tail = head;//定义尾节点
while (tail->next != NULL) {//找到尾节点
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = newNode;//尾节点的指针指向新节点
}
return head;
}示例
依次插入4 3 2 1
int main() {
//初始化单链表
struct ListNode* head = NULL;
for (int i = 4; i > 0; i--) {
head = insertAtEnd(head, i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
cout << head->data << " ";
head = head->next;
}
return 0;
}结果为
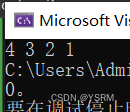
结果与输入顺序相同,看似更好,但是时间复杂度较高(while循环)。
4.3 在指定位置插入元素
struct ListNode* insertAtEnd_index(struct ListNode* head, int elem,int index) {
struct ListNode* newNode = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
if (newNode == NULL) {
cout << "内存分配失败" << endl;
return head;
}
//设置新节点的数据和指针
newNode->data = elem;
newNode->next = NULL;
struct ListNode* current = head;
struct ListNode* prev = NULL;
//index是否合法
if (index == 1) {//插入的节点为头节点
head = newNode;
newNode->next = current->next;
return;
}
while (current != NULL && index!=1) {
prev = current;
current = current->next;
index--;
}
if (current == NULL) {//遍历到末尾
if (index != 0) {
cout << "索引越界" << endl;
}
else {//prev后插入
prev->next = newNode;
}
}
else {//中间插入
prev->next = newNode;
newNode->next = current;
}
return head;
}5. 单链表的删除
5.1?删除指定数值的节点
删除链表中所有数值域与指定数值相同的节点。
struct ListNode* deleteNodeWithValue(struct ListNode* head, int target) {
struct ListNode* current = head;
struct ListNode* prev = NULL;//prev只有刚开始等于NULL的时候才发挥作用,其余时候没用
// 遍历链表删除所有匹配的节点
while (current != NULL) {
if (current->data == target) {//如果符合条件
if (prev == NULL) {// 如果目标节点是头结点
head = current->next;
free(current);
current = head;
}
else {
prev->next = current->next;
free(current);
current = prev->next;
}
}
else {//不符合条件,直接右移
prev = current;
current = current->next;
}
}
return head;
}示例,尾插法插入1 2? 1 3
再删除1
int main() {
//初始化单链表
struct ListNode* head = NULL;
head = insertAtEnd(head, 1);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 2);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 1);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 3);
head = deleteNodeWithValue(head, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
cout << head->data << " ";
head = head->next;
}
return 0;
}结果为
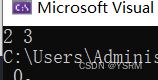
5.2 删除指定位置的节点
若指定位置无节点,会特殊处理
struct ListNode* deleteNodeAtPosition(struct ListNode* head, int index) {
if (index < 1) {
cout << "输入无效" << endl;
return head;
}
struct ListNode* current = head;
struct ListNode* prev = NULL;
while (index != 1 && current!=NULL) {
index--;
prev = current;
current = current->next;
}
if (current == NULL) {//越界
cout << "访问越界" << endl;
return head;
}
if (index == 1) {
if (current == head) {//删除的节点是头节点
head = current->next;
free(current);
}
else {
current = current->next;
prev->next = current;
}
}
return head;
}示例,尾插法插入1 2? 1 3
再删除第一个节点
int main() {
//初始化单链表
struct ListNode* head = NULL;
head = insertAtEnd(head, 1);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 2);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 1);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 3);
head = deleteNodeAtPosition(head, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
cout << head->data << " ";
head = head->next;
}
return 0;
}结果为
2 1 3
6. 单链表的查找
在链表中查找元素的操作通常包括遍历链表,逐一比较节点的值,直到找到匹配的元素或者到达链表的末尾。
6.1 按照值域查找
void search_target(struct ListNode* head,int target) {
struct ListNode* current = head;
int count = 1;
while (current != NULL) {
if (current->data == target) {
cout << "在第"<<count<<"个位置" << endl;
return;
}
count++;
current=current->next;
}
cout << "不存在" << endl;
}依次插入1 2 1 3
查找1 4
int main() {
//初始化单链表
struct ListNode* head = NULL;
head = insertAtEnd(head, 1);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 2);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 1);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 3);
search_target(head, 1);
search_target(head, 4);
return 0;
}结果为
1在第一个位置
4不存在
6.2 按照位置查找
void search_index(struct ListNode* head, int index) {
if (index < 1) {
cout << "输入无效" << endl;
return;
}
struct ListNode* current = head;
while (index != 1 && current != NULL) {
index--;
current = current->next;
}
if (current == NULL) {//越界
cout << "访问越界" << endl;
return;
}
cout << current->data;
}依次插入1 2 1 3
查找1 4
int main(){
struct ListNode* head = NULL;
head = insertAtEnd(head, 1);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 2);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 1);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 3);
search_index(head, 1);
search_index(head, 4);
return 0;
}结果为
1
3
7. 链表的遍历
从头节点遍历
void traversal(struct ListNode* head) {
struct ListNode* current = head;
while (current != NULL) {
cout << current->data<<" ";
current = current->next;
}
cout << endl;
}三、实验内容
问题描述
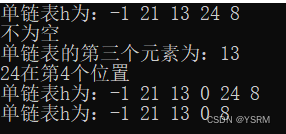
1、 初始化单链表 h;
2、 依次采用头插法插入元素-1,21,13,24,8;
3、 输出单链表 h;
4、 输出单链表 h 长度;
5、 判断单链表 h 是否为空;
6、 输出单链表 h 的第 3 个元素;
7、 输出元素 24 的位置;
8、 在 h 的第 4 个元素前插入元素 0;
9、 输出单链表 h;
10、 删除 h 的第 5 个元素;
11、 输出单链表 h
代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct ListNode {
int data;// 数据域,存储节点的数据
struct ListNode* next;// 指针域,指向下一个节点的地址
};
struct LinkedList {
struct ListNode* head;
};
struct ListNode* insertAtBeginning(struct ListNode* head, int elem) {
//创建新节点
struct ListNode* newNode = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
if (newNode == NULL) {
cout << "内存分配失败" << endl;
return head;
}
newNode->data = elem;//赋值
newNode->next = head;//newNode的指针指向head
head = newNode;//newNode成为新的头节点
return head;
}
struct ListNode* insertAtEnd(struct ListNode* head, int elem) {
struct ListNode* newNode = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
if (newNode == NULL) {
cout << "内存分配失败" << endl;
return head;
}
//设置新节点的数据和指针
newNode->data = elem;
newNode->next = NULL;
//查找尾节点
if (head == NULL) {//如果该链表为空链表,头节点指向该新节点
head = newNode;
}
else {
struct ListNode* tail = head;//定义尾节点
while (tail->next != NULL) {//找到尾节点
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = newNode;//尾节点的指针指向新节点
}
return head;
}
struct ListNode* insertAtEnd_index(struct ListNode* head, int elem,int index) {
struct ListNode* newNode = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
if (newNode == NULL) {
cout << "内存分配失败" << endl;
return head;
}
//设置新节点的数据和指针
newNode->data = elem;
newNode->next = NULL;
struct ListNode* current = head;
struct ListNode* prev = NULL;
//index是否合法
if (index == 1) {//插入的节点为头节点
head = newNode;
newNode->next = current->next;
return head;
}
while (current != NULL && index!=1) {
prev = current;
current = current->next;
index--;
}
if (current == NULL) {//遍历到末尾
if (index != 0) {
cout << "索引越界" << endl;
}
else {//prev后插入
prev->next = newNode;
}
}
else {//中间插入
prev->next = newNode;
newNode->next = current;
}
return head;
}
struct ListNode* deleteNodeWithValue(struct ListNode* head, int target) {
struct ListNode* current = head;
struct ListNode* prev = NULL;//prev只有刚开始等于NULL的时候才发挥作用,其余时候没用,prev的next指向current
// 遍历链表删除所有匹配的节点
while (current != NULL) {
if (current->data == target) {//如果符合条件
if (prev == NULL) {// 如果目标节点是头结点
head = current->next;
free(current);
current = head;
}
else {
prev->next = current->next;
free(current);
current = prev->next;
}
}
else {//不符合条件,直接右移
prev = current;
current = current->next;
}
}
return head;
}
struct ListNode* deleteNodeAtPosition(struct ListNode* head, int index) {
if (index < 1) {
cout << "输入无效" << endl;
return head;
}
struct ListNode* current = head;
struct ListNode* prev = NULL;
while (index != 1 && current!=NULL) {
index--;
prev = current;
current = current->next;
}
if (current == NULL) {//越界
cout << "访问越界" << endl;
return head;
}
if (index == 1) {
if (current == head) {//删除的节点是头节点
head = current->next;
free(current);
}
else {
current = current->next;
prev->next = current;
}
}
return head;
}
void search_target(struct ListNode* head,int target) {
struct ListNode* current = head;
int count = 1;
while (current != NULL) {
if (current->data == target) {
cout << "在第"<<count<<"个位置" << endl;
return;
}
count++;
current=current->next;
}
cout << "不存在" << endl;
}
void search_index(struct ListNode* head, int index) {
if (index < 1) {
cout << "输入无效" << endl;
return;
}
struct ListNode* current = head;
while (index != 1 && current != NULL) {
index--;
current = current->next;
}
if (current == NULL) {//越界
cout << "访问越界" << endl;
return;
}
cout << current->data<<endl;
}
void traversal(struct ListNode* head) {
struct ListNode* current = head;
while (current != NULL) {
cout << current->data<<" ";
current = current->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
//初始化单链表
struct ListNode* head = NULL;
head = insertAtEnd(head, -1);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 21);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 13);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 24);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 8);
cout << "单链表h为:";
traversal(head);
if (head == NULL) {
cout << "单链表为空"<<endl;
}
else {
cout << "不为空" << endl;
}
cout << "单链表的第三个元素为:";
search_index(head, 3);
cout << "24";
search_target(head, 24);
insertAtEnd_index(head, 0, 4);
cout << "单链表h为:";
traversal(head);
deleteNodeAtPosition(head, 5);
cout << "单链表h为:";
traversal(head);
return 0;
}截图
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 强大矢量图编辑器 Boxy SVG 激活最新
- 【mysql5.7】全网最全最新最细的MYSQL5.7下载安装图文教程
- 非线性方程求根迭代法(C++)
- Github 2023-12-27 开源项目日报 Top10
- APP跳转小程序 , 小程序返回APP
- 2 - Electron 核心概念
- pinia的理解
- 一个正则快速找到在ES中使用profile的时产生慢查询的分片
- 使用 KVM 管理程序优化虚拟化
- 西门子消防主机控制面板显示盘维修B3Q565