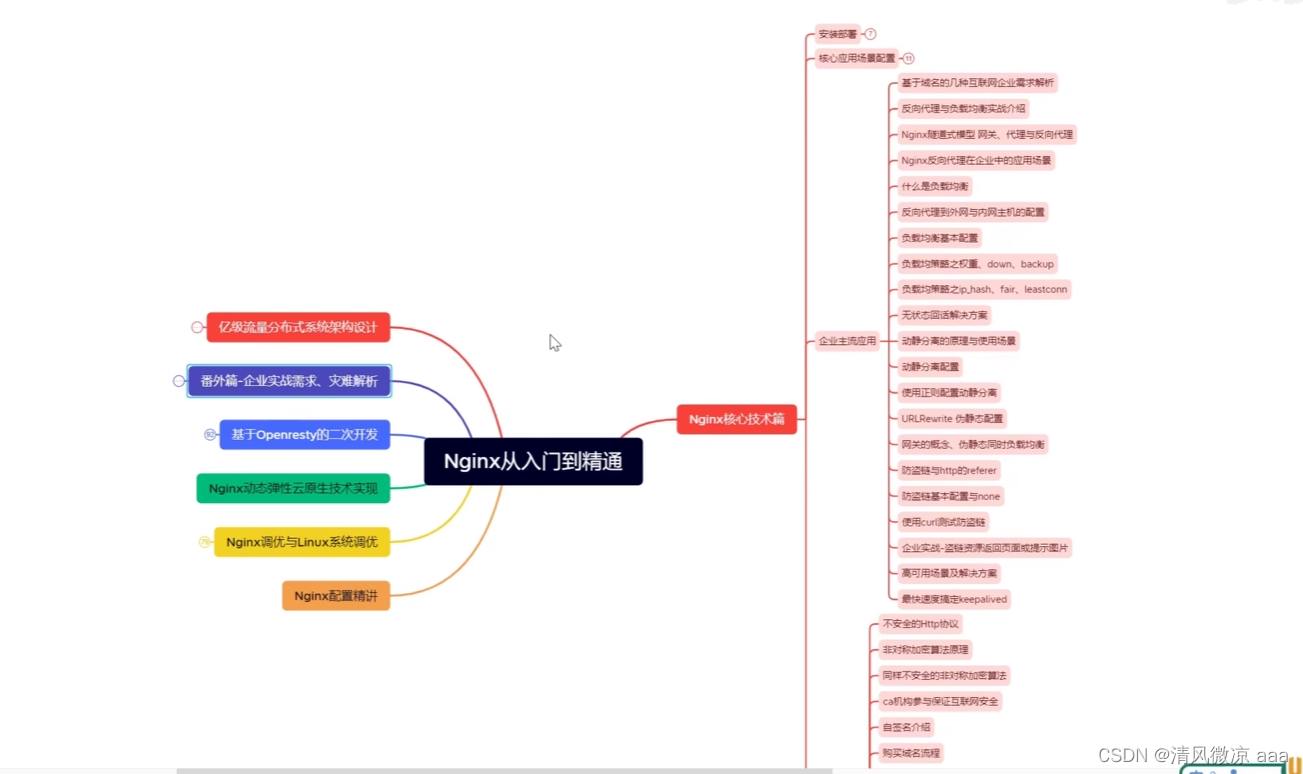
Nginx基础+高级(2022版):待更新
1. 文章说明
- 说明:目前讲的是第一部分nginx核心技术篇,后需篇章会以第一部分为核心技术篇为基础来展开深度讲解,详情关注后续课程的发布。
2. 介绍和准备环境
2.1 介绍
Nginx (engine x) 是一个高性能的HTTP和反向代理web服务器,同时也提供了IMAP/POP3/SMTP服务。Nginx是由伊戈尔·赛索耶夫为俄罗斯访问量第二的Rambler.ru站点(俄文:Рамблер)开发的,第一个公开版本0.1.0发布于2004年10月4日。其将源代码以类BSD许可证的形式发布,因它的稳定性、丰富的功能集、简单的配置文件和低系统资源的消耗而闻名。2011年6月1日,nginx 1.0.4发布。Nginx是一款轻量级的Web 服务器/反向代理服务器及电子邮件(IMAP/POP3)代理服务器,在BSD-like 协议下发行。其特点是占有内存少,并发能力强,事实上nginx的并发能力在同类型的网页服务器中表现较好,中国大陆使用nginx网站用户有:百度、京东、新浪、网易、腾讯、淘宝等。
2.2 准备环境
说明:环境准备指的是安装虚拟机,安装linux系统,配置虚拟机等,之前在学习linux时候已经配置过一遍了,所以这里直接克隆虚拟机然后修改ip和主机名即可。
- ip:
192.168.10.31 - 主机名:
nginx01
2.2.1 虚拟机安装
使用虚拟机安装学习Nginx
特点:
- 安装使用简单
- 使用于传统公司
- 适用于VPS
- 适用于高性能服务器部署
2.2.2 学习时的电脑配置
- 内存:建议8G以上
- 磁盘:建议使用SSD
- CPU:4核以上主流即可
2.2.3 虚拟机安装与配置
准备:
- Vmware、Virtualbox、Parallels
- CentOS7.4镜像
安装与配置操作系统:
- 配置虚拟机上网
- 配置静态ip地址
2.2.4 虚拟机不能上网简单排错
- Vmware中网关是否正确
- 直接ping ip是否能通(物理连接排查)
- 使用和老师一样版本的软件
- 卸载重装最快
3. nginx的安装
3.1 介绍4个发行版本
常用版本分为四大阵营
- Nginx开源版
- http://nginx.org/
- 直接从官网上下载的原始版本,比较干净只有基础功能(网站服务器,代理服务器,负载均衡),想要做二次开发难度比较大需要集成很多第三方的Modul
- Nginx plus 商业版(对基础nginx的扩展)
- https://www.nginx.com
- F5官方提供的nginx全家桶,什么功能都有
- Openresty(免费开源,对基础nginx的扩展)
- http://openresty.org
- 基于nginx和Lua脚本进行的整合,功能比较强大,支持定制功能。
- Tengine(免费开源,对基础nginx的扩展)
- http://tengine.taobao.org/
- 淘宝网开发出来的版本,以C语言的形式扩展的功能,二次开发功能较少但做集群时更安全性能更加稳定。
3.2 linux系统安装nginx开源版
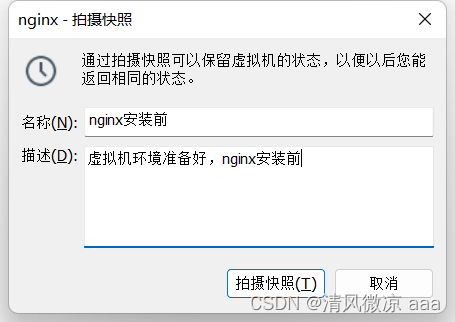
3.2.1 备份环境
目的是方便之后的安装报错,可以快速的恢复之前未安装的状态。
-
方式一:使用快照(以快照为例)
-
方式二:克隆此时的虚拟机
3.2.2 安装步骤
1) 下载之后上传到虚拟机
2)解压压缩包
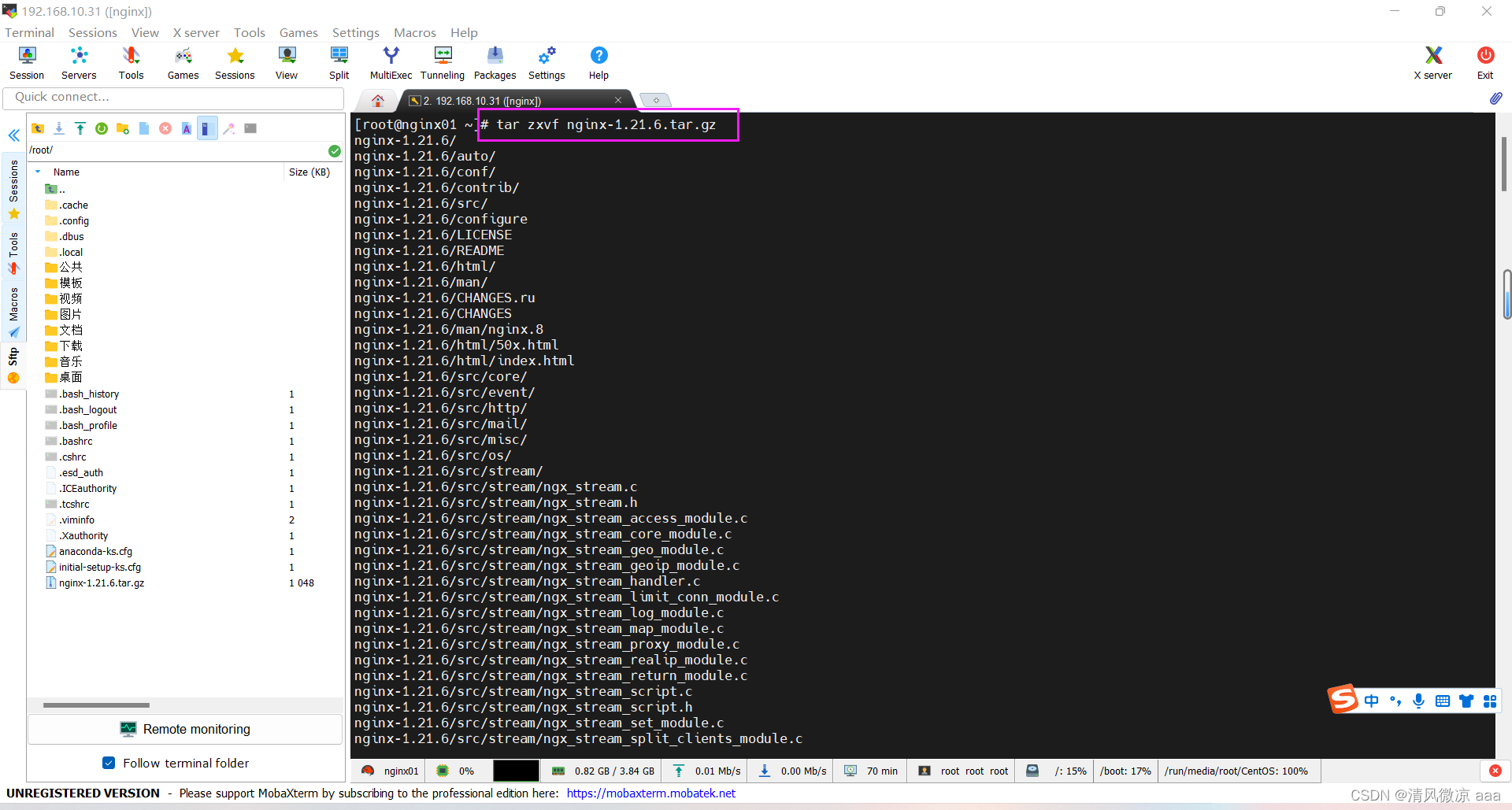
tar zxvf nginx-1.21.6.tar.gz
3)依赖检查
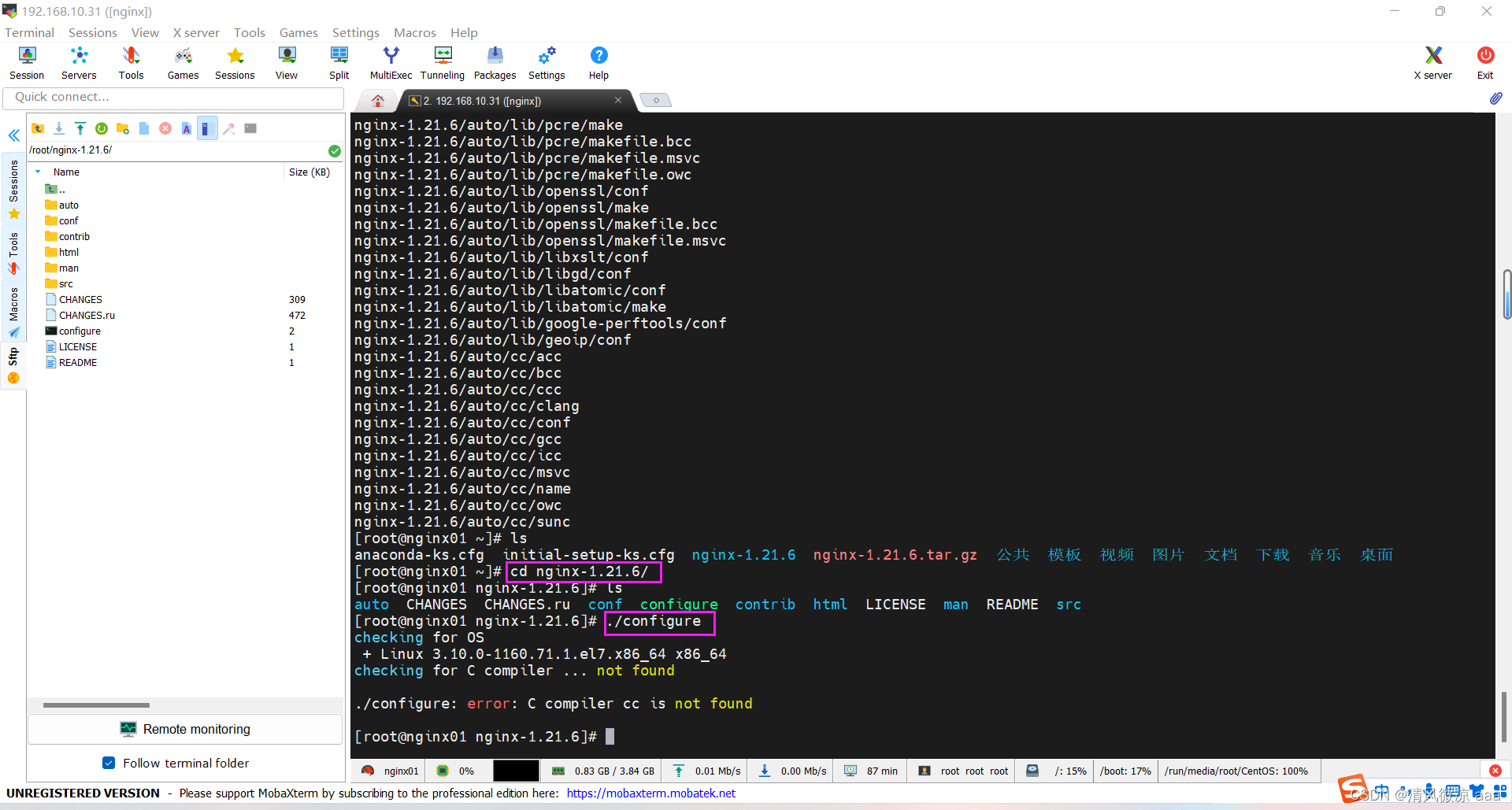
# 进入到解压后的nginx目录
cd nginx-1.21.6/
# 检查依赖
./configure
- 如果出现错误:缺少c语言编译器
checking for OS
+ Linux 3.10.0-693.el7.x86_64 x86_64
checking for C compiler ... not found
./configure: error: C compiler cc is not found
- 解决:安装gcc
yum install -y gcc
- 把它安装到系统的nginx目录下
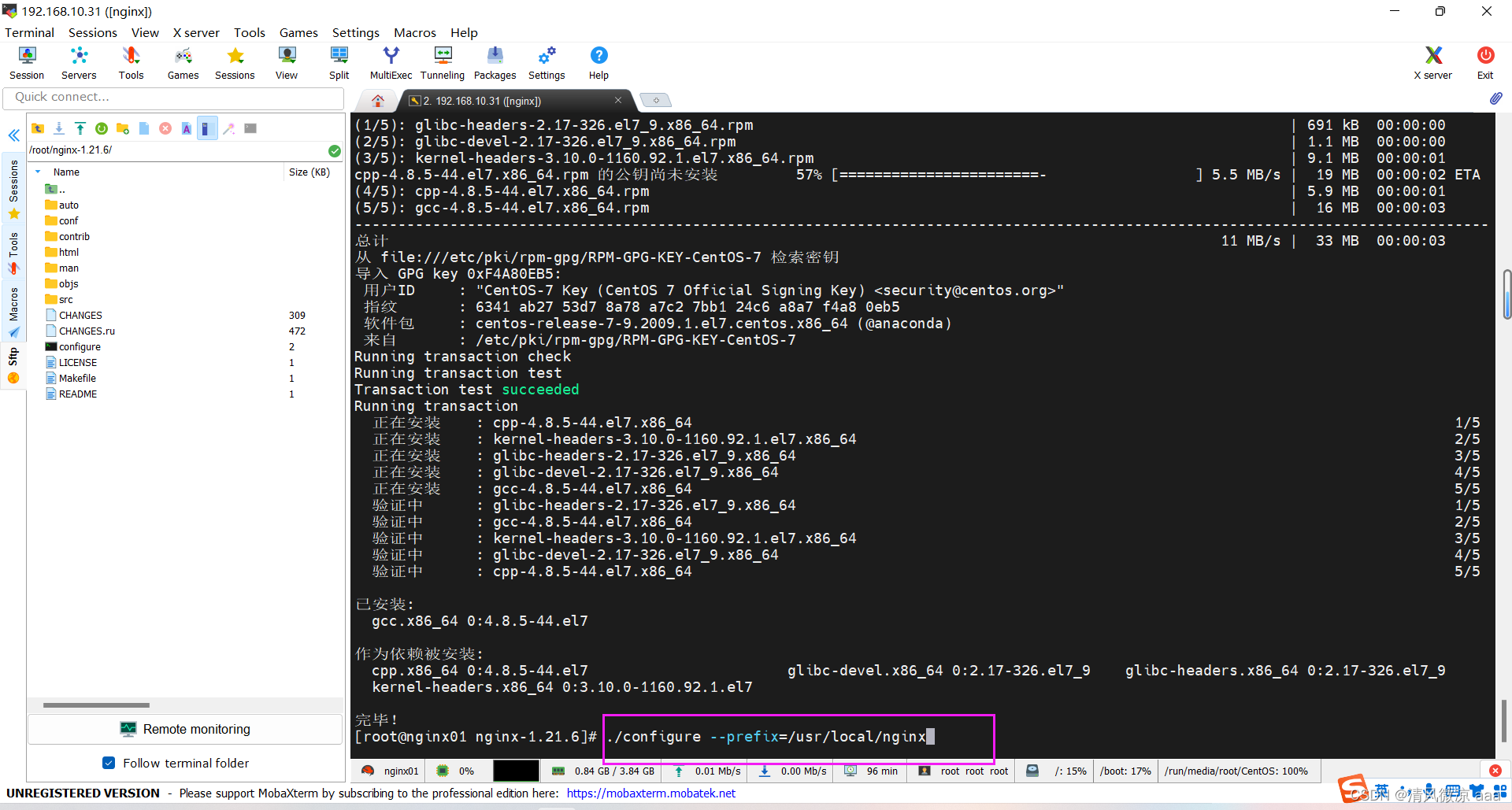
# 此目录会自动生成
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx
- 如果出现错误
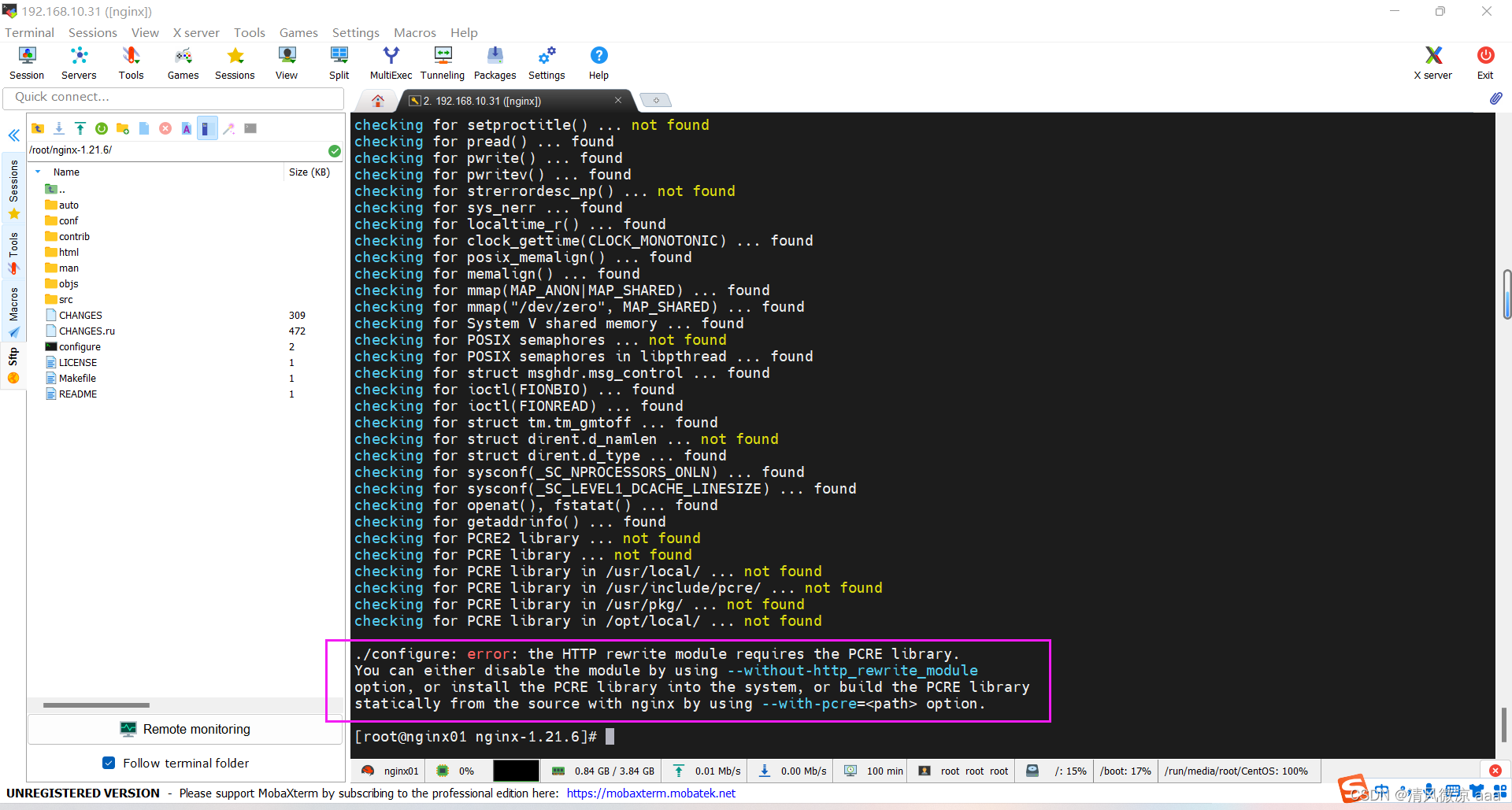
./configure: error: the HTTP rewrite module requires the PCRE library.
You can either disable the module by using --without-http_rewrite_module
option, or install the PCRE library into the system, or build the PCRE library
statically from the source with nginx by using --with-pcre=<path> option.
- 解决:安装perl库
yum install -y pcre pcre-devel
- 再次检查是否还缺少依赖
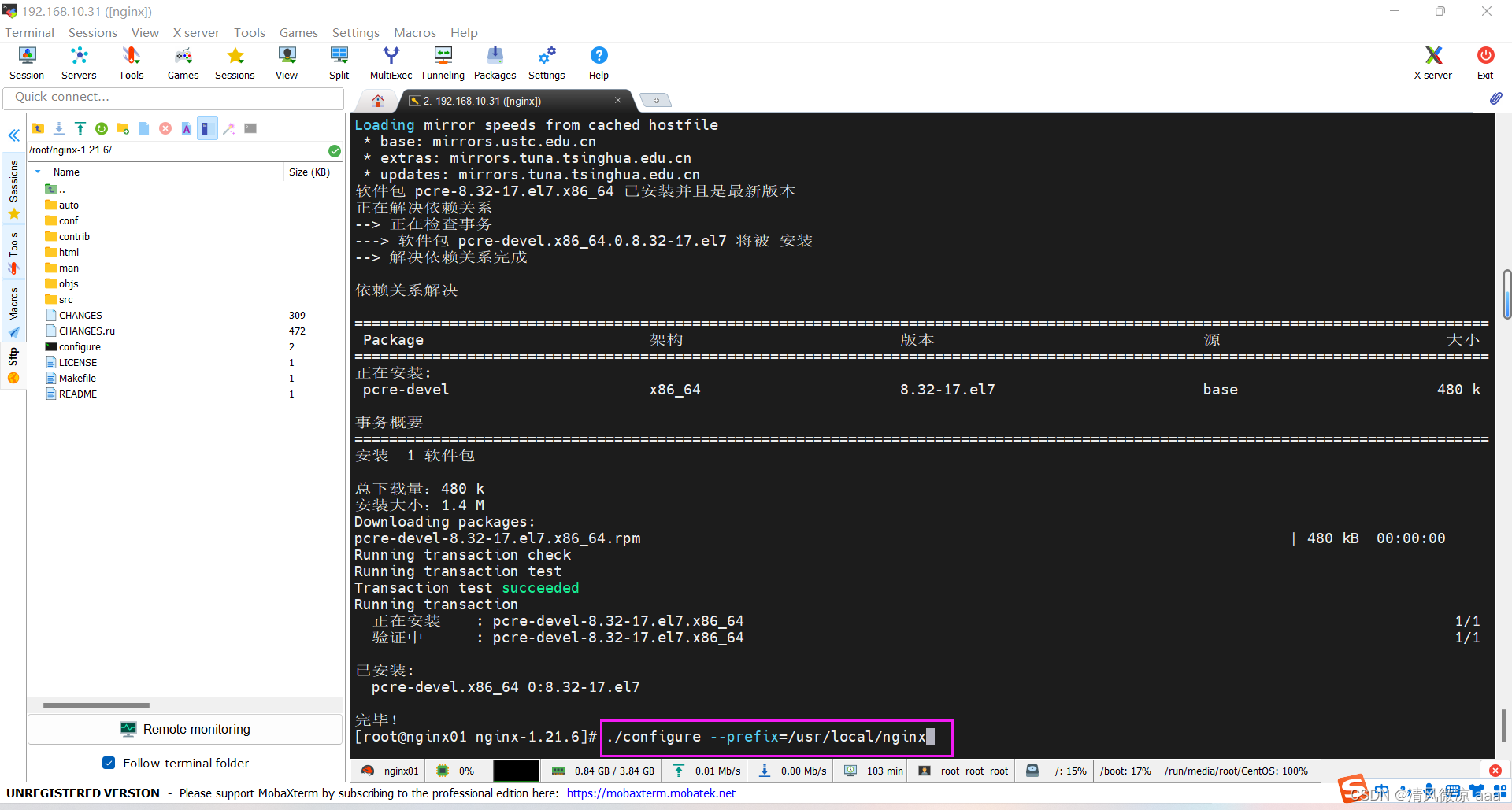
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx
- 出现错误
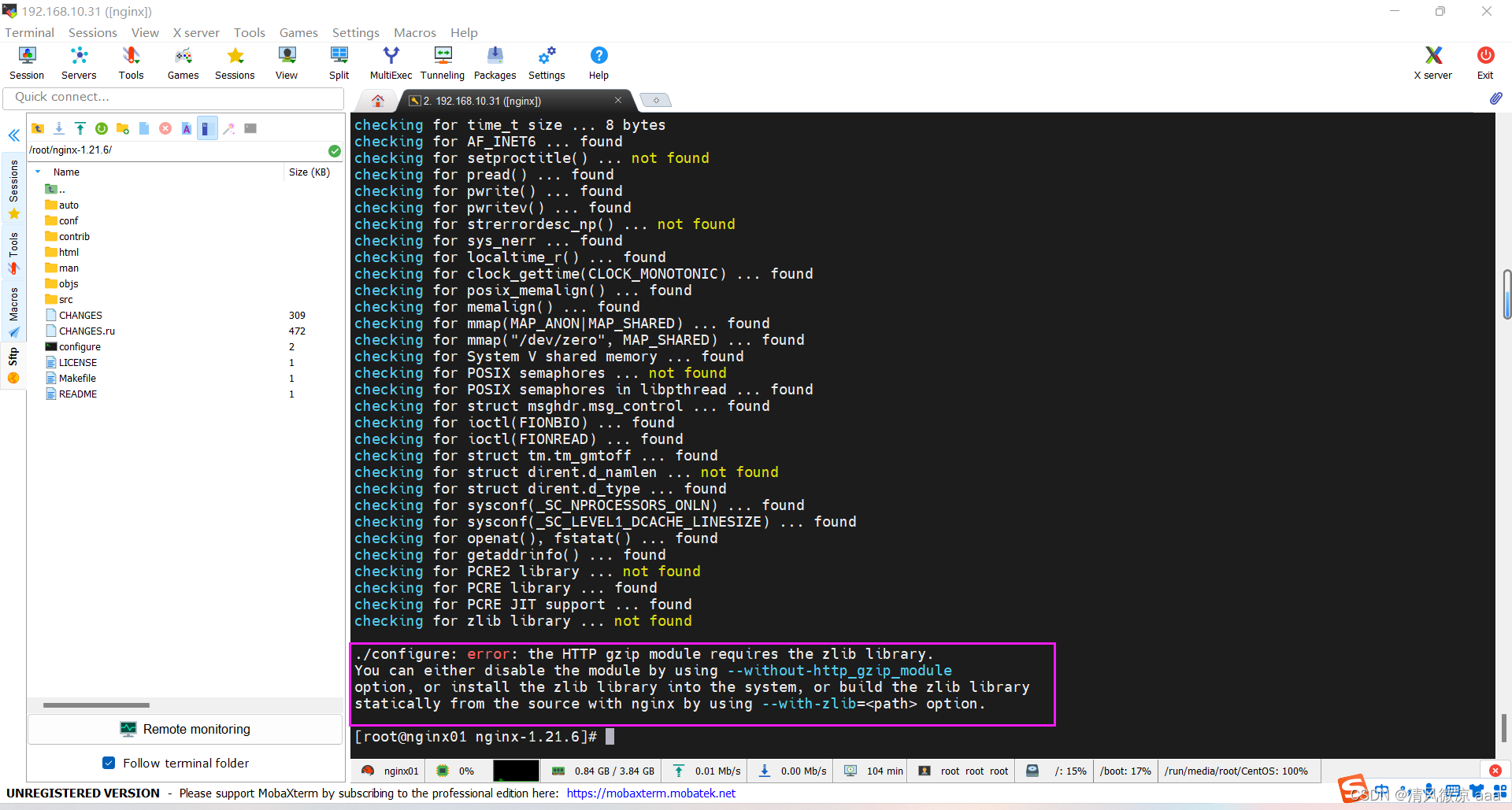
./configure: error: the HTTP gzip module requires the zlib library.
You can either disable the module by using --without-http_gzip_module
option, or install the zlib library into the system, or build the zlib library
statically from the source with nginx by using --with-zlib=<path> option.
- 解决:安装zlib库
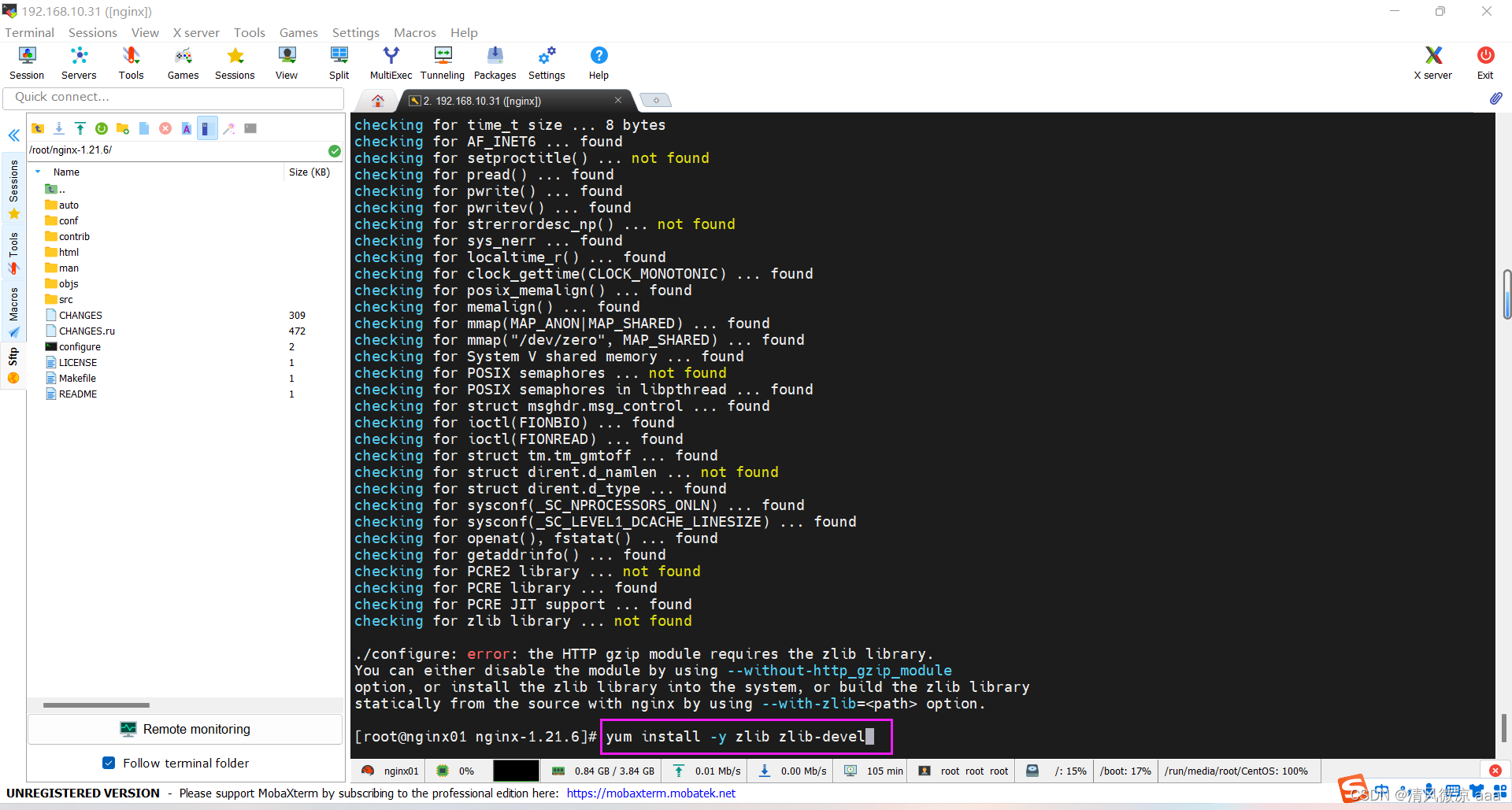
yum install -y zlib zlib-devel
- 再一次的检查是否还缺少依赖
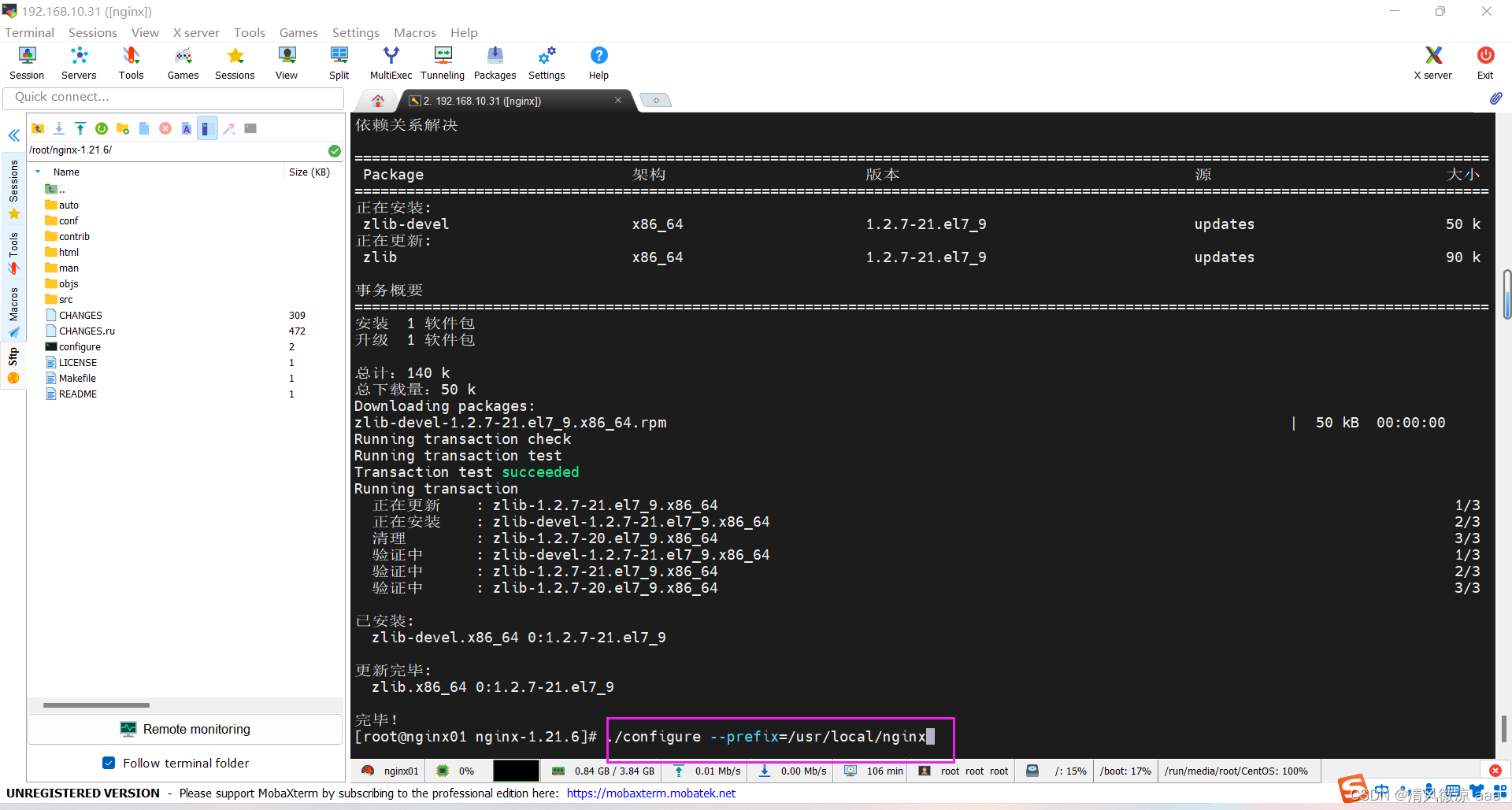
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx
- 发现已经不缺少依赖了,日志错误不影响。
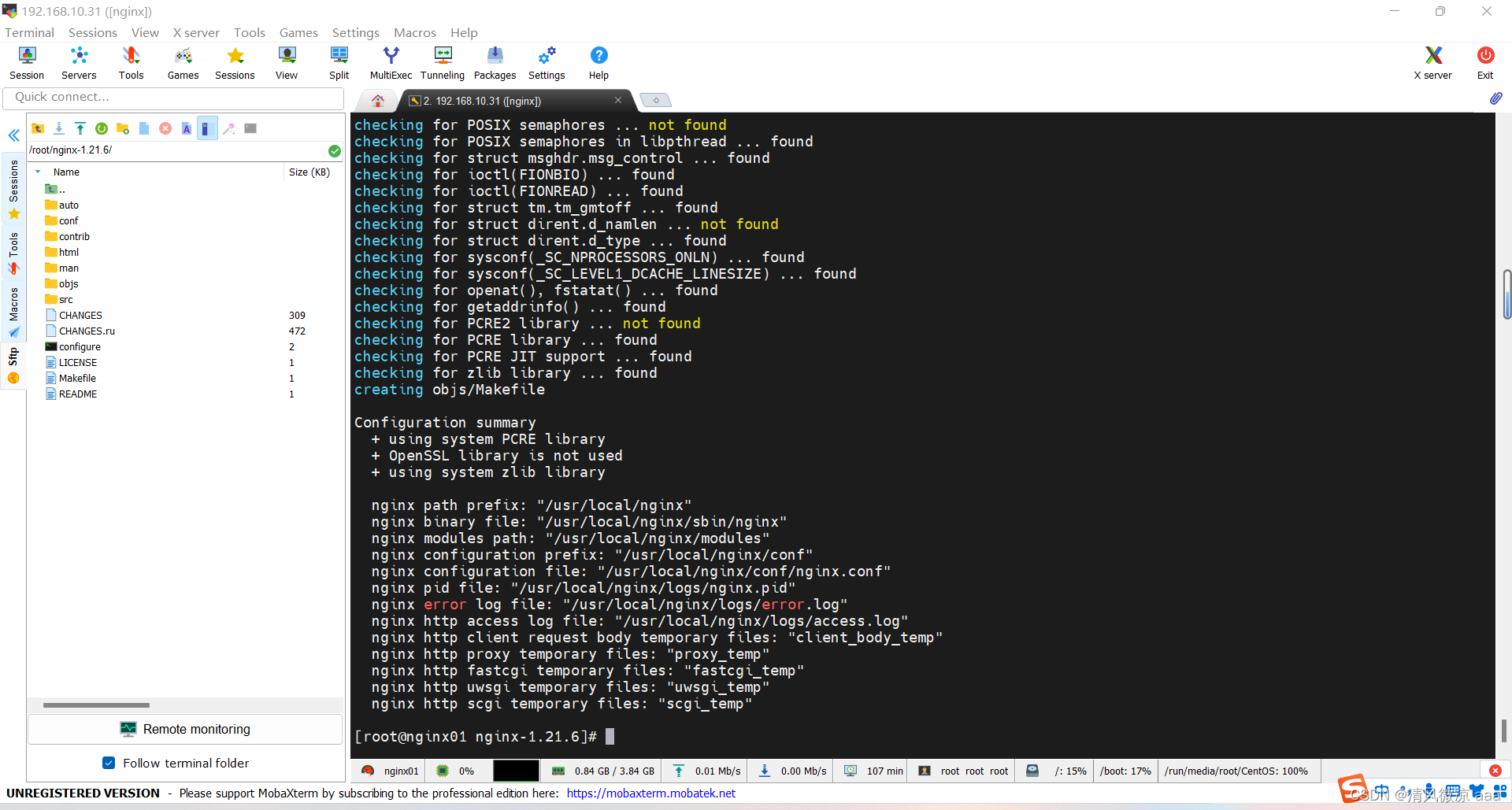
4)进行安装
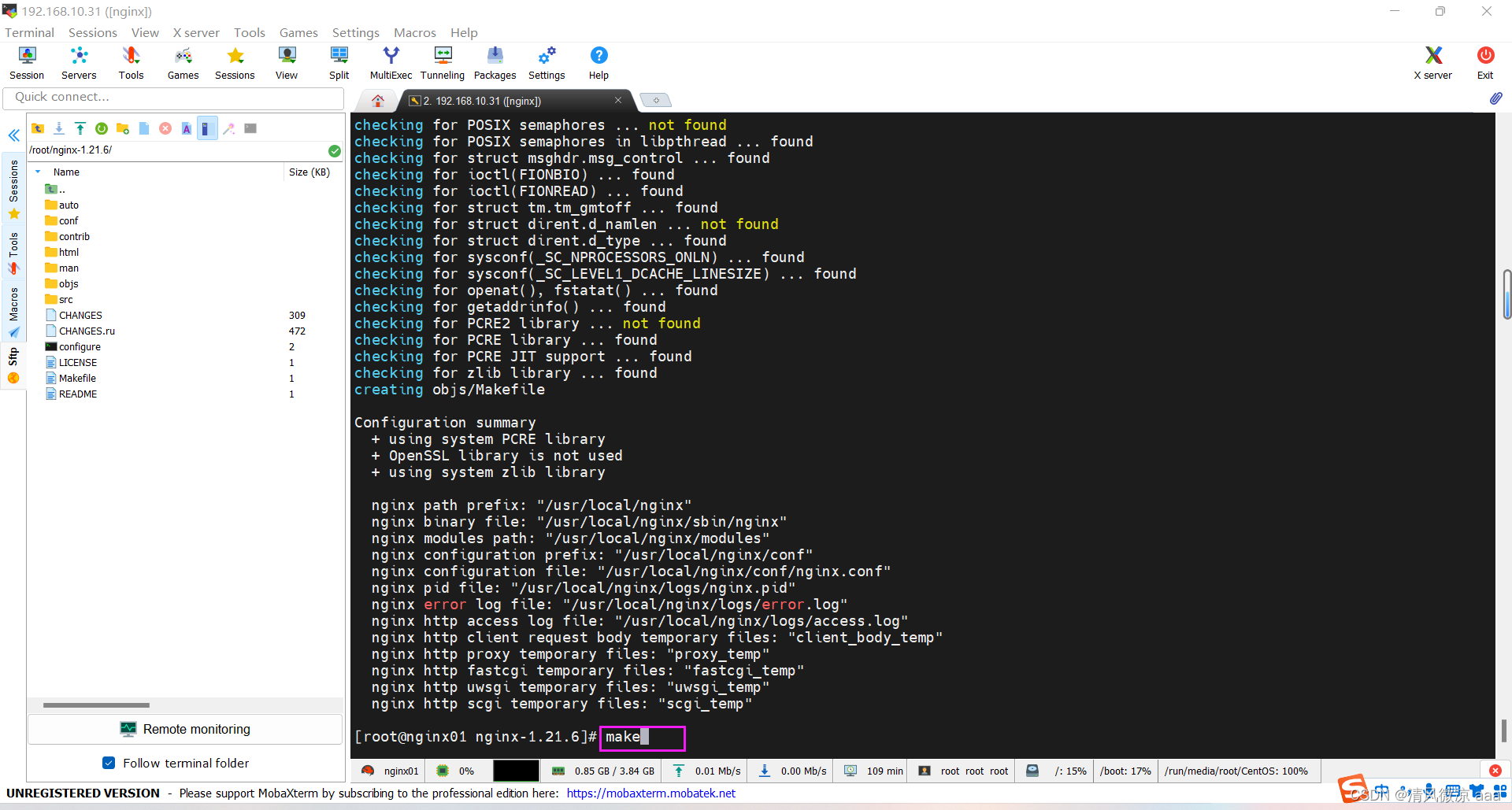
# 2条命令依次执行
make
make install
查看nginx安装好后是否在之前设置的/usr/local/nginx目录下
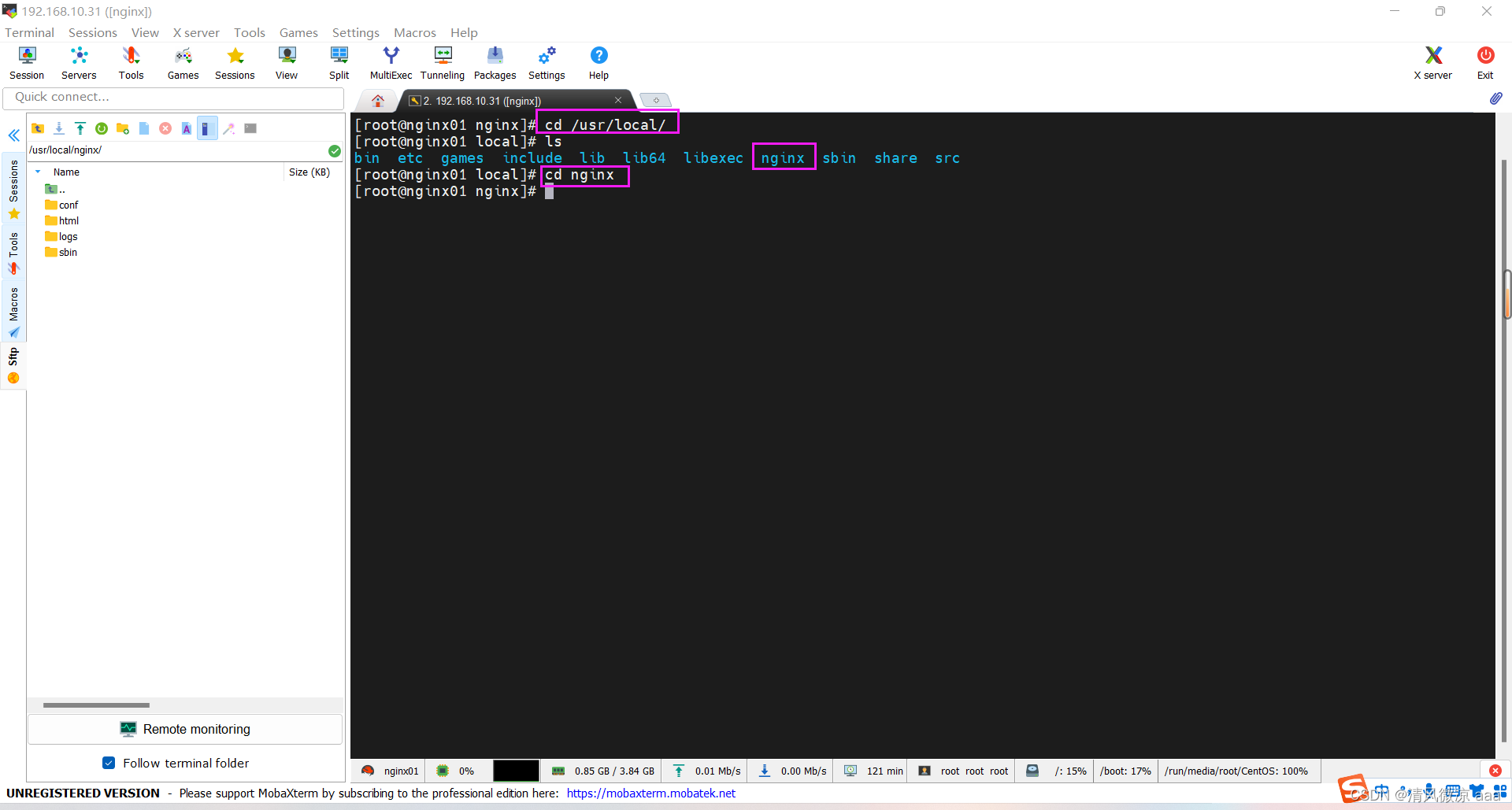
5)启动nginx(常用命令)
- 安装成功之后,在usr多出来一个文件夹local/nginx,在nginx目录中有sbin目录,在sbin目录中有启动脚本。
- 进入安装好的目录 /usr/local/nginx/sbin
./nginx 启动
./nginx -s stop 快速停止
./nginx -s quit 优雅关闭,在退出前完成已经接受的连接请求
./nginx -s reload 重新加载配置
./nginx -v 查看 nginx 版本号
3.2.3 关于防火墙
在 windows 系统中访问 linux 中 nginx,默认不能访问的,因为防火墙问题
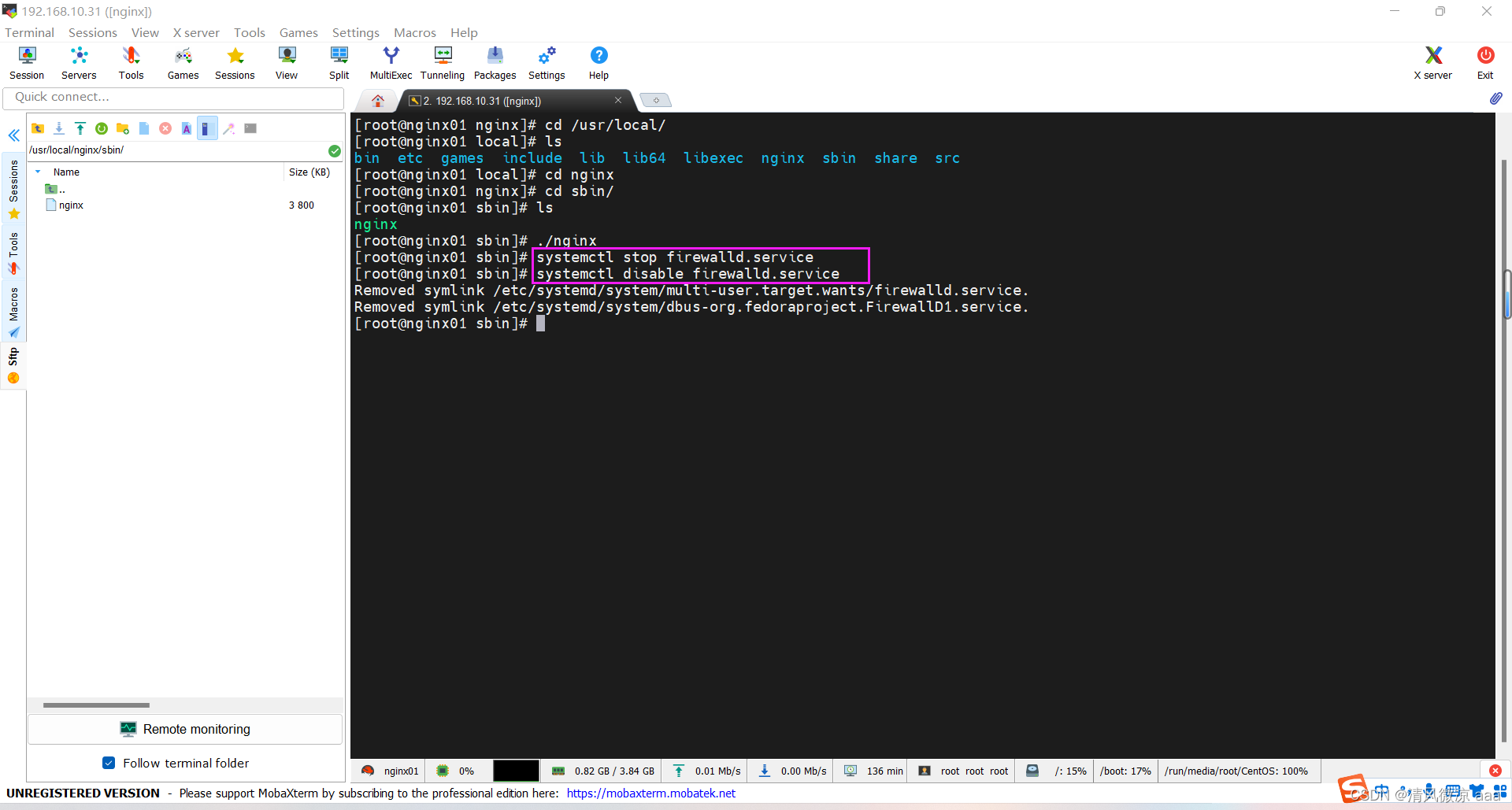
- 方式一:关闭防火墙
# 关闭防火墙
systemctl stop firewalld.service
# 禁止防火墙开机启动
systemctl disable firewalld.service
- 方式二:开放访问的端口号,80 端口
# 放行端口
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=80/tcp --permanent
# 重启防火墙
firewall-cmd --reload
查看防火墙开放的端口号有哪些
firewall-cmd --list-all
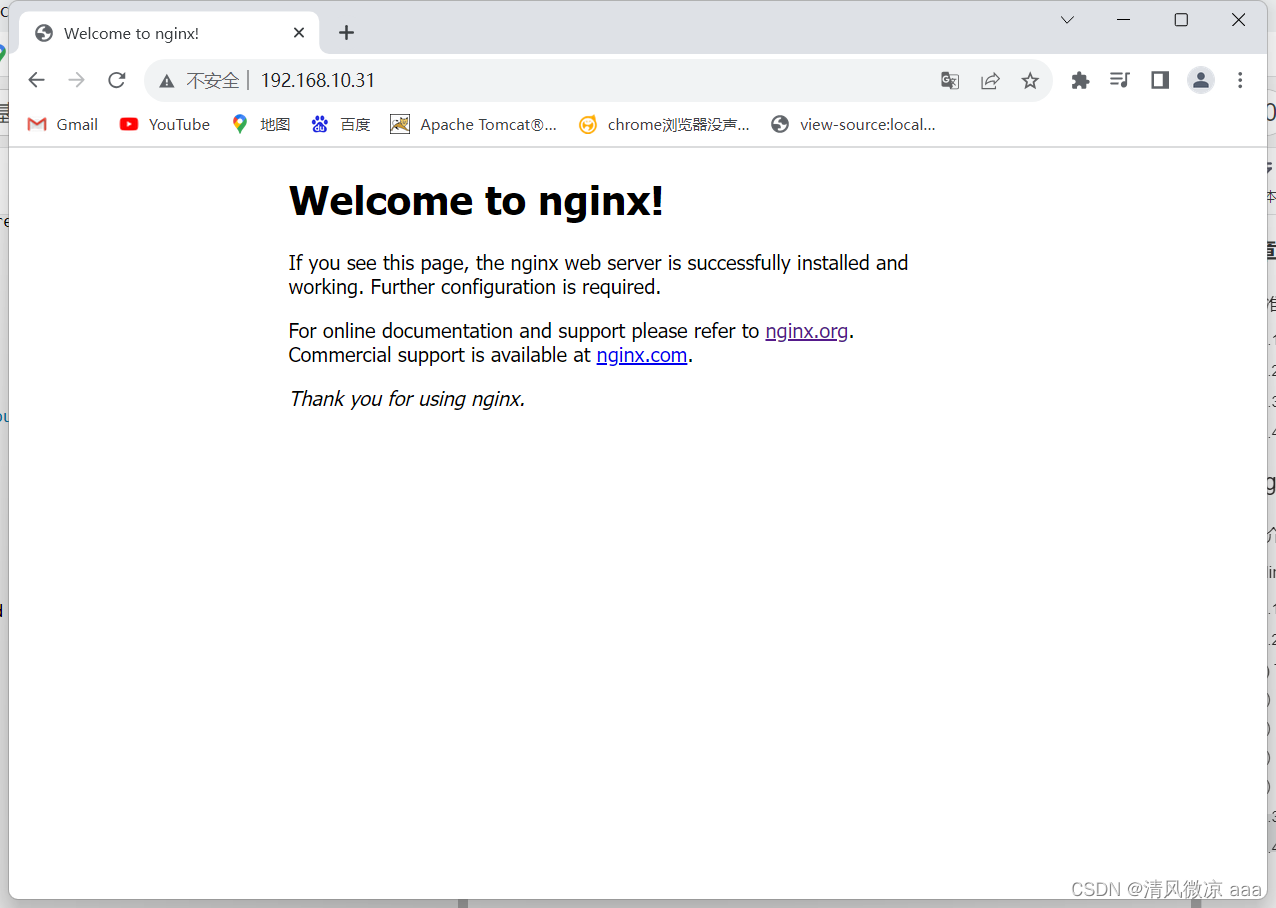
3.2.4 访问测试
前提是关闭了防火墙
端口号默认是:80,可省略
http://192.168.10.31/
3.2.5 安装成系统服务(使用脚本命令启动)
说明:当前启动需要进入到sbin目录执行nginx可执行文件非常的麻烦,可以把它安装成脚本这样用起来就比较简单了。
创建服务脚本
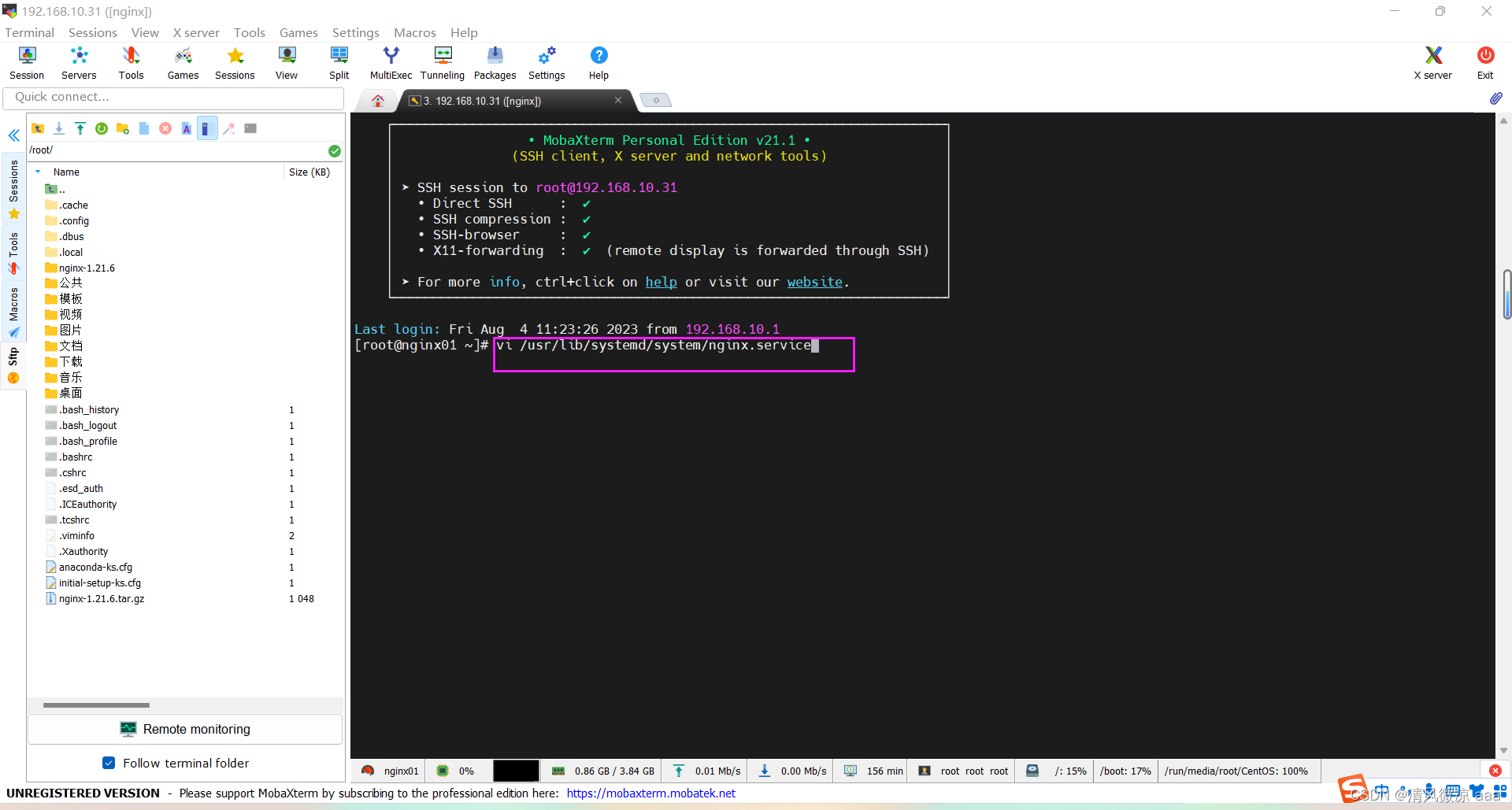
# 创建目录和文件
vi /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service
服务脚本内容
注意:要和之前nginx安装的路径保持一致
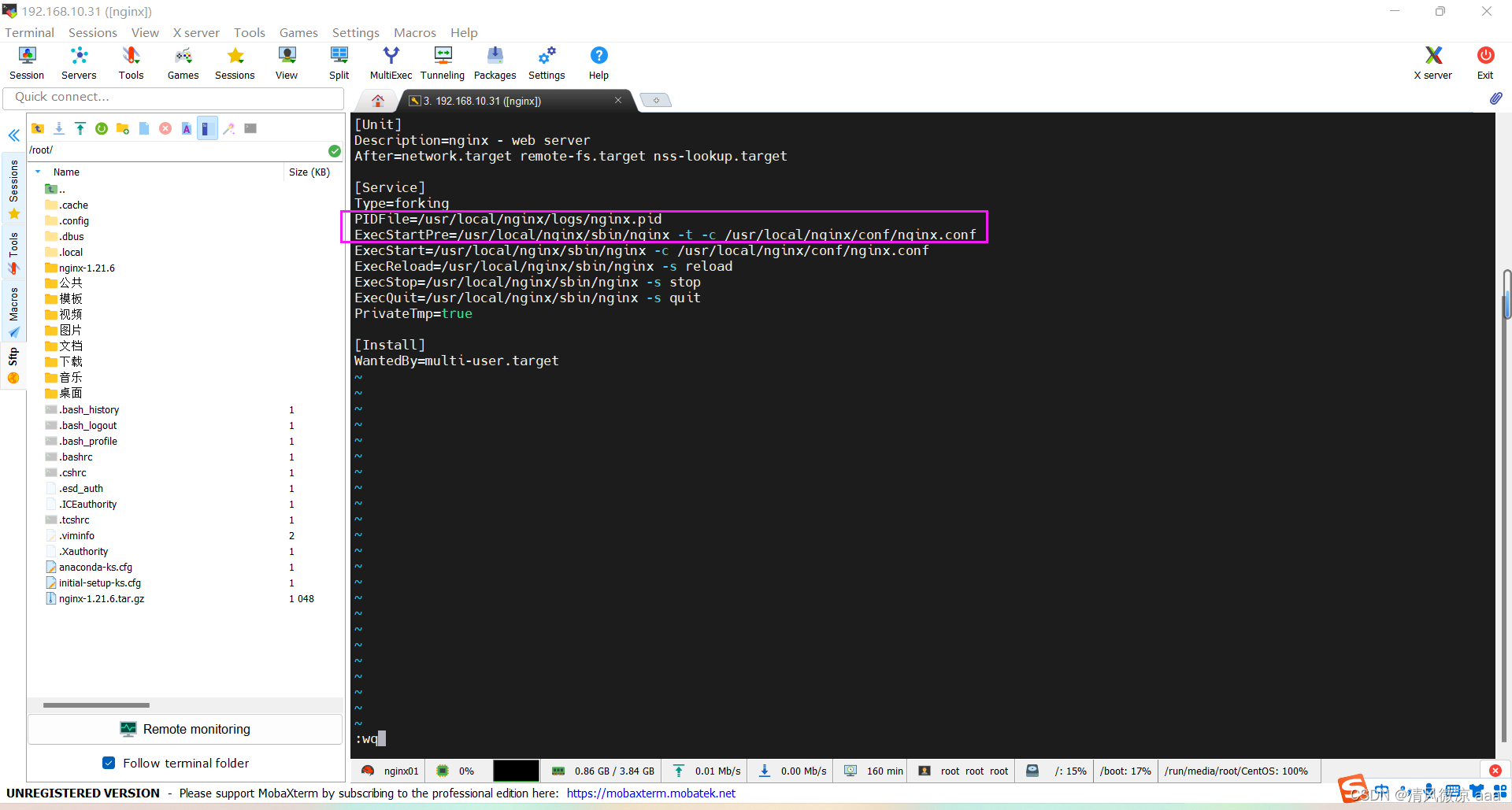
[Unit]
Description=nginx - web server
After=network.target remote-fs.target nss-lookup.target
[Service]
Type=forking
PIDFile=/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid
ExecStartPre=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
ExecStart=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
ExecReload=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
ExecStop=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s stop
ExecQuit=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s quit
PrivateTmp=true
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
重新加载系统服务&关闭之前使用可执行程序启动的方式
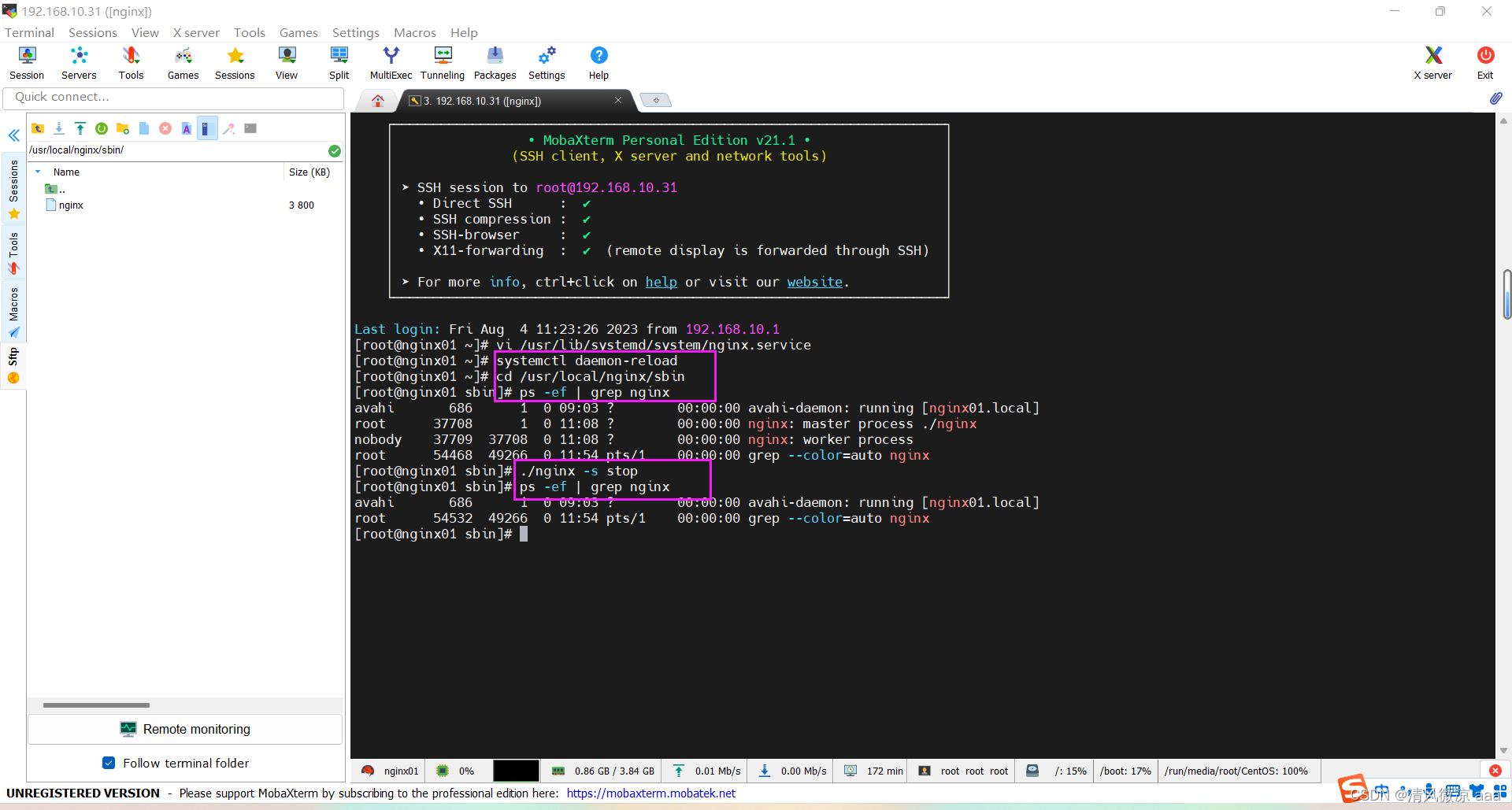
#重新加载系统服务
systemctl daemon-reload
#查看使用ngin可执行程序启动的方式是否还在
ps -ef | grep nginx
#关闭之前使用可执行程序启动的方式,否则2种方式都有可能会造成冲突
./nginx -s stop 快速停止
启动服务
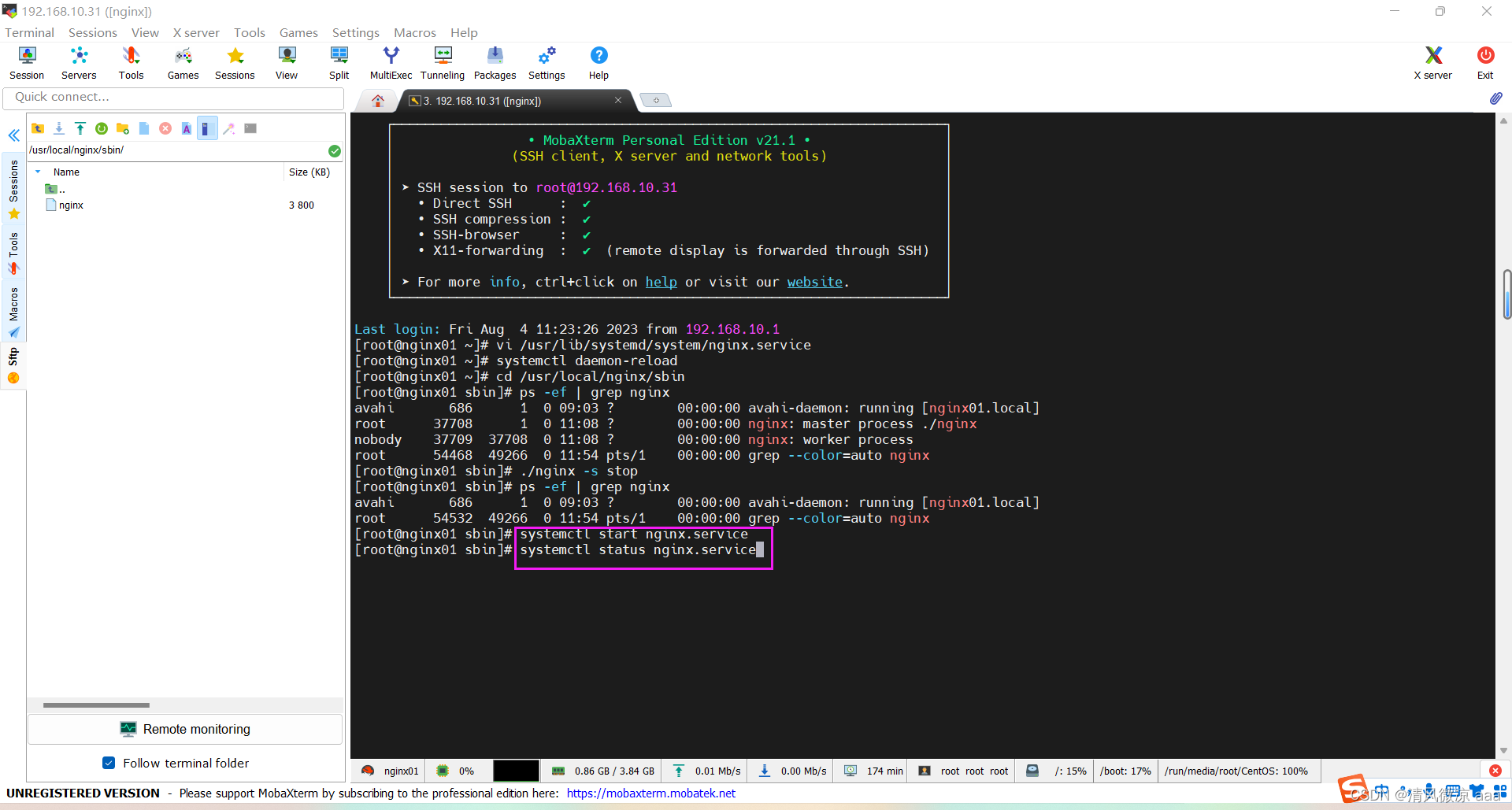
# 启动服务
systemctl start nginx.service
# 停止服务
systemctl stop nginx.service
#查看启动状态
systemctl status nginx.service
3.2.6 开机启动
systemctl enable nginx.service
4 .目录结构与基本运行原理
4.1 目录
进入Nginx的主目录我们可以看到这些文件夹
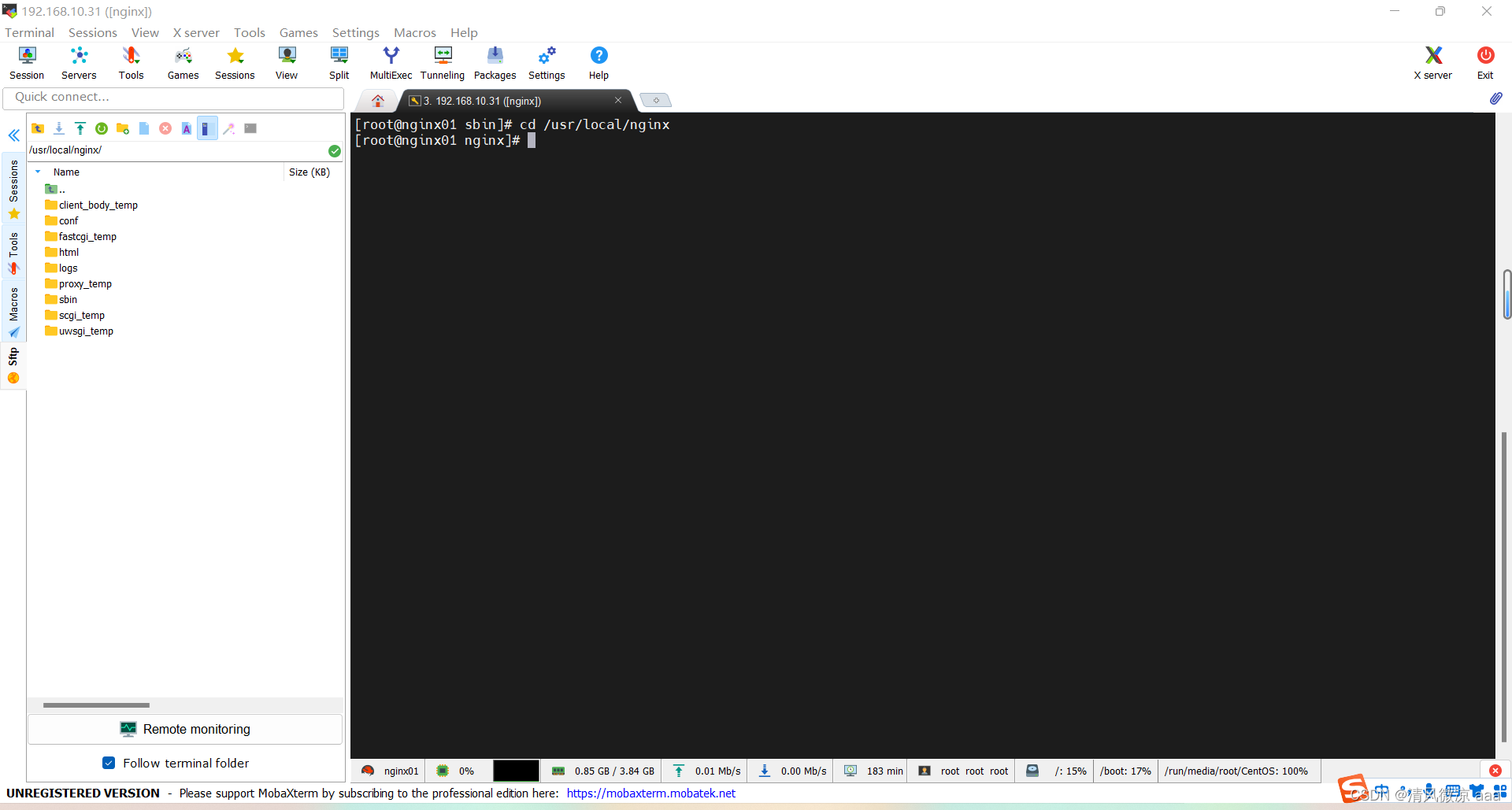
client_body_temp
conf 用来存放配置文件相关
fastcgi_temp
html 用来存放静态文件的默认目录 html、css等
logs
proxy_temp
sbin nginx的主程序
scgi_temp
uwsgi_temp
其中这几个文件夹在刚安装后是没有的,主要用来存放运行过程中的临时文件
client_body_temp
fastcgi_temp
proxy_temp
scgi_temp
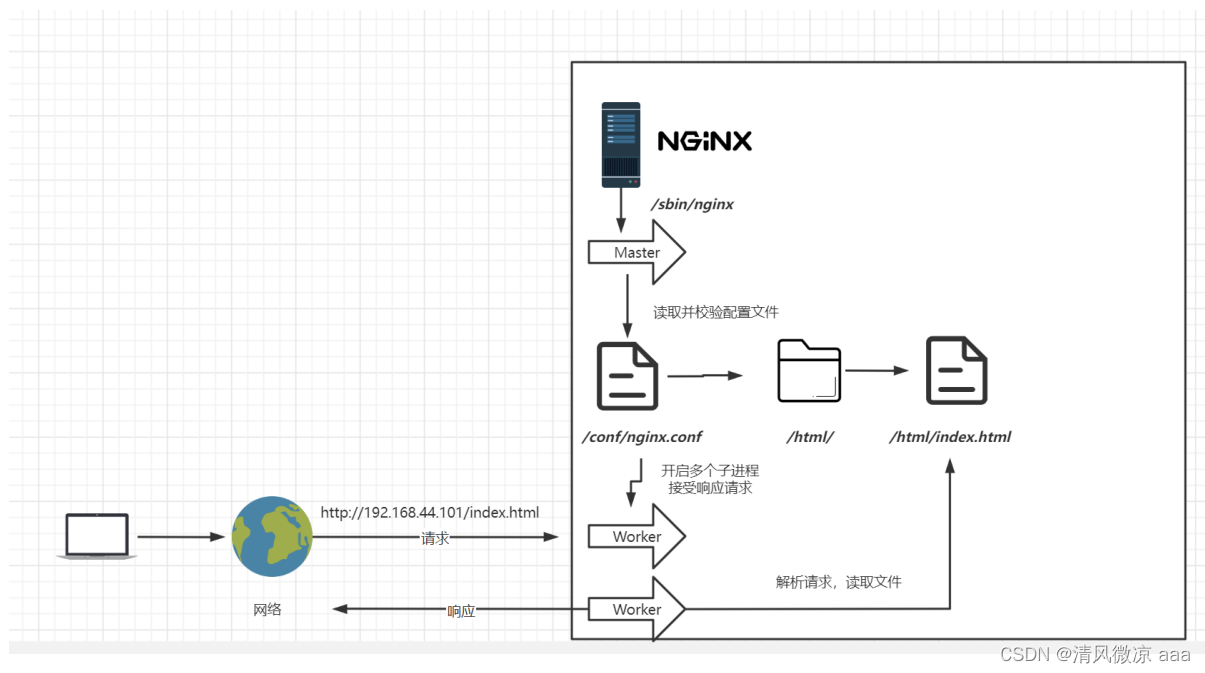
4.2 基本运行原理
总结:nginx启动之后它不只是启动一个进程,而是多进程同时运行的模式。主进程Master不工作只是用来来协调子进程Worker,配置文件的校验是由主进程来完成的,Worker读取配置文件去寻找具体的文件。
5. Nginx基础配置
-
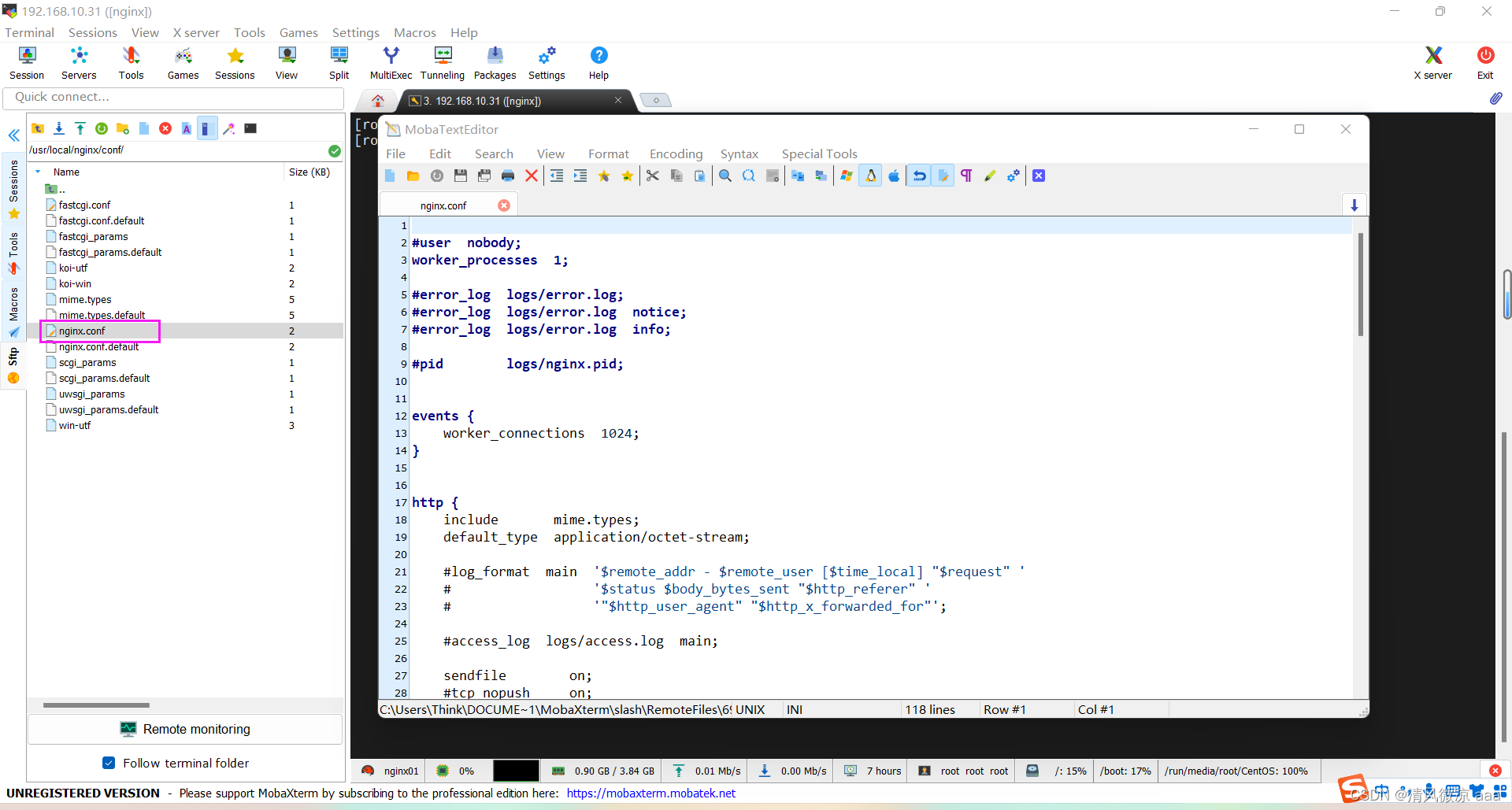
配置文件所在目录:
cd /usr/local/nginx/conf/ -
配置文件:
nginx.config
-
配置文件完整的信息
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}
- 配置文件去掉注释部分的信息
- 这里只学习的是精简后的配置文件,至于注释部分到下面在讲解。
worker_processes 1;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
}
5.1 最小配置文件
worker_processes
# 默认为1,表示开启一个业务进程(一般一个cpu内核对应一个业务进程)
worker_processes 1;
worker_connections
# 单个业务进程可接受连接数
worker_connections 1024;
include mime.types;
# 引入额外的配置文件
# 这个文件设置的是请求的头,标名当前返回或者发送的文件是什么类型
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
# 如果mime配置文件中的类型没匹配上,默认使用二进制流的方式传输。
default_type application/octet-stream;
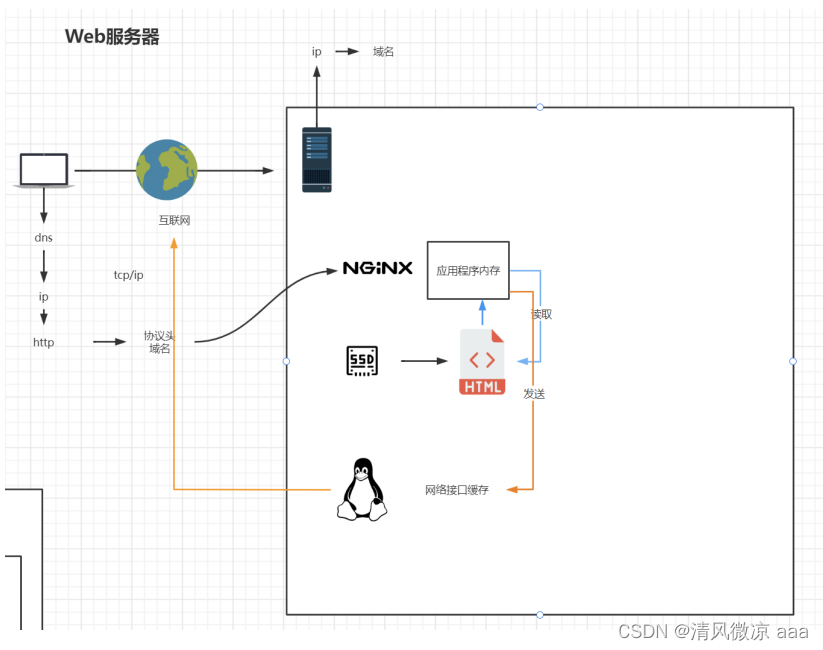
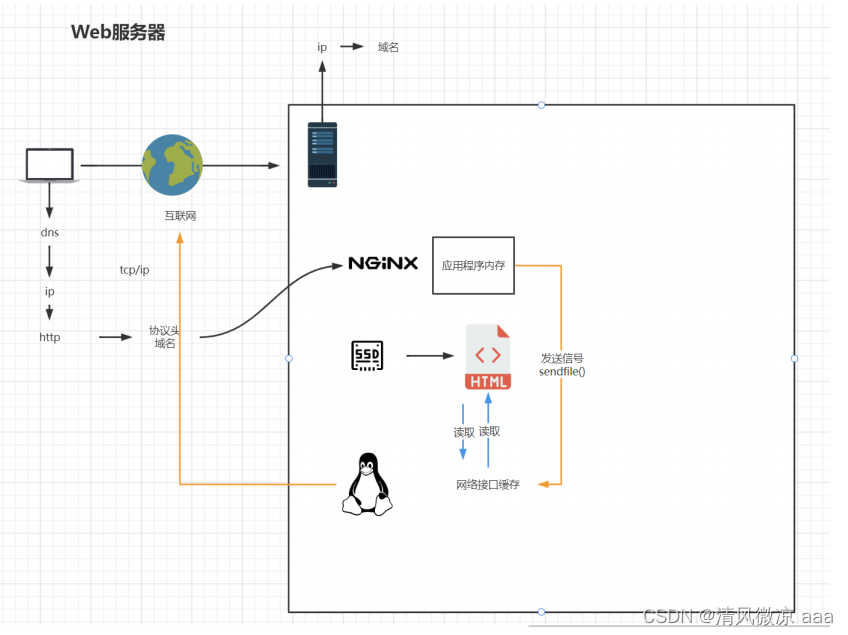
sendfile on;
# 使用linux的 sendfile(socket, file, len) 高效网络传输,也就是数据0拷贝。
# 所谓的零拷贝,其目的并不是说不需要拷贝数据,而是通过一些手段省略 CPU 拷贝环节,减少了不必要的拷贝次数,提升数据拷贝效率。
sendfile on;
未开启sendfile
开启后
keepalive_timeout 65;
# 保持连接超时的时间
keepalive_timeout 65;
server:虚拟主机配置
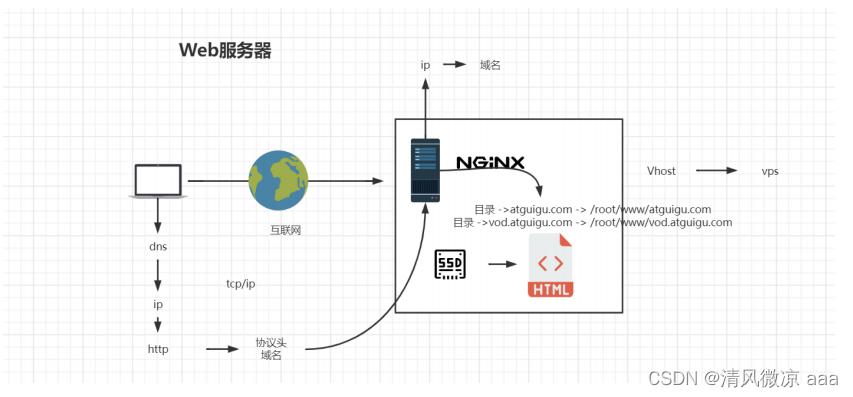
#一个server代表一台虚拟主机(vhost)
#一个主机,多个主机都可以配置在nginx的配置文件中
server {
listen 80; 监听当前服务器的端口号
server_name localhost; 域名或主机名
#域名后面跟的子路径(到后面在详解)
# 举例:http://atguigu.com/xxoo/index.html,匹配atguigu.com域名后的路径。
location / { 匹配路径
root html; 文件根目录(nginx的安装路径)
index index.html index.htm; 默认页名称
}
#http://atguigu.com/xxoo/index.html一旦报错会替换为
#http://atguigu.com/50x.html,跳转到50x.html页面
#但是没有这个50x.html页面,所以在下面定义这个页面路径
#逻辑:跳转到这个页面,但是这个页面没有,用户一旦访问/50x.html,
#会从root html这个目录下去寻找50x.html页面
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; 报错编码对应页面
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
6.虚拟主机与域名解析
6.1 浏览器、Nginx与http协议
-
TCP协议:tcp是一个广泛的浏览器协议,它是以流的形式,进行传递数据的(数据是二进制的)
-
数据流:相当于一个水龙头,开启之后一直流通,没有关掉的动作
-
HTTP协议:是一个在TCP之上的协议,它会在里面告诉TCP协议什么时候关掉流,当用户的浏览器和Nginx服务器都遵守和实现了HTTP协议之后,他们之间就可以进行信息的交流、传递了。
-
HTTPS协议:HTTP之上的一个协议,加了一层数据加密的措施,保护数据。
-
请求流程:用户浏览器发送请求—> 网关(层层网关)—>—>互联网—>Nginx服务器—>解析请求—>找到资源—>返回给用户
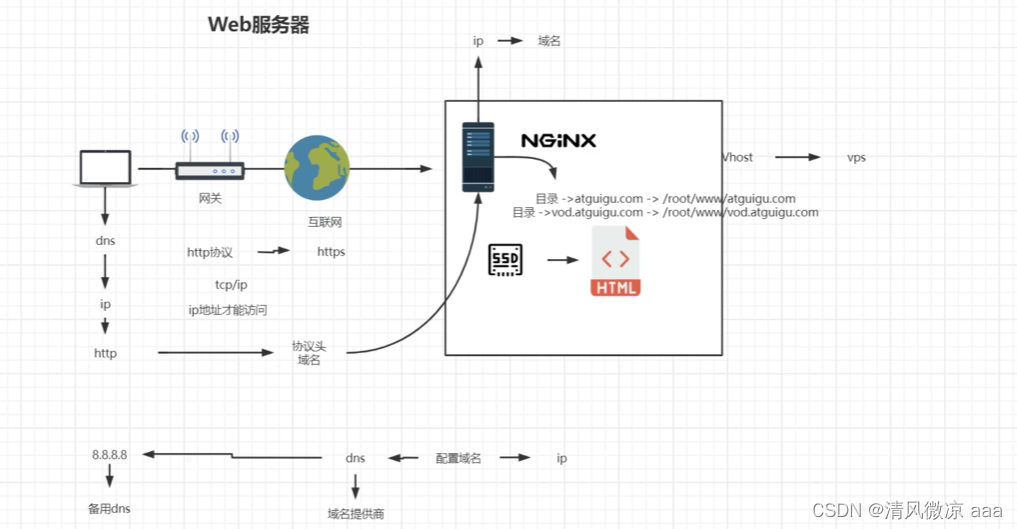
6.2 虚拟主机原理
-
原本一台服务器只能对应一个站点,通过虚拟主机技术可以虚拟化成多个站点同时对外提供服务
-
如果有这样一个场景,假如一台主机只挂载了一个站点,当这个站点并没有太多的访问量时,就会造成资源过剩(有剩余资源),这时我们可以开启虚拟主机,挂载多个站点,合理的利用主机的资源。
-
一个IP地址可以对应多个域名,根据域名的不同,我们去寻找这些域名对应的资源目录,找到这些资源之后,返回给用户。
-
当然,我们需要在请求报文中加上这个域名,不然服务器不知道我们需要哪个域名的资源
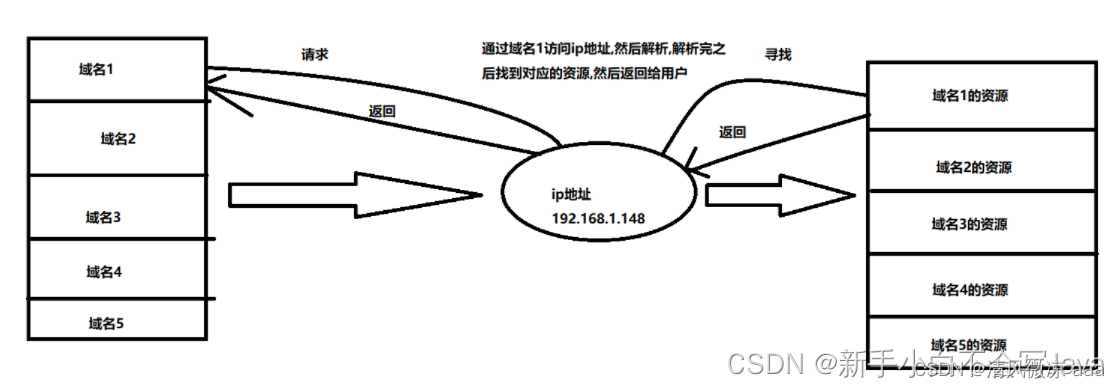
6.3 域名解析与泛域名解析实战
6.3.1 使用hosts文件解析域名
什么是hosts文件: 简单的说,hosts文件是用于本地dns服务的,采用ip 域名的格式写在一个文本文件当中,Hosts是一个没有扩展名的系统文件,可以用记事本等工具打开,其作用就是将一些常用的网址域名与其对应的IP地址建立一个关联“数据库”,当用户在浏览器中输入一个需要登录的网址时,系统会首先自动从Hosts文件中寻找对应的IP地址,一旦找到,系统会立即打开对应网页,如果没有找到,则系统再会将网址提交DNS域名解析服务器进行IP地址的解析。
- 以管理员的方式使用switchhosts打开hosts文件,进行以下配置。
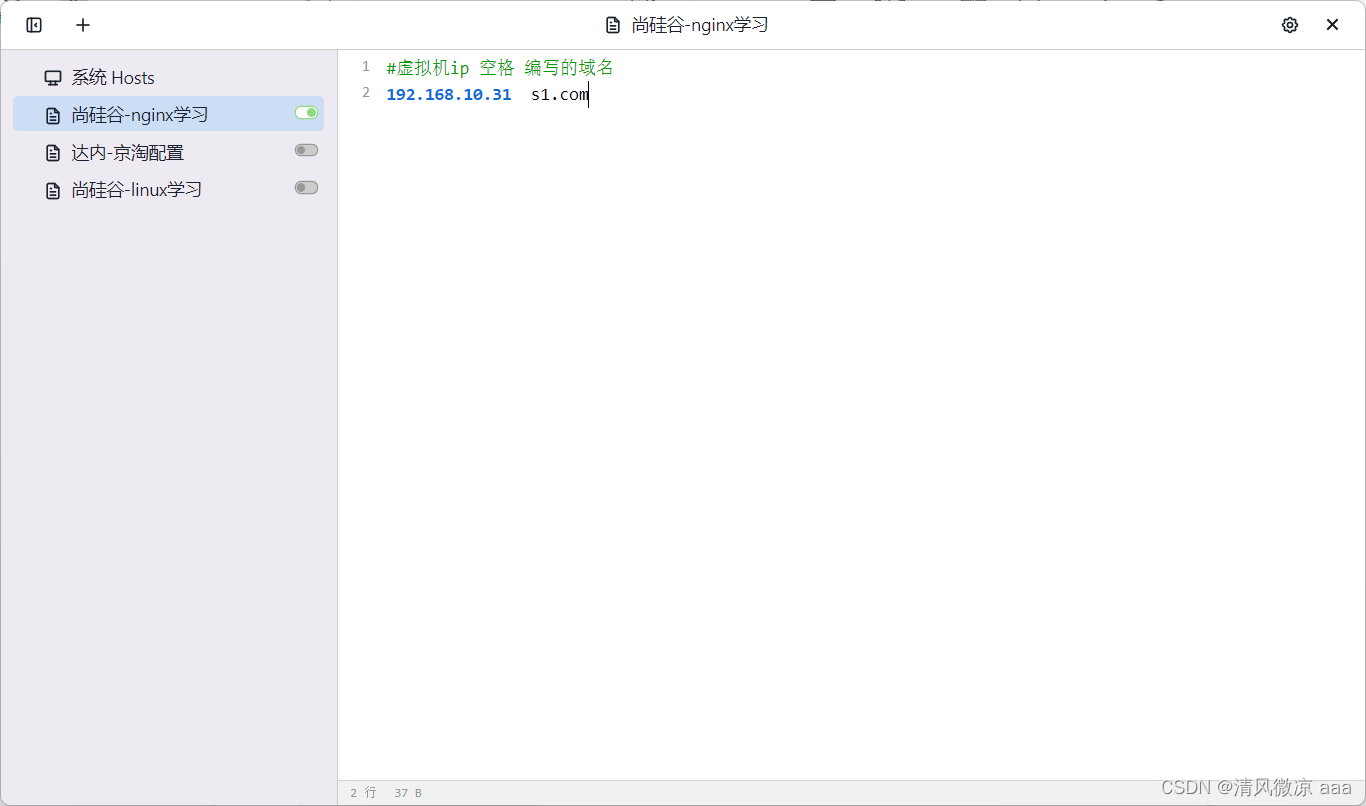
#虚拟机ip 空格 编写的域名
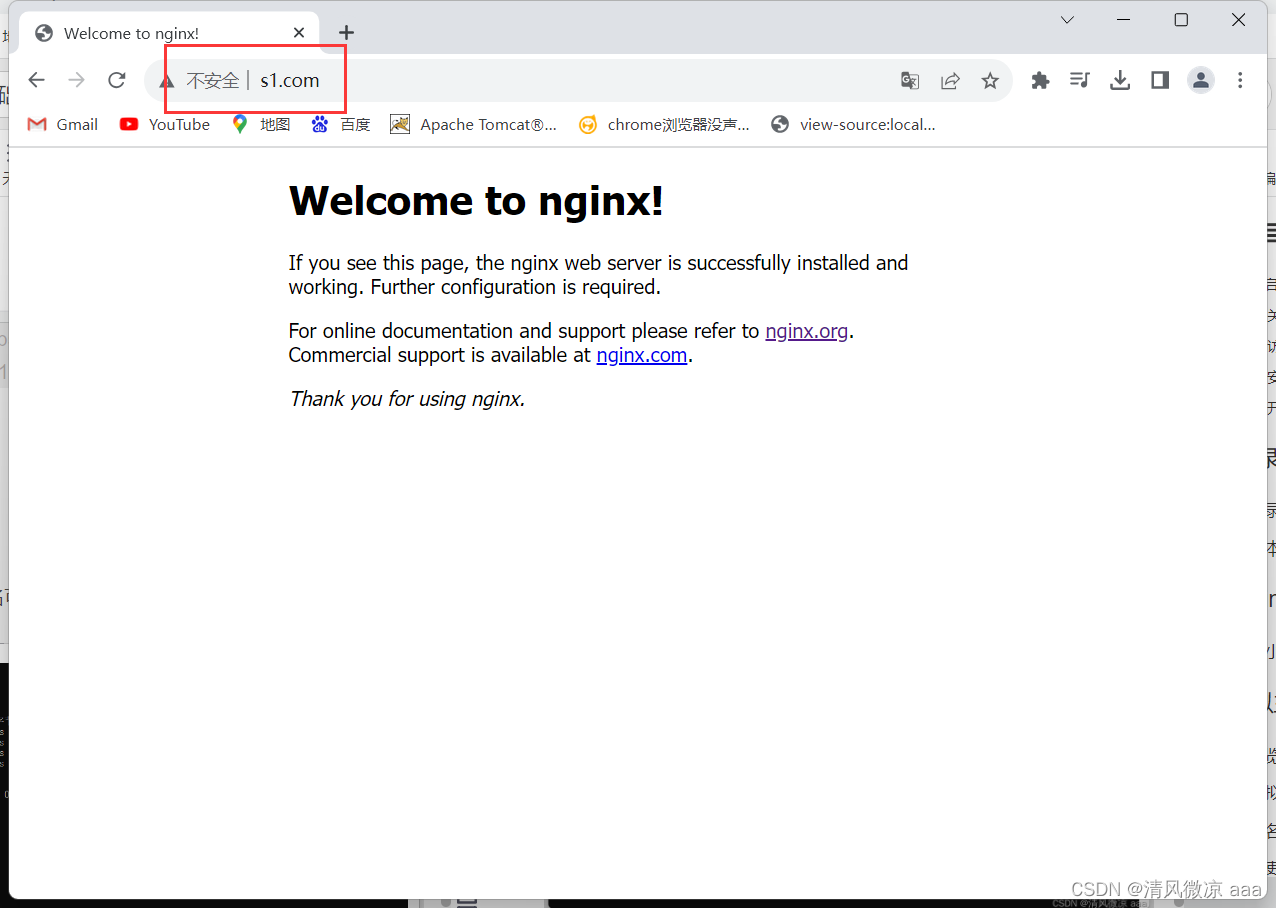
192.168.10.31 s1.com
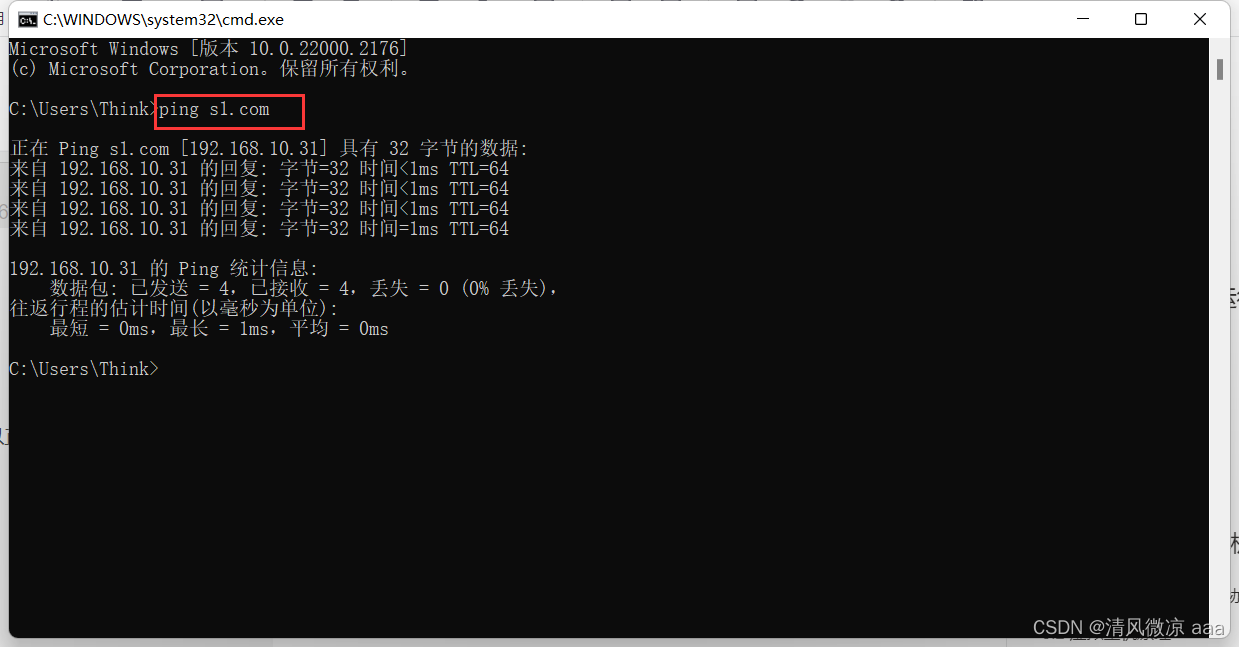
- 测试效果:发现使用域名可以ping通,也可以正确访问到默认页面。
6.3.2 公网域名配置&泛域名解析实战
说明:上面是在hosts文件中假装配置了一个域名解析,在企业中一般是买一个真正的域名使用,在这里就讲解使用真正的域名该如何配置和解析,以及里面配置的选项是什么含义。
- 域名最大的供应商是万网,被阿里云收购了,所以直接登录阿里云购买域名即可。
- 推荐在大品牌的供应商购买域名,小的供应商可能会跑路。
- 新人可以免费试用域名,此案例以使用域名为例,注册步骤如下:
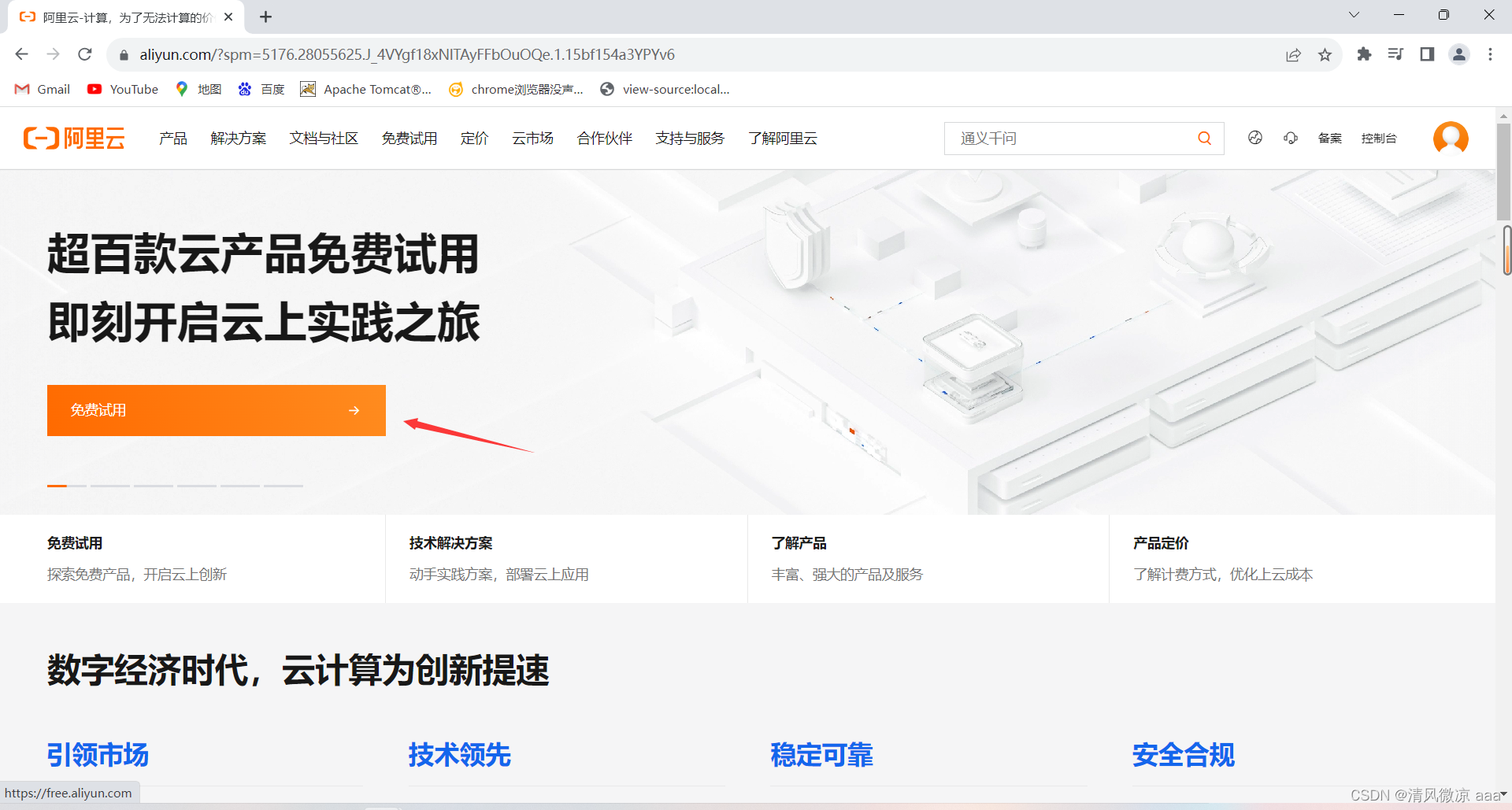
-
登录阿里云首页,点击免费试用
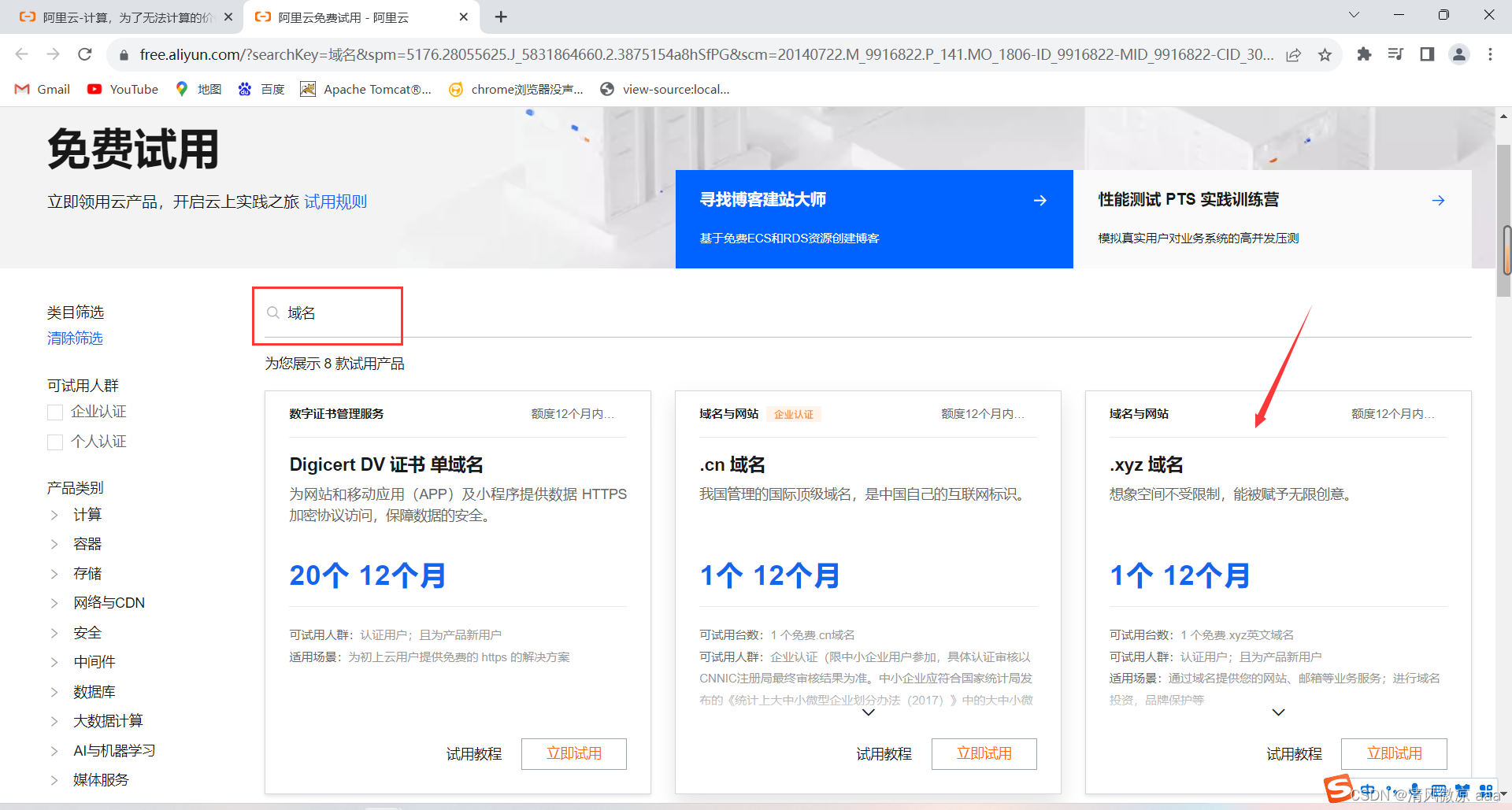
-
搜索域名
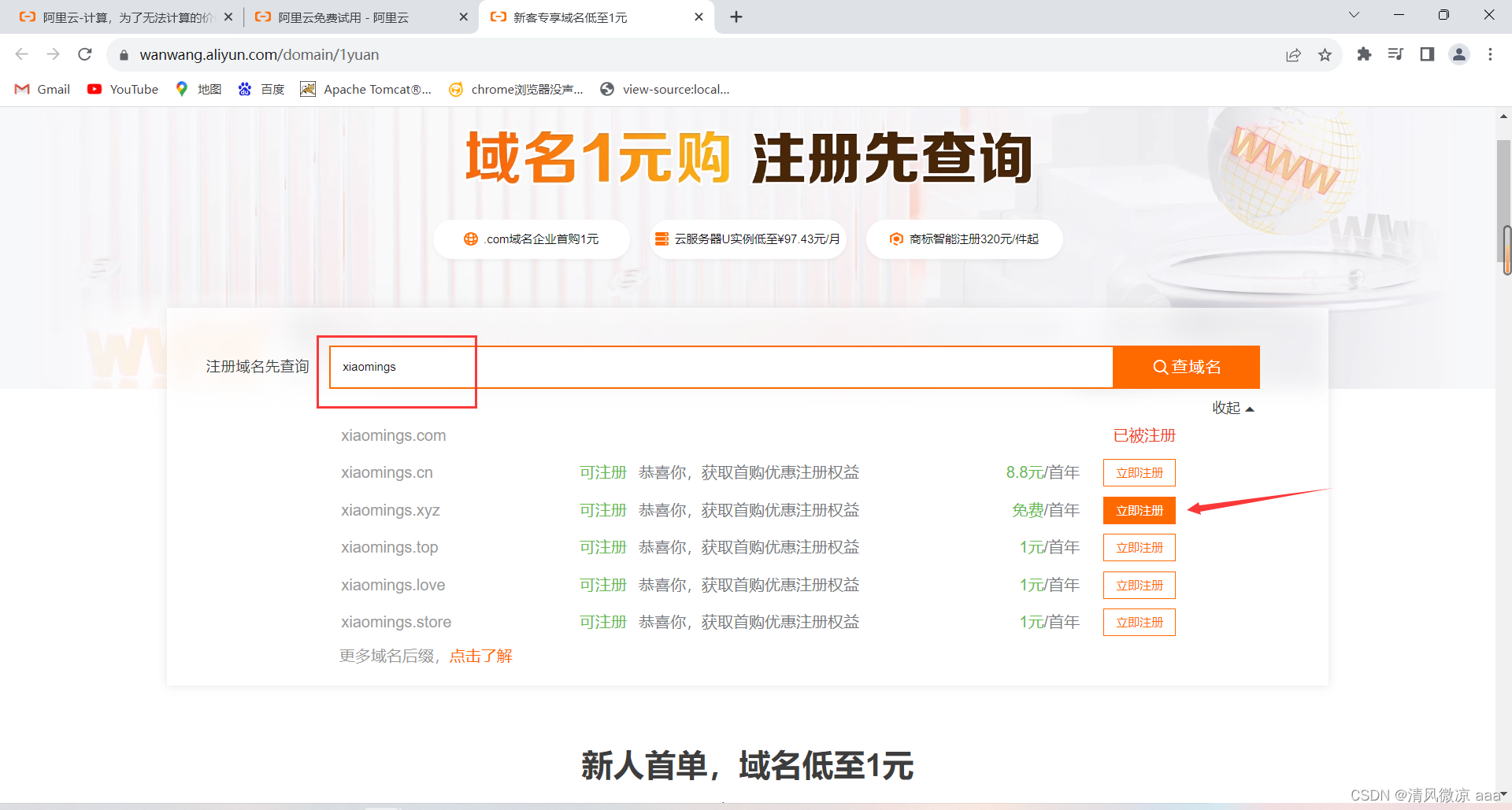
-
查询想要使用的域名是否被注册
-
进行注册,需要填写信息模版
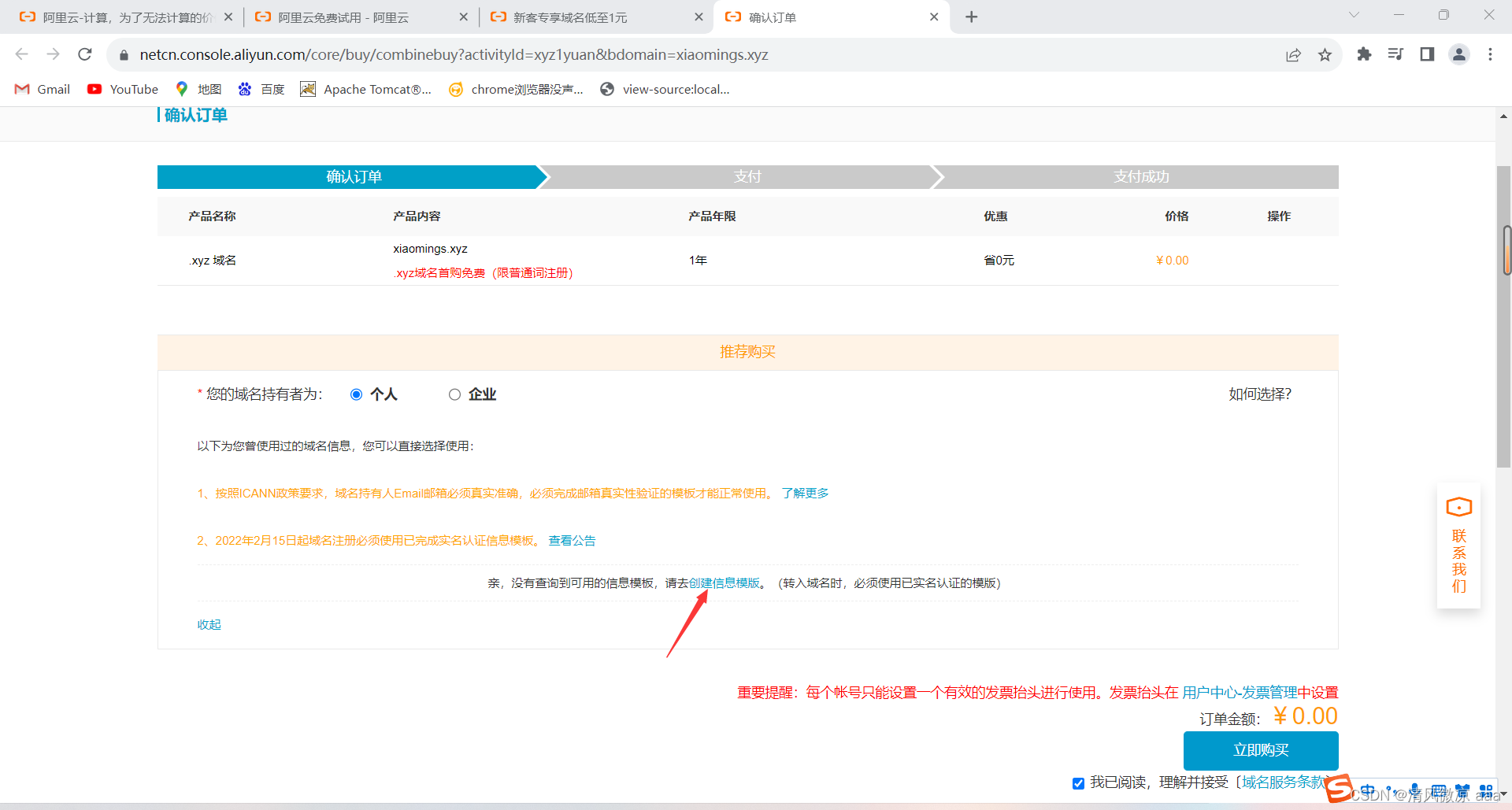
-
在信息模版页面填写个人信息进行提交,之后需要时间审核信息模版。
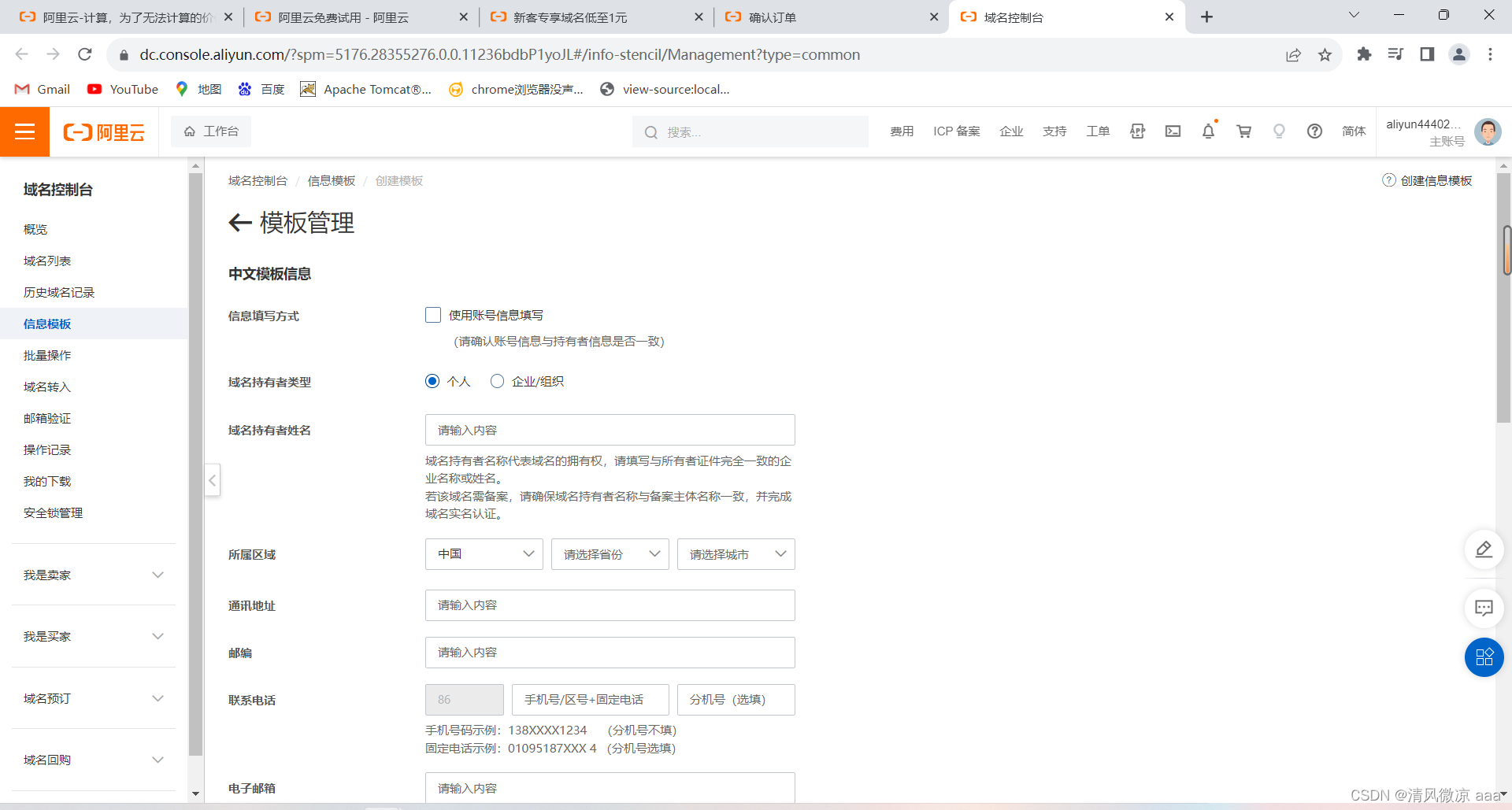
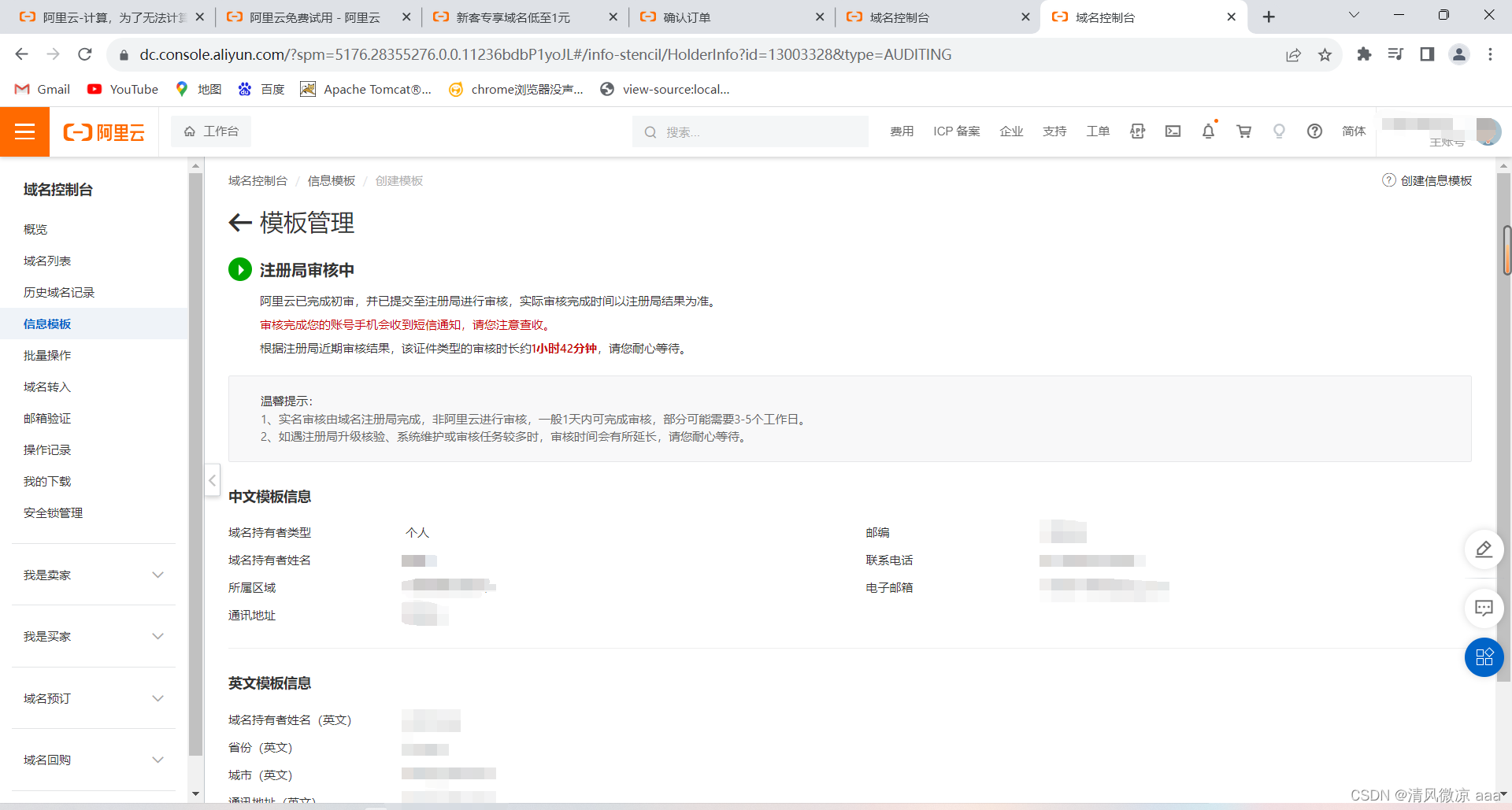
-
信息模版审核成功后,返回确认订单页面进行购买支付。
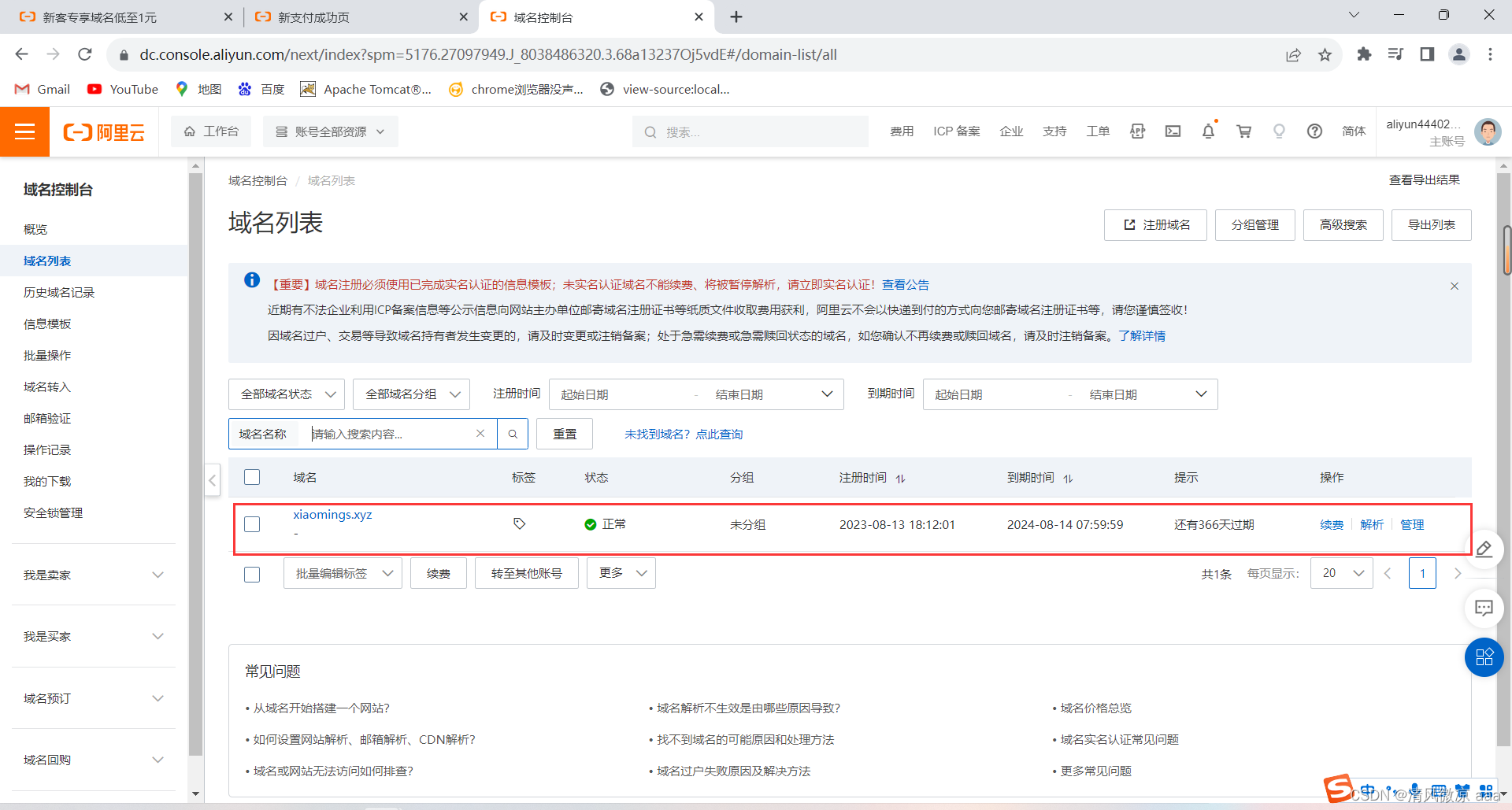
-
在域名控制台可以看到刚才注册好的域名(注册局审核需要时间)。
-
- 使用注册好的域名:
-
解析域名:把域名解析到虚拟机的ip地址上(可以是内网,也可以是外网),即把域名指向IP地址
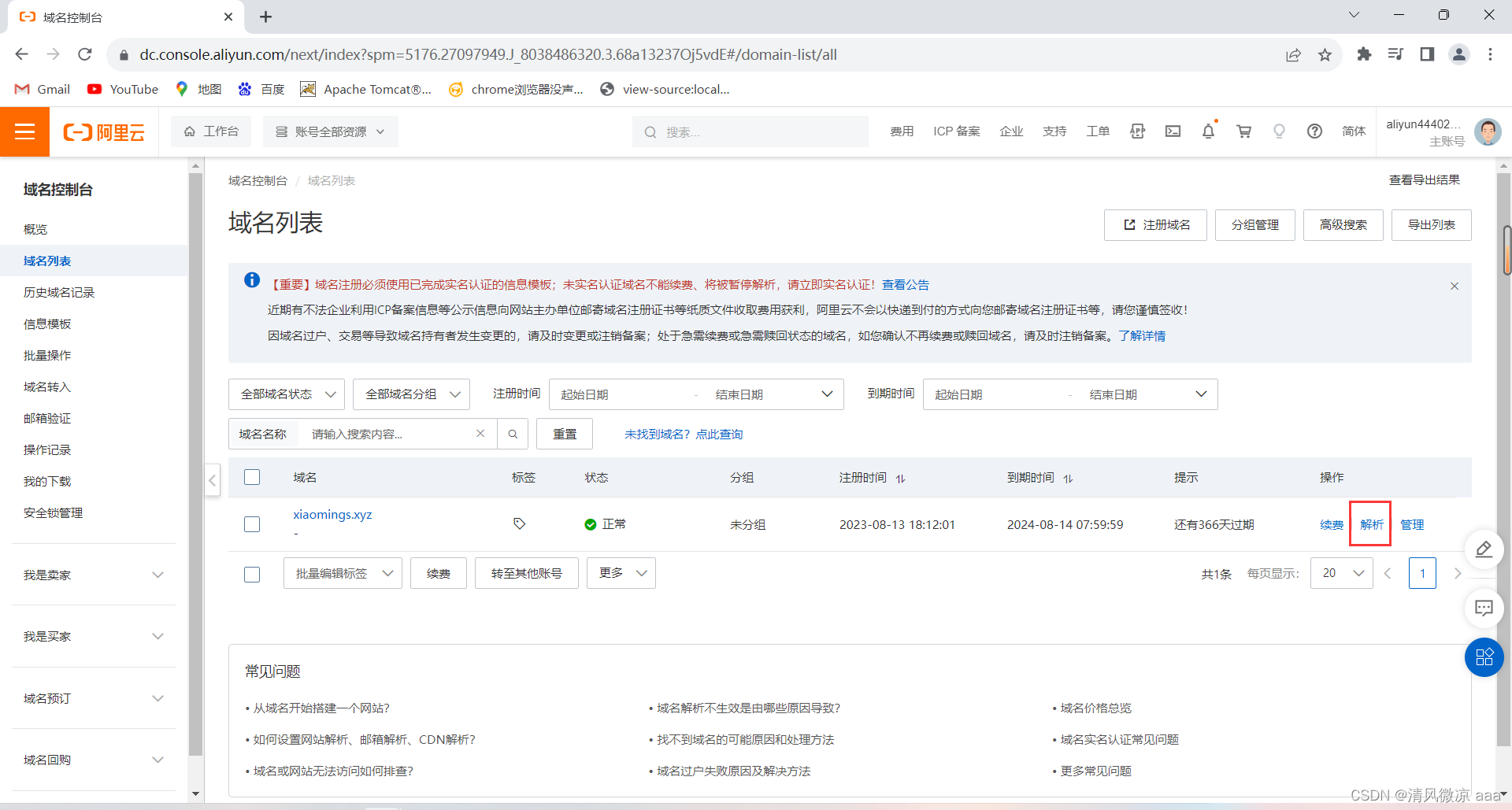
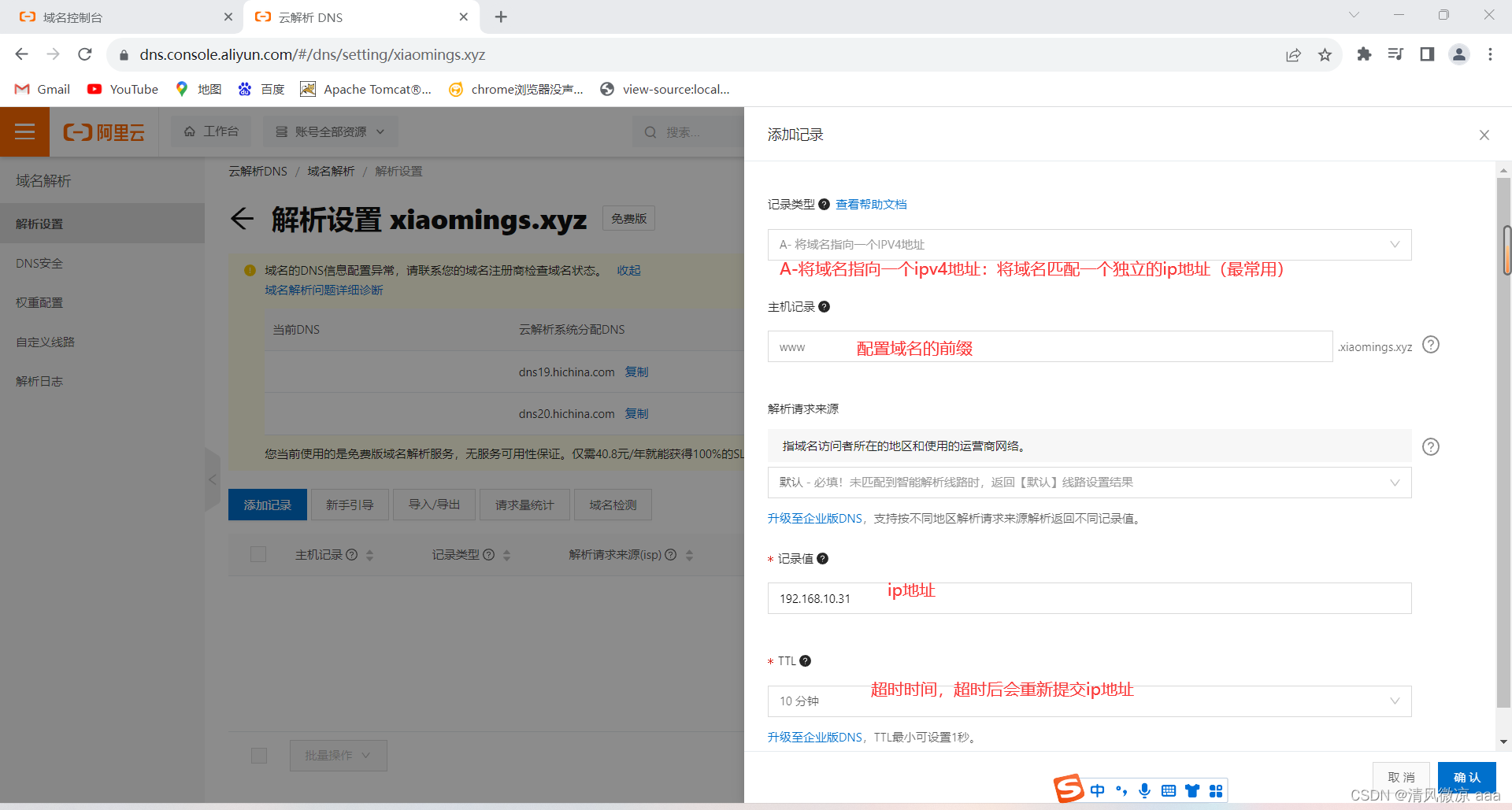
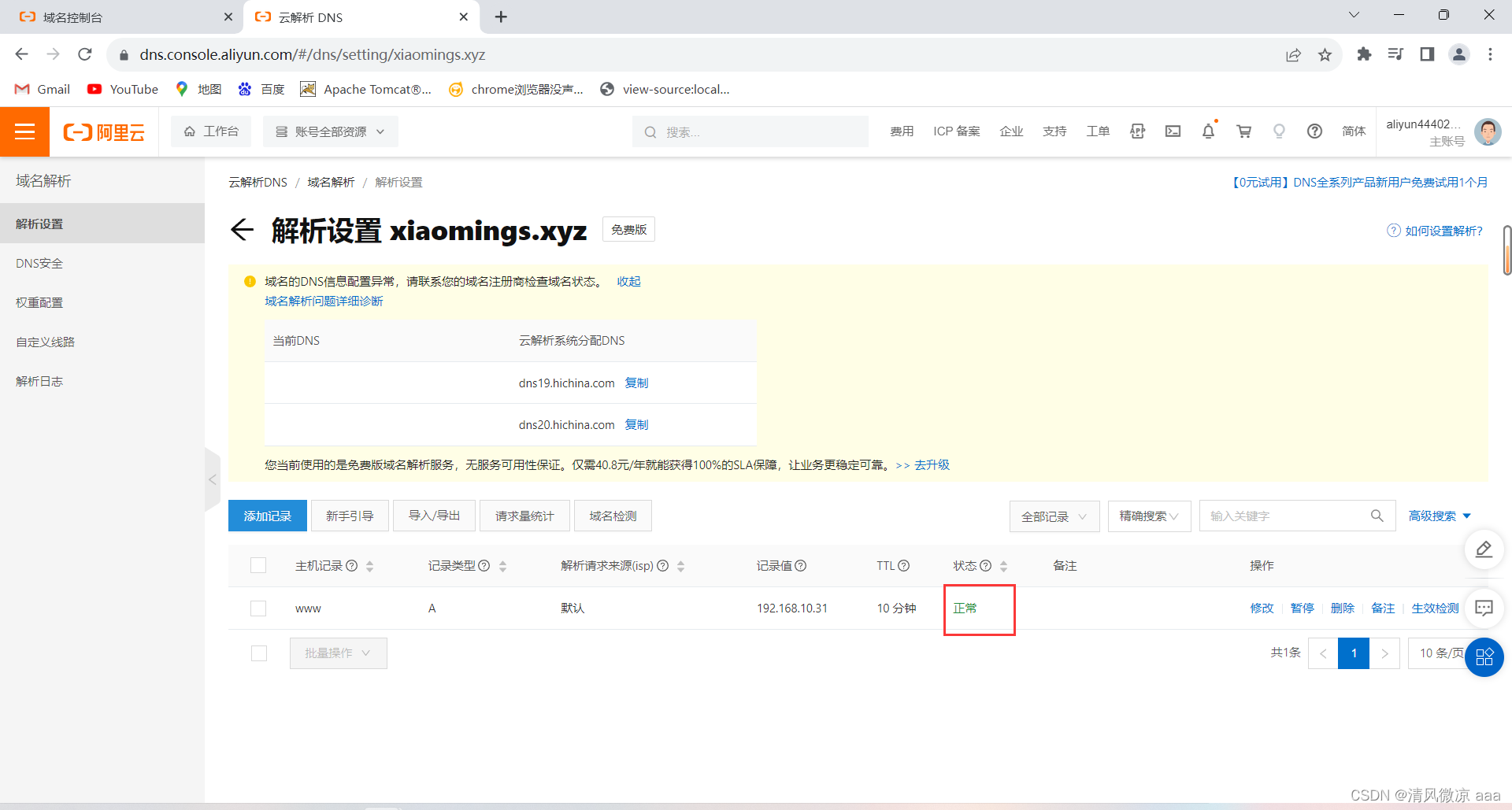
-
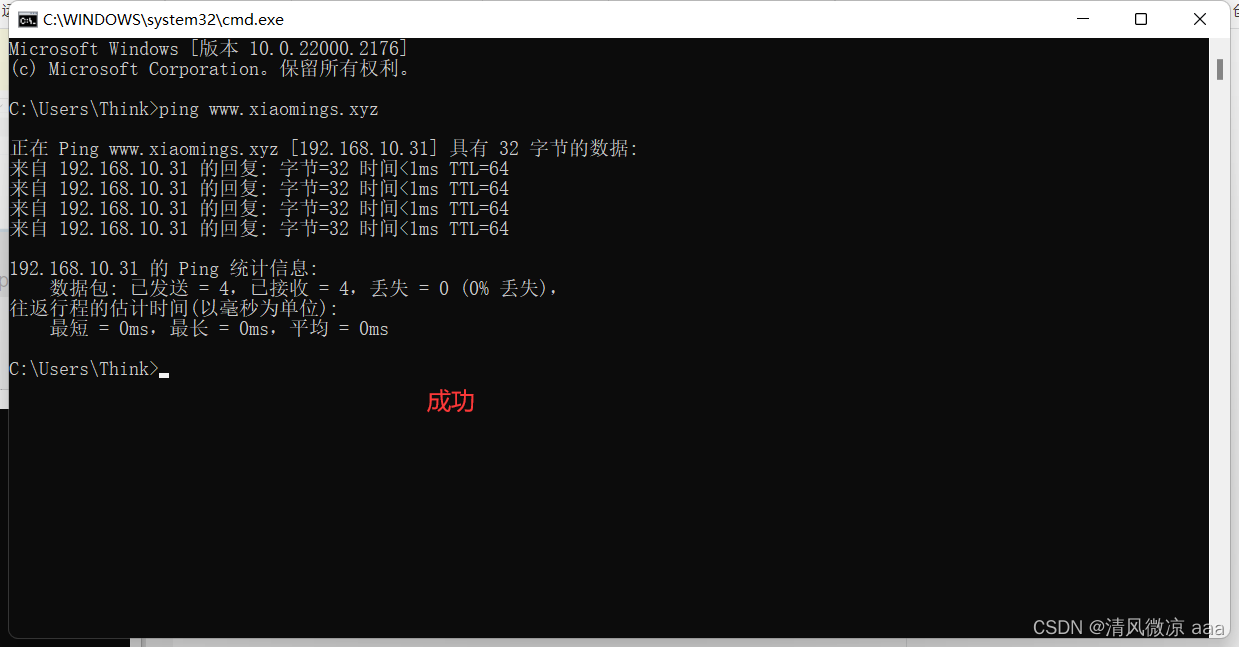
验证是否解析成功:
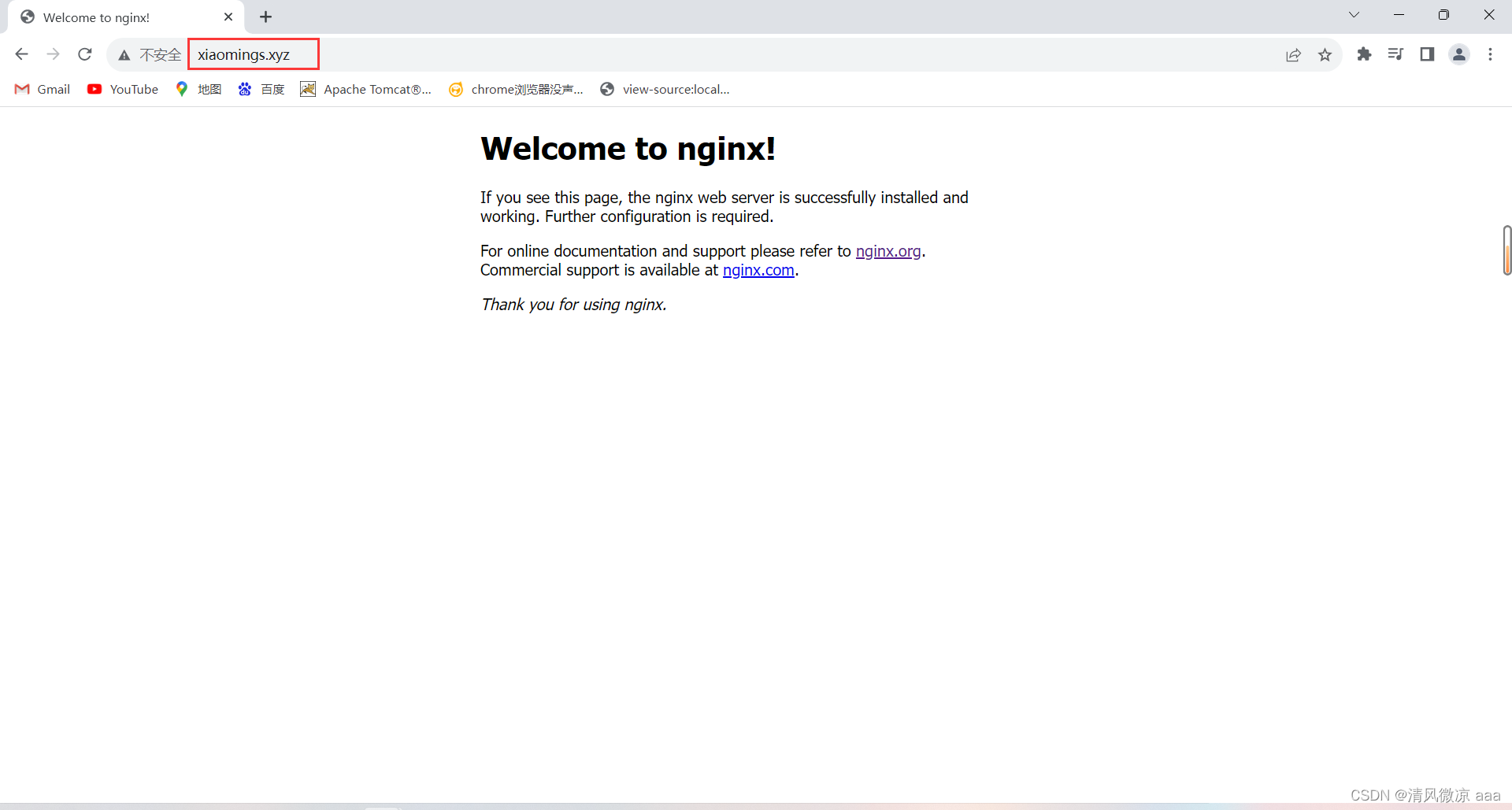
ping www.xiaomings.xyz
-
使用域名访问nginx的默认页面:访问成功
-
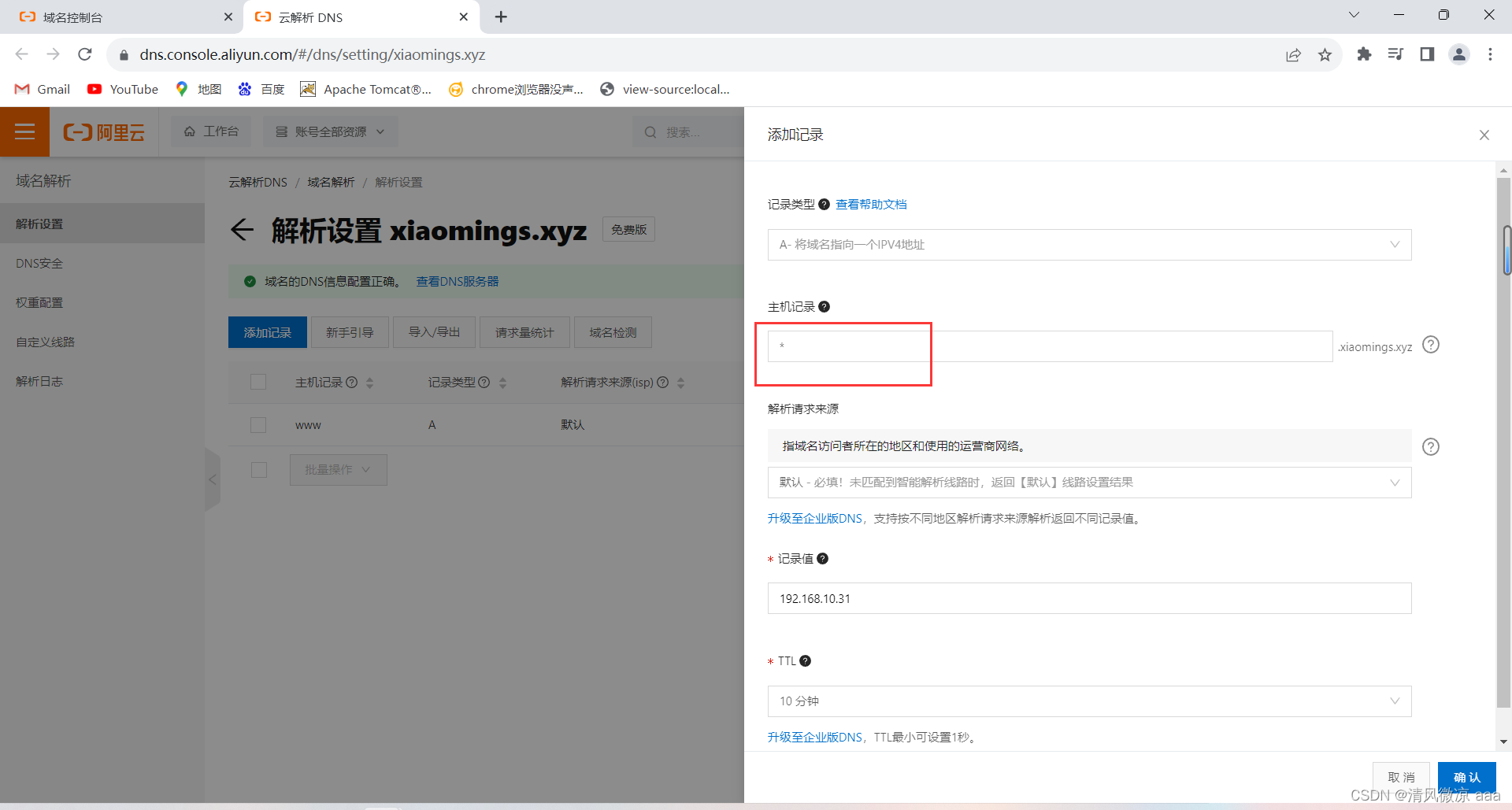
如果域名有很多,那么需要一个个的添加记录进行解析。
-
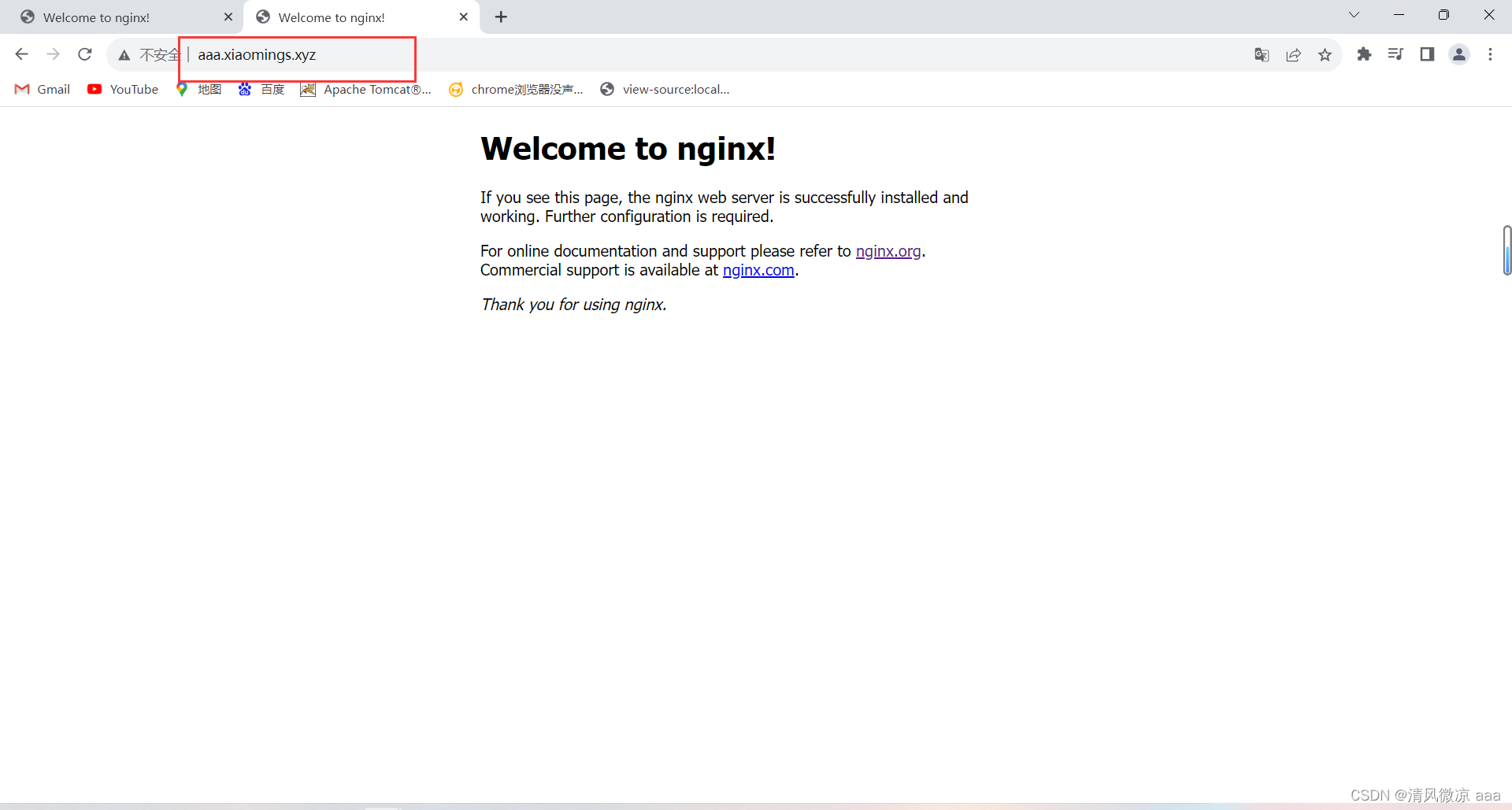
如果二级、三级域名比较多,比如域名的前缀有很多个那么可以使用通配符来进行设置,此时任何前缀的域名都可以访问。
-
6.3.3 Nginx虚拟主机域名配置
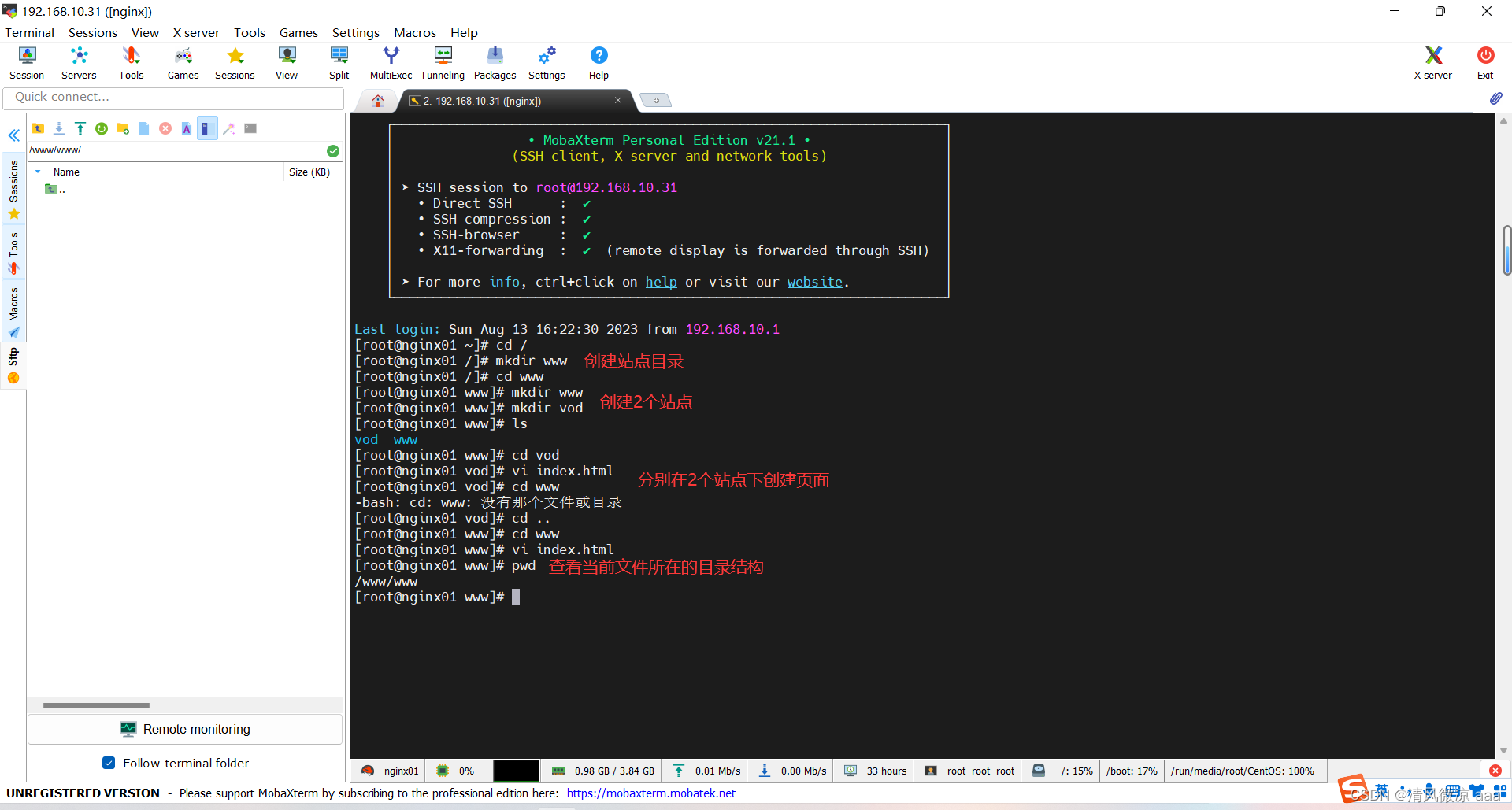
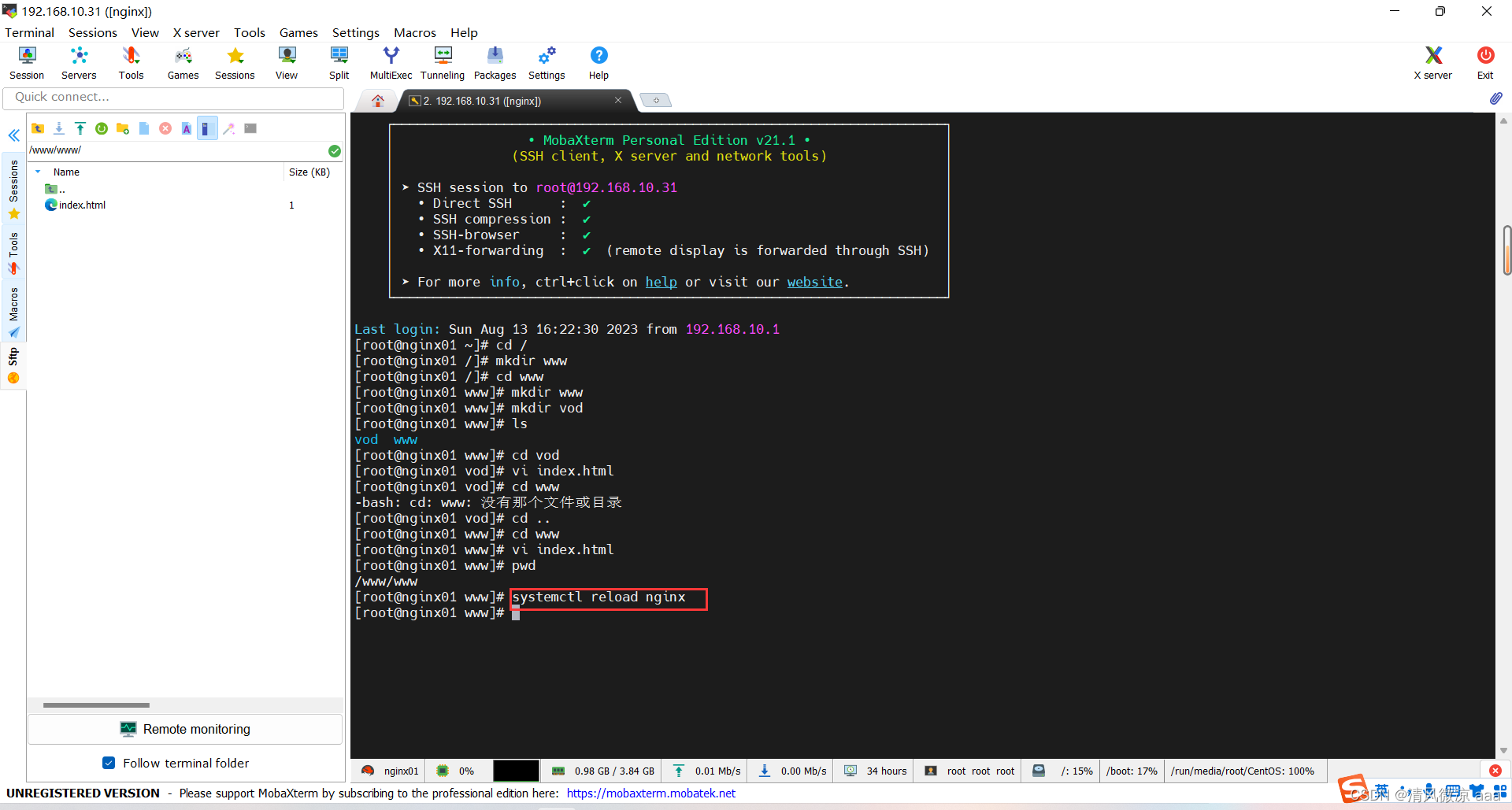
- 当前访问所有域名都指向一个ip地址,只有一个站点可以提供服务。现在配置多个站点进行访问。
步骤:
- 创建站点目录:www
- 在www目录下创建2个站点:www、vod
- 分别在2个站点中创建页面进行测试
- 修改配置文件:不用怕改错,下面还有个nginx的默认配置文件,改错之后可以把它复原回去。
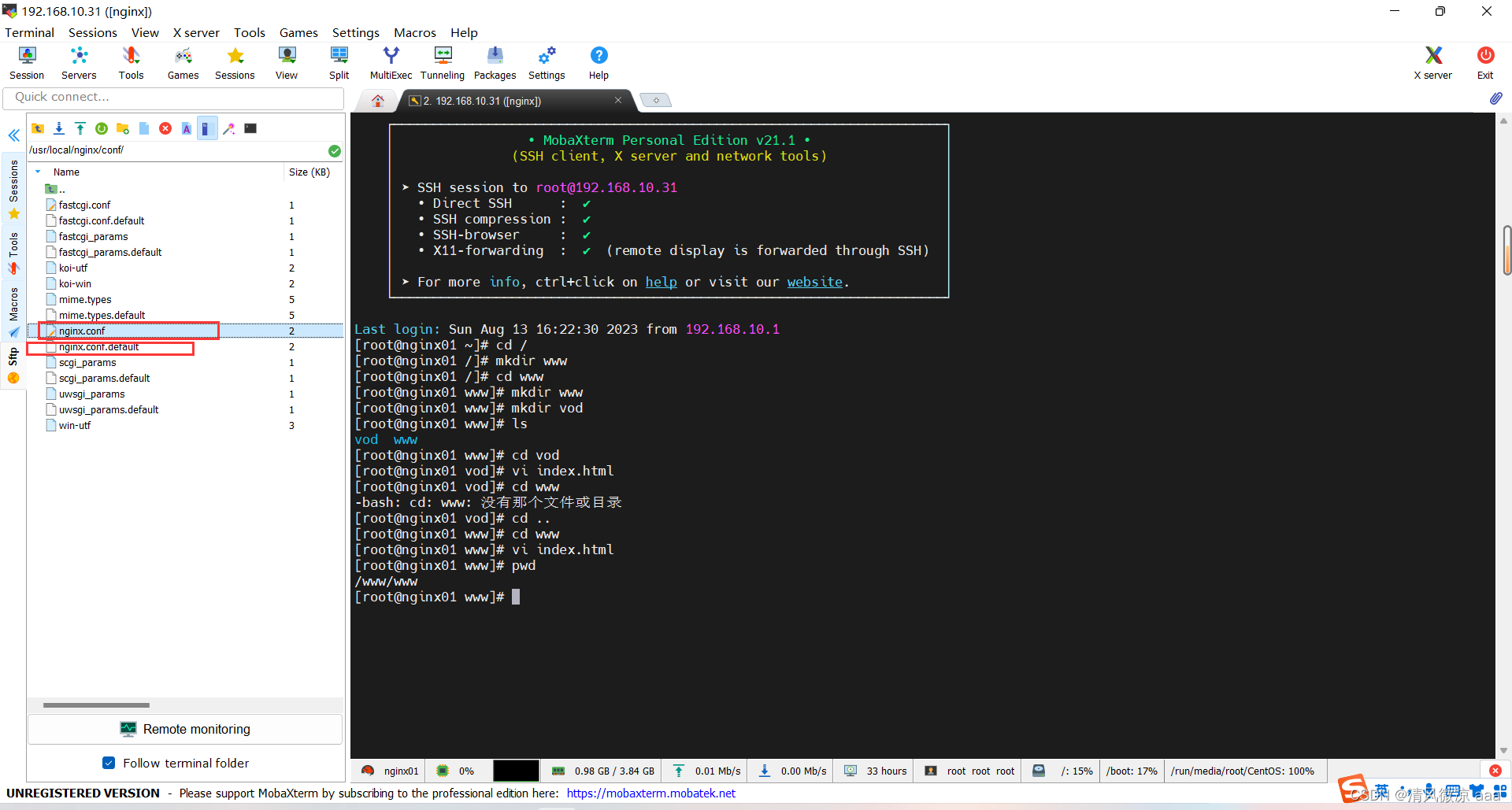
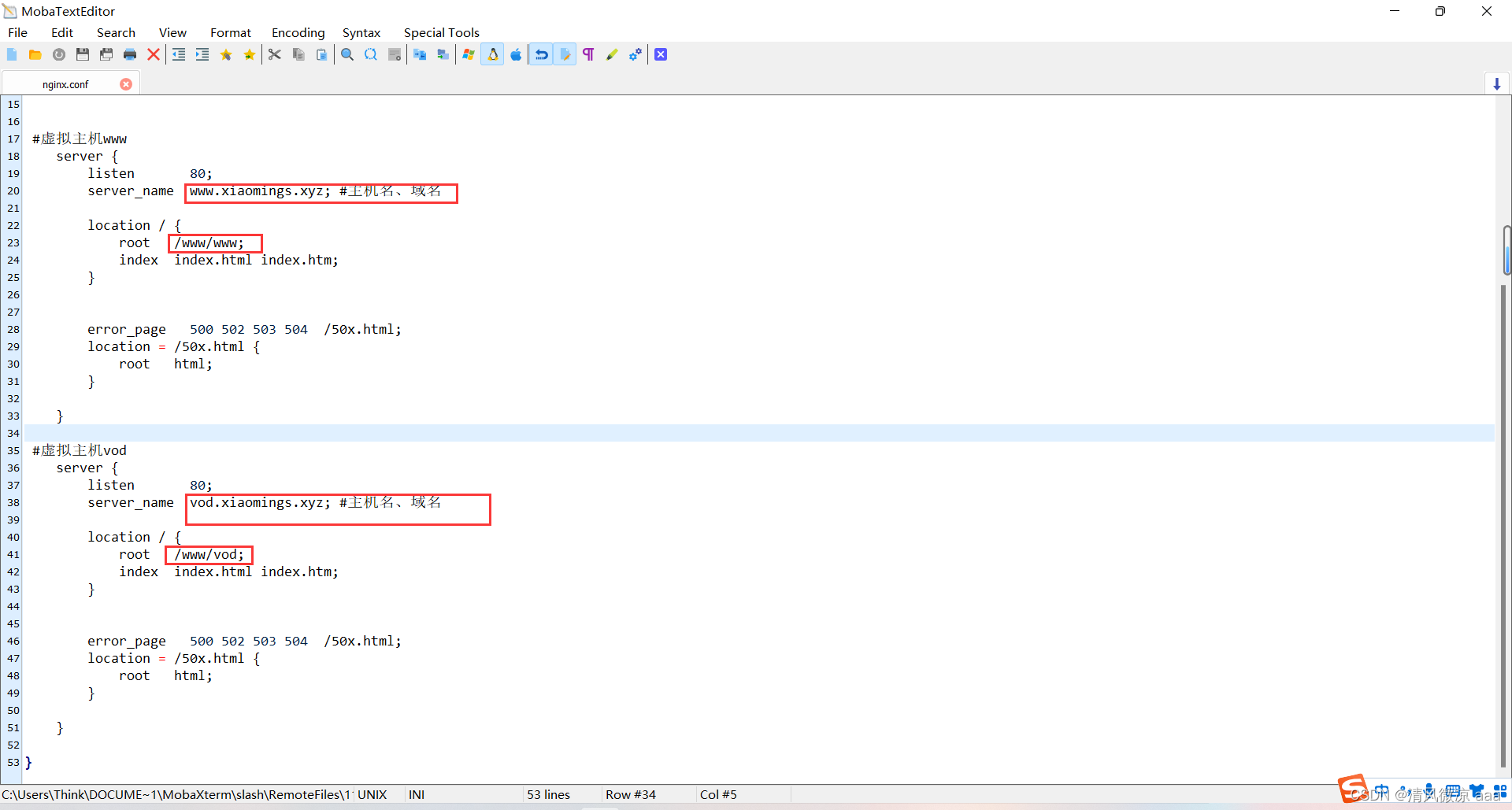
worker_processes 1;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
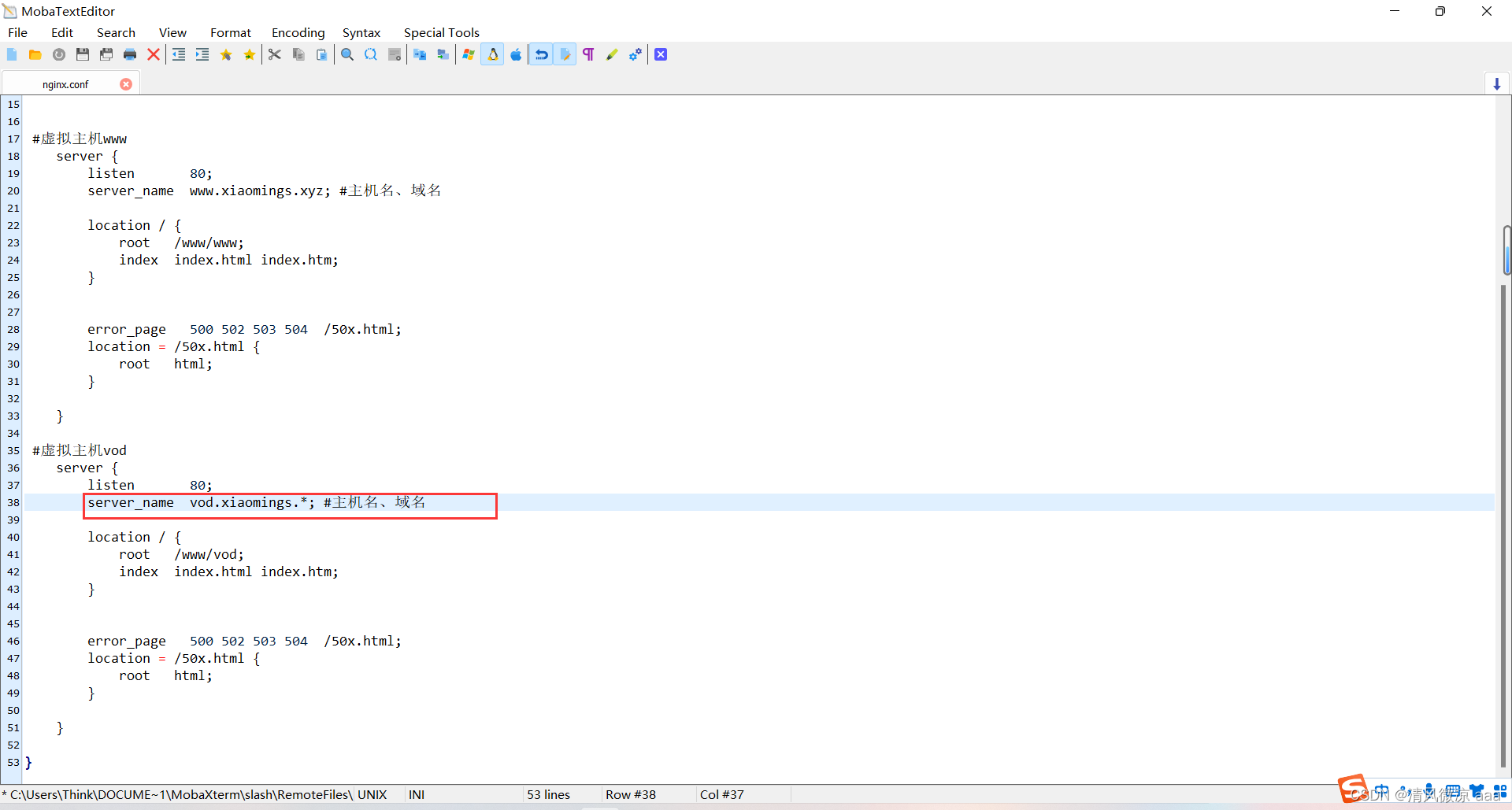
#虚拟主机www
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.xiaomings.xyz; #主机名、域名
location / {
root /www/www;
index index.html index.htm;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
#虚拟主机vod
server {
listen 80;
server_name vod.xiaomings.xyz; #主机名、域名
location / {
root /www/vod;
index index.html index.htm;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
}
-
重启nginx生效:
systemctl reload nginx
-
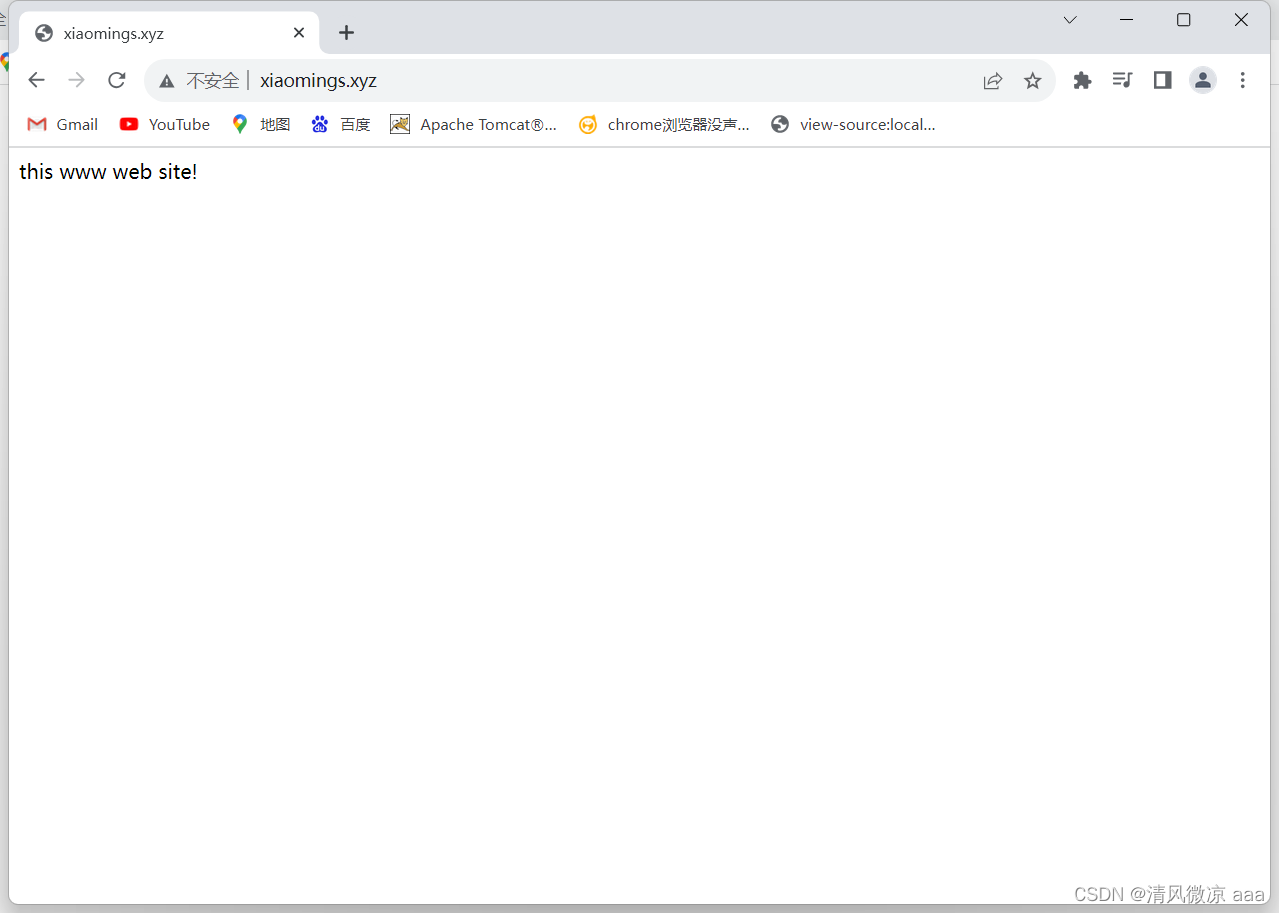
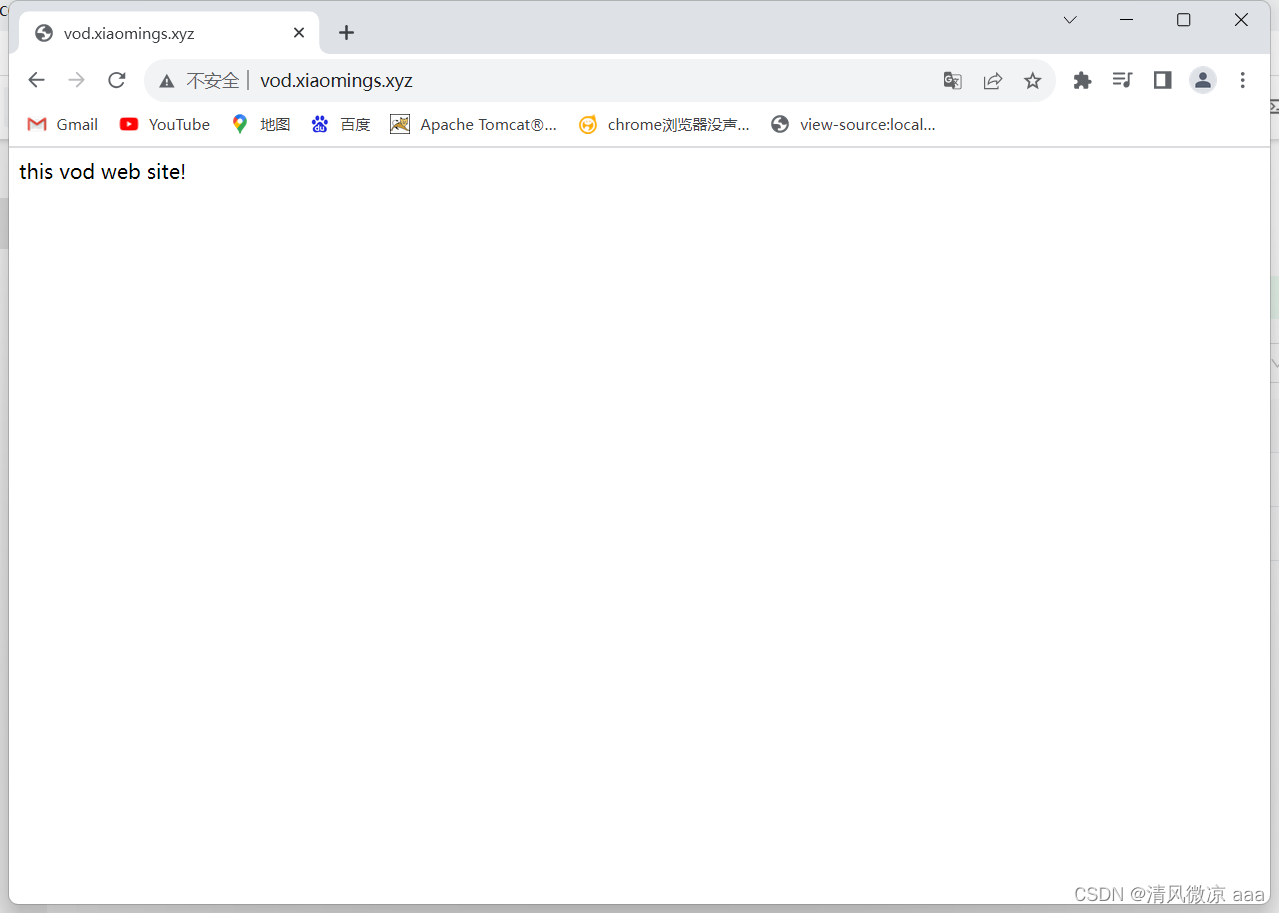
访问测试:分别使用2个域名进行访问,发现都可以访问到页面。
6.3.4 servername匹配规则
我们需要注意的是servername匹配分先后顺序,写在前面的匹配上就不会继续往下匹配了。
DNS是将域名解析成ip地址,这里是根据匹配规则找服务器上的资源。
完整匹配
我们可以在同一servername中匹配多个域名
server_name vod.mmban.com www1.mmban.com;
通配符匹配
server_name *.mmban.com
通配符结束匹配
server_name vod.*;
正则匹配
server_name ~^[0-9]+\.mmban\.com$;
6.3.5 基于域名的几种互联网企业需求
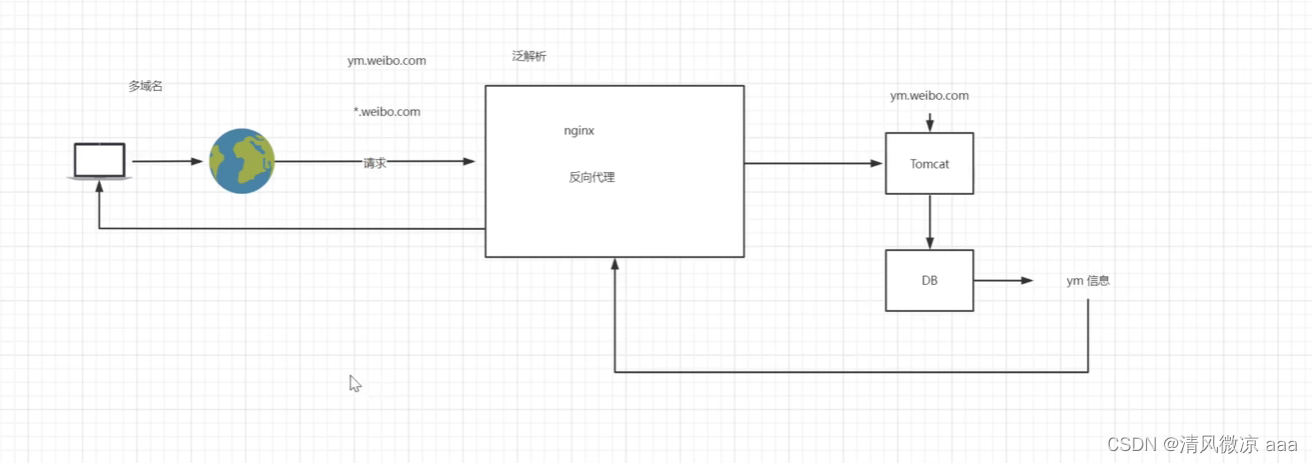
? 多用户二级域名
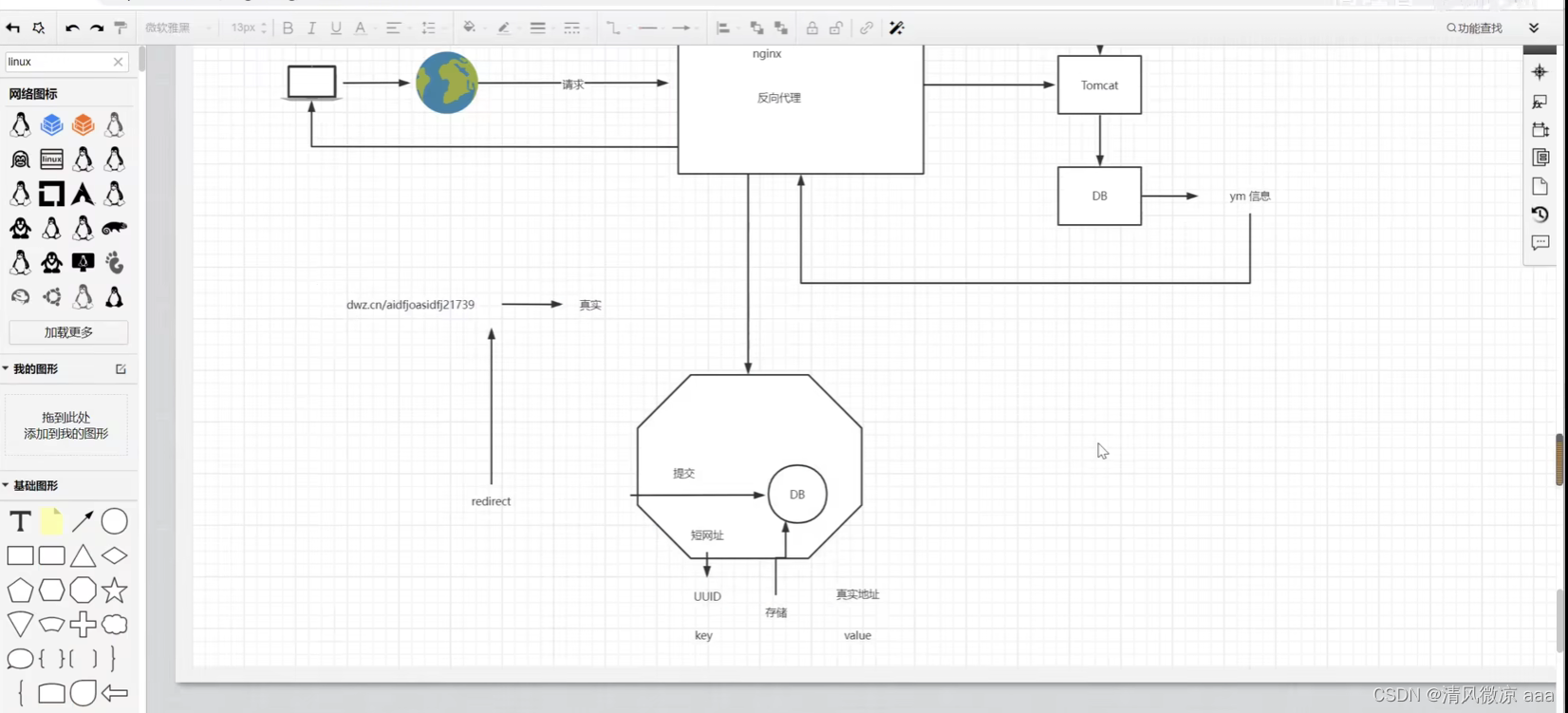
? 短网址
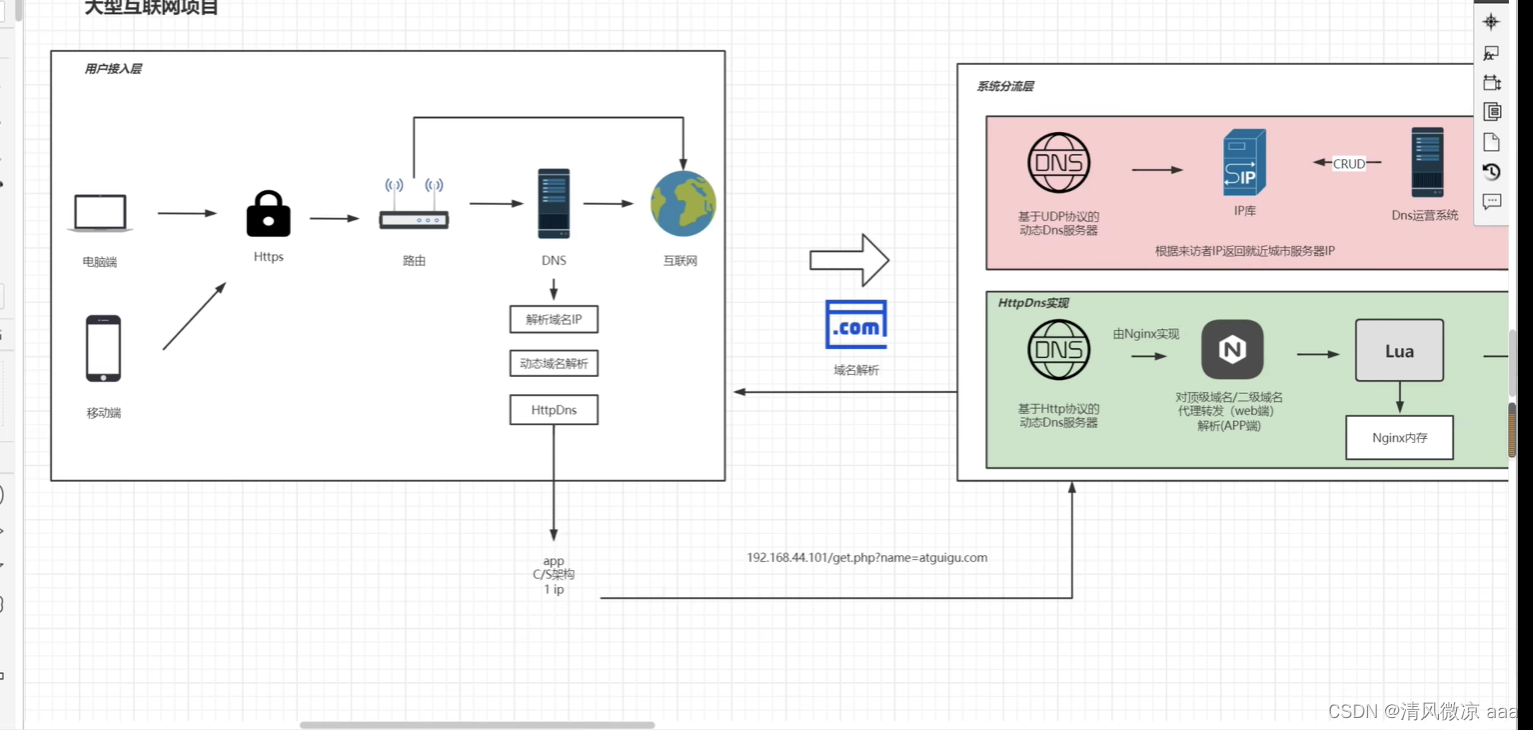
? httpdns
7. 反向代理
反向代理服务器位于用户与目标服务器之间,但是对于用户而言,反向代理服务器就相当于目标服务器,即用户直接访问反向代理服务器就可以获得目标服务器的资源。同时,用户不需要知道目标服务器的地址,也无须在用户端作任何设定。反向代理服务器通常可用来作为Web加速,即使用反向代理作为Web服务器的前置机来降低网络和服务器的负载,提高访问效率。
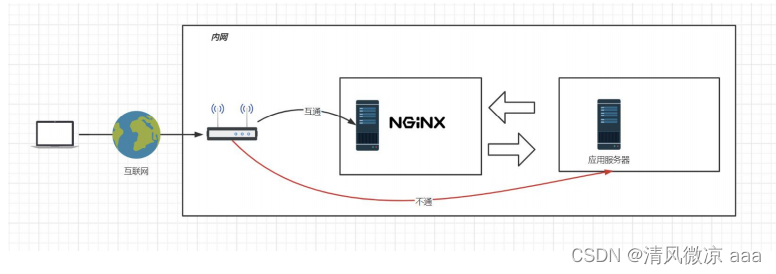
7.1 网关,代理与反向代理
-
网关:访问网络的入口就是网关,代理服务器也是网关。所有的请求都要经过网关。所以就出现了一个缺点:如果网关的带宽不够,就算你网络的带宽再高也没用。这个问题可用lvs的DR模型解决,DR模型是请求进入时经过网关,但是从服务器向客户端传数据时就不经过网关了。
-
正向代理:有明确目标的请求是从客户端发出的,客户端发起的请求知道明确的目的地,只不过自己访问不到,比如外网,此时就需要借助一个代理服务器帮助从而去访问要访问的目标。正向代理中,被代理的是客户端,服务器端不知道请求是谁发的。
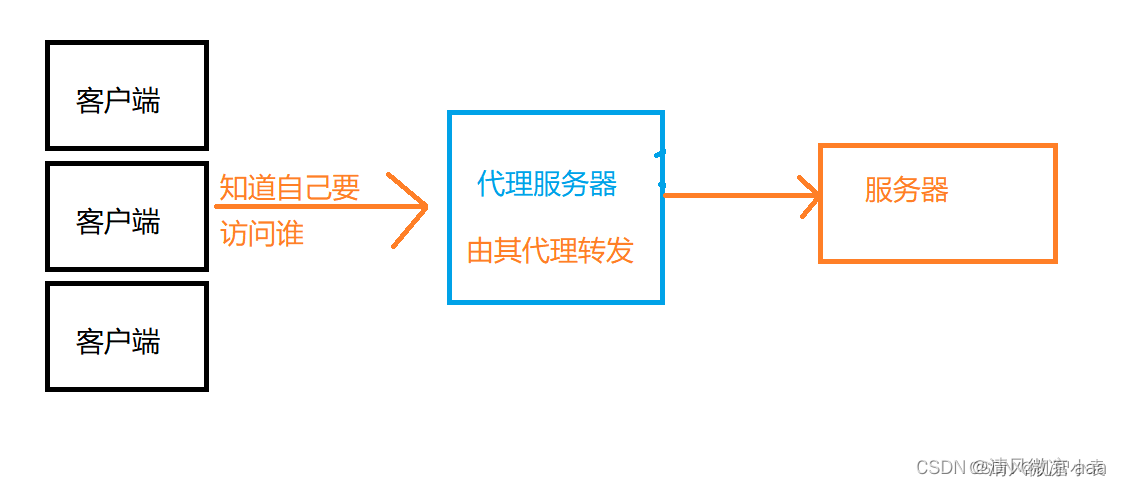
-
反向代理:有明确目标的请求是从服务器发出的。客户端并不知道自己的请求真实的会发送到那已台服务器,而服务器是知道谁发给他的请求的。反向代理中,被代理的是服务器,客户端不知道请求真实发给谁。
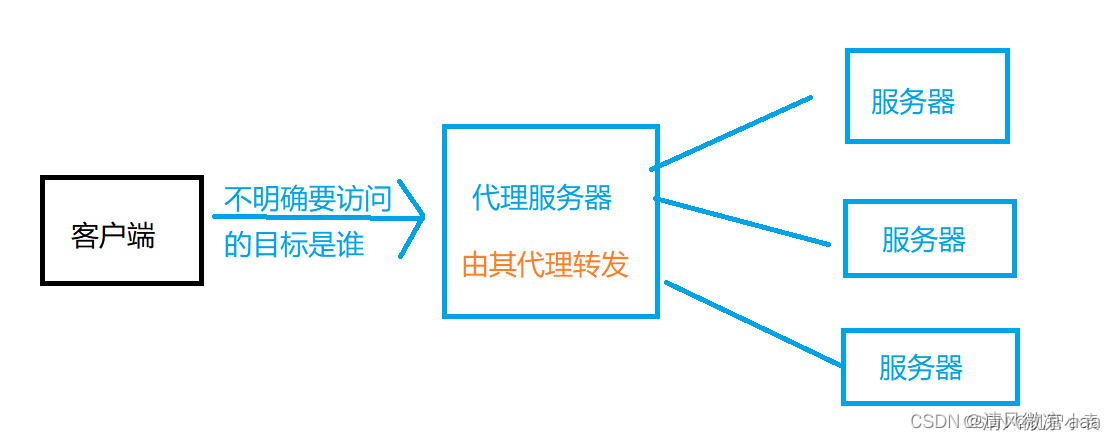
-
正向代理与反向代理,正向与反向是如何区分的?
- 正向与反向的目标是客户端,是对于客户端来说是正向还是反向。
7.2 反向代理在系统架构中的应用场景
- 传统公司系统架构:
首先用户通过路由,域名解析,到互联网,从而发送到机房网关,然后经过防火墙到nginx服务器,之后由nginx服务器代理转发到真正的服务器。
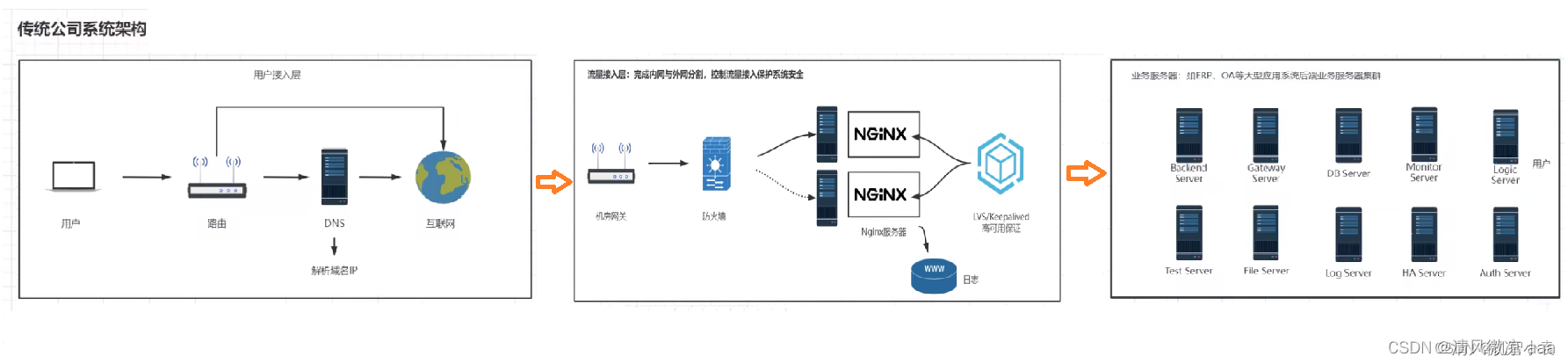
- 中小型互联网企业中:
nginx在其中不只是充当一个反向代理的功能,还回去做一些业务逻辑上功能上的作用,再就是回去做文件网关服务器等。
8. 负载均衡
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Android studio 简单登录APP设计
- 不务正业的Python
- 10 个 Kubernetes 最佳实践(规划和设置)
- 【Spring 篇】深入浅出:用Spring注解开发的奇妙之旅
- PCIe 5.0硬件
- 【嵌入式】Makefile 学习笔记记录 | 嵌入式Linux
- ruoyi-ai 基于ruoyi-plus实现AI聊天和绘画功能-后端
- Unity中URP下统一不同平台下的z值
- P1011 [NOIP1998 提高组] 车站
- Ubuntu20.04纯命令配置PCL(点云库)