IPC之十六:D-Bus的标准接口、自省机制和服务接口的具体实现方法
D-Bus的规范中提供了一系列的标准接口,绝大多数有D-Bus接口的系统调用都会实现这些标准接口,这些标准接口中包括D-Bus的自省(Introspection)机制,自省机制可以让我们通过一个标准接口了解一个D-Bus服务的各种方法的调用方法,本文将介绍D-Bus的这些标准接口及实现方式,同时也会介绍如何在D-Bus上提供自有服务,本文附有完整的实例和完整的源代码;本文实例在 Ubuntu 20.04 上编译测试通过,gcc版本号为:9.4.0;本文不适合 Linux 编程的初学者阅读。
1 D-Bus 基本概念
-
在阅读本文前,建议先阅读有关 D-Bus 的其它文章,以便对 D-Bus 有个基本了解,本文将不再讨论以下文章已经介绍过的内容,这些文章包括:
-
在文章 《IPC之十三:使用libdbus通过D-Bus请求系统调用实现域名解析的实例》 中,我们介绍了 D-Bus 大多数的基本数据类型以及数组(ARRAY)和结构(STRUCT);
-
数组和结构在 D-Bus Specification 中被归类在容器类型(Container Type)中,容器类型中还有两个数据类型:
VARIANT和DICT_ENTRY,本节将介绍这两种类型,其它数据类型的介绍请参考 《IPC之十三:使用libdbus通过D-Bus请求系统调用实现域名解析的实例》; -
容器类型:
VARIANTVARIANT类型的编码是 ‘v’;VARIANT类型可以包含一个(只能一个)完整的类型,举例来说,可以是:“i”(整数)、“ai”(整数数组)、“(ii)”(两个整数组成的结构),但是不能是 “ii”(两个整数);- 在当输入或输出参数的数据类型不确定时,便可以使用
VARIANT类型;
-
容器类型:
DICT_ENTRYDICT_ENTRY类型的编码为 ‘e’,实际应用中常以 “{}” 来表示一个DICT_ENTRY类型,和STRUCT类型用 “[]” 表示类似DICT_ENTRY类型其实就是key-value对,实际上就是一个由两个字段组成的结构(STRUCT),其第一个字段必须是键(Key),其类型必须是 D-Bus 的基本类型,不能是容器类型,第二个字段是键值(Value),理论上可以是任意类型;
2 D-Bus 的标准接口
-
D-Bus Specification 中定义了一些标准接口(Standard Interface),有 D-Bus 接口的系统调用都会实现这些标准接口,本节将介绍这些标准接口;
-
接口:
org.freedesktop.DBus.Peer- 这个接口下提供两个方法,
Ping和GetMachineId,定义如下:org.freedesktop.DBus.Peer.Ping() org.freedesktop.DBus.Peer.GetMachineId(out STRING machine_uuid) - 调用
Ping方法没有任何参数,服务端也只需要回复一个空信息(没有参数)即可,不需要添加任何参数; - 调用
GetMachineId方法也没有任何参数,服务端要回复一个字符串参数给客户端,这个字符串应该为当前电脑的 UUID,在 Linux 上,可以使用/var/lib/dbus/machine-id或者/etc/machine-id文件中的值; - 当使用
dbus_connection_register_object_path()向 D-Bus 注册一个对象路径的消息处理程序时,这两个方法在 D-Bus 中会自动实现,无需自己编程实现;
- 这个接口下提供两个方法,
-
接口:
org.freedesktop.DBus.Introspectable- 这个接口下只有一个方法:
Introspect,定义如下:org.freedesktop.DBus.Introspectable.Introspect(out STRING xml_data) - 调用
Introspect方法没有任何参数,服务端要返回一个 xml 的字符串,这个字符串定义了对象下所有实现的方法(Method)、属性(Property)和信号(Signal); - 这个方法就是 D-Bus 的内省(Introspection)机制,一个对象的实例在实现了这个接口后,客户调用这个接口可以了解这个对象中各个接口的调用方法,调用参数和返回参数;
- 在 《IPC之十三:使用libdbus通过D-Bus请求系统调用实现域名解析的实例》 和 《IPC之十五:使用libdbus通过D-Bus请求系统调用实现任意DNS记录解析的实例》 都调用了
systemd-resolved系统调用的 D-Bus 接口,下面命令调用了systemd-resolved系统调用中内省(Introspection)接口,可以直观地看一下返回的 XML 数据;$ dbus-send --print-reply --system \ > --dest=org.freedesktop.resolve1 \ > /org/freedesktop/resolve1 \ > org.freedesktop.DBus.Introspectable.Introspect dbus-send是一个非常有用的 D-Bus 命令行工具,使用man dbus-send在线手册可以了解其详细使用方法;- 这条命令的含义是,在系统总线(
--system)上请求一个接口上的方法,总线名称:org.freedesktop.resolve1(--dest),对象路径:/org/freedesktop/resolve1,接口:org.freedesktop.DBus.Introspectable,方法:Introspect,注意,接口和方法用 “.” 连接; --print-reply表示需要打印服务端的回复信息;- 返回的数据是 XML 格式,在 D-Bus Specification 中,对格式有明确的描述,在刚刚执行的命令中,有两个曾经在前面的文章中使用过的接口,把对这两个方法的定义放在这里;
<node> ...... <interface name="org.freedesktop.resolve1.Manager"> ...... <method name="ResolveHostname"> <arg type="i" direction="in"/> <arg type="s" direction="in"/> <arg type="i" direction="in"/> <arg type="t" direction="in"/> <arg type="a(iiay)" direction="out"/> <arg type="s" direction="out"/> <arg type="t" direction="out"/> </method> ...... <method name="ResolveRecord"> <arg type="i" direction="in"/> <arg type="s" direction="in"/> <arg type="q" direction="in"/> <arg type="q" direction="in"/> <arg type="t" direction="in"/> <arg type="a(iqqay)" direction="out"/> <arg type="t" direction="out"/> </method> ...... </interface> ...... </node> - 其实这个格式很容易理解,不需要更多的解释,“in” 表示输入参数,“out” 表示输出参数,
type后面的字母是 D-Bus 的数据类型定义,在文章 《IPC之十三:使用libdbus通过D-Bus请求系统调用实现域名解析的实例》 中有介绍; - 本文的实例中将实现该接口;
- 这个接口下只有一个方法:
-
接口:
org.freedesktop.DBus.Properties-
这个接口下有三个方法:
Get、Set和GetAll:org.freedesktop.DBus.Properties.Get(in STRING interface_name, in STRING property_name, out VARIANT value); org.freedesktop.DBus.Properties.Set(in STRING interface_name, in STRING property_name, in VARIANT value); org.freedesktop.DBus.Properties.GetAll(in STRING interface_name, out ARRAY of DICT_ENTRY<STRING,VARIANT> props); -
在一个对象实例中,每个接口下可以有一些属性(Properties/Attributes),这些属性可以是只读的,也可以是可读/写的,这个接口用于操作这些属性;
-
方法 Get 用于获取单个属性的值,输入参数 interface_name 表示接口名称,property_name表示属性名称,两个参数都是字符串,输出参数为属性值,由于并不清楚该属性值的数据类型,所以其输出参数的数据类型为
VARIANT; -
方法 Set 用于设置单个属性的值,这个方法其实就是 Get 方法的逆操作;
-
方法 GetAll 可以获取某个接口中的所有属性的值,它的输入参数只有一个,interface_name,表示接口名称,因为并不知道会有多少个属性返回,所以输出参数 props 是一个数组,数组中是
DICT_ENTRY,其中的键值对表示属性名称和属性值; -
这个接口下还有一个信号:
PropertiesChanged:org.freedesktop.DBus.Properties.PropertiesChanged(STRING interface_name, ARRAY of DICT_ENTRY<STRING, VARIANT> changed_properties, ARRAY<STRING> invalidated_properties); -
当一个或者多个属性发生变化时,可以发出这个信号通知连接的客户端;
-
interface_name为接口名称,changed_properties 为一个Key-Value对的数组,每一组Key-Value记录着一个变化的属性名称和新的属性值,invalidated_properties是一个字符串数组,记录已经无效的属性名称; -
本文的实例中将实现 Get 和 GetAll 两个方法
-
-
接口:
org.freedesktop.DBus.ObjectManager- 这个接口下有一个方法:
GetManagedObjectsorg.freedesktop.DBus.ObjectManager.GetManagedObjects(out ARRAY of DICT_ENTRY<OBJPATH, ARRAY of DICT_ENTRY<STRING, ARRAY of DICT_ENTRY<STRING, VARIANT>>> objpath_interfaces_and_properties); - 这个方法没有输入参数,输出参数是整个 Objects 树;
- 本文实例中并没有实现这个方法;
- 这个接口下有一个方法:
3 D-Bus 注册服务的基本方法
-
在文章 《IPC之十一:使用D-Bus实现客户端向服务端请求服务的实例》 中的实例,已经可以在 D-Bus 上为客户端提供方法调用的服务,大致的流程如下:
...... while (dbus_connection_read_write_dispatch(conn, -1)) { DBusMessage *message; message = dbus_connection_pop_message(conn); if (message == NULL) { continue; } ret = dbus_message_get_type(message); if (ret != DBUS_MESSAGE_TYPE_METHOD_CALL) { dbus_message_unref(message); continue; } if (!dbus_message_is_method_call(message, INTERFACE_NAME, METHOD_NAME)) { print_dbus_error(&dbus_error, "Server: dbus_message_is_method_call"); dbus_message_unref(message); continue; } // codes for providing the service ...... } -
作为简单的范例,提供一种客户端调用服务端方法的服务当然是可以的,但是在 D-Bus 的编程规范中,发布一个服务应该向 D-Bus 注册一个对象路径(Object Path)的处理程序,其具体步骤如下:
DBusHandlerResult server_message_handler(DBusConnection *conn, DBusMessage *message, void *data) { ...... } const DBusObjectPathVTable server_vtable = { .message_function = server_message_handler }; int main(void) { DBusConnection *conn; DBusError err; dbus_error_init(&err); conn = dbus_bus_get(DBUS_BUS_SESSION, &err); dbus_bus_request_name(conn, SERVER_BUS_NAME, DBUS_NAME_FLAG_REPLACE_EXISTING , &err); // registers the object if (!dbus_connection_register_object_path(conn, OBJECT_PATH_NAME, &server_vtable, NULL)) { printf("Failed to register an object pth.\n"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } ...... return EXIT_SUCCESS; } -
重点是
dbus_connection_register_object_path(),在以前的文章中没有介绍过,其定义如下:dbus_bool_t dbus_connection_register_object_path(DBusConnection *connection, const char *path, const DBusObjectPathVTable *vtable, void *user_data);connection是dbus_bus_get()获得的连接;path是要在 D-Bus 上注册的对象路径(Object Path),连接(connection)和对象路径(object path)的概念在以前的文章里都有过介绍;- 参数
vtable是这个函数的重点,这个参数的数据类型是DBusObjectPathVTable,这是一个结构,其定义如下:struct DBusObjectPathVTable { DBusObjectPathUnregisterFunction unregister_function; /**< Function to unregister this handler */ DBusObjectPathMessageFunction message_function; /**< Function to handle messages */ void (* dbus_internal_pad1) (void *); /**< Reserved for future expansion */ void (* dbus_internal_pad2) (void *); /**< Reserved for future expansion */ void (* dbus_internal_pad3) (void *); /**< Reserved for future expansion */ void (* dbus_internal_pad4) (void *); /**< Reserved for future expansion */ }; - 可以看到这个结构中有用的只有两个字段,
message_function和unregister_function; message_function是一个消息处理函数,准备注册的对象下的消息将全部由这个函数处理,unregister_function用于在取消注册时需要执行的函数,通常用于释放message_function可能占用的资源;- 在本文的实例中,我们并没有用到
unregister_function这个字段,因为取消注册时,我们并不需要释放资源; user_data是在调用message_function时传递给这个函数的用户数据,可以是结构、数组或者字符串等任意数据;- 再看看
message_function是如何定义的,message_function的类型为DBusObjectPathMessageFunction,其定义如下:typedef DBusHandlerResult(* DBusObjectPathMessageFunction) (DBusConnection *connection, DBusMessage *message, void *user_data); - 所以,这个函数要写成下面的样子:
DBusHandlerResult server_message_handler(DBusConnection *connection, DBusMessage *message, void *user_data) { // Codes for processing messages ...... } - 这里面的
user_data就是在注册对象路径时定义的user_data,D-Bus 在调用这个函数时会把connection、收到的消息message以及user_data传递给函数;
-
注册好对象路径的消息处理函数后,还需要在主程序中建立一个主循环才可以让这个处理函数发挥作用:
while (dbus_connection_read_write_dispatch(conn, 100)) { // main loop ...... } -
只有运行这个主循环,D-Bus 才会去分发消息,前面注册的消息处理程序才会被调用;
-
以前文章实例中在调用
dbus_connection_read_write_dispatch(),都是以阻塞方式,即把超时时间设为 -1,上面的代码片段将超时设置为 100 ms,这是通常的做法,因为通常情况下,程序除了处理消息外还需要处理别的事务,在主循环里可以处理其它事务,而在message_function中处理消息;
4 实例
-
源程序:dbus-service.c (点击文件名下载源程序,建议使用UTF-8字符集)演示了 D-Bus 标准接口和服务接口的实现方法;
-
该程序实现了两个标准接口中的三个方法,加上 D-Bus 自动实现的两个方法,一共实现了三个标准接口下的五个方法,分别是:
- 标准接口
org.freedesktop.DBus.Introspectable下的Introspect方法(D-bus 内省机制); - 标准接口
org.freedesktop.DBus.Properties下的Get方法; - 标准接口
org.freedesktop.DBus.Properties下的GetAll方法; - 标准接口
org.freedesktop.DBus.Peer下的Ping方法; - 标准接口
org.freedesktop.DBus.Peer下的GetMachineId方法;
- 标准接口
-
该程序在自定义的接口(
cn.whowin.TestInterface)上实现了三个方法:Hello方法:请求参数为一个字符串,该方法在请求参数前面加上 "Hello ",并作为参数回复给客户端;EmitSignal方法:收到请求后,该方法将广播一个 “OnEmitSignal” 信号给订阅该信号的客户端;quit方法:收到该请求后,服务程序回复给客户端一个空消息(没有参数),并主动退出程序;
-
该程序在自定义的接口(
cn.whowin.TestInterface)上实现了两个只读属性:Version和Author,可以使用标准接口的Get或GetAll获取属性值; -
该程序在自定义的接口(
cn.whowin.TestInterface)上实现了一个信号:OnEmitSignal,在收到EmitSignal请求后将发送该信号; -
编译:
gcc -Wall -g dbus-service.c -o dbus-service `pkg-config --libs --cflags dbus-1` -
有关
pkg-config --libs --cflags dbus-1可以参阅文章 《IPC之十一:使用D-Bus实现客户端向服务端请求服务的实例》 中的简要说明; -
运行:
./dbus-service -
测试方法如下,启动两个终端,一个终端上运行
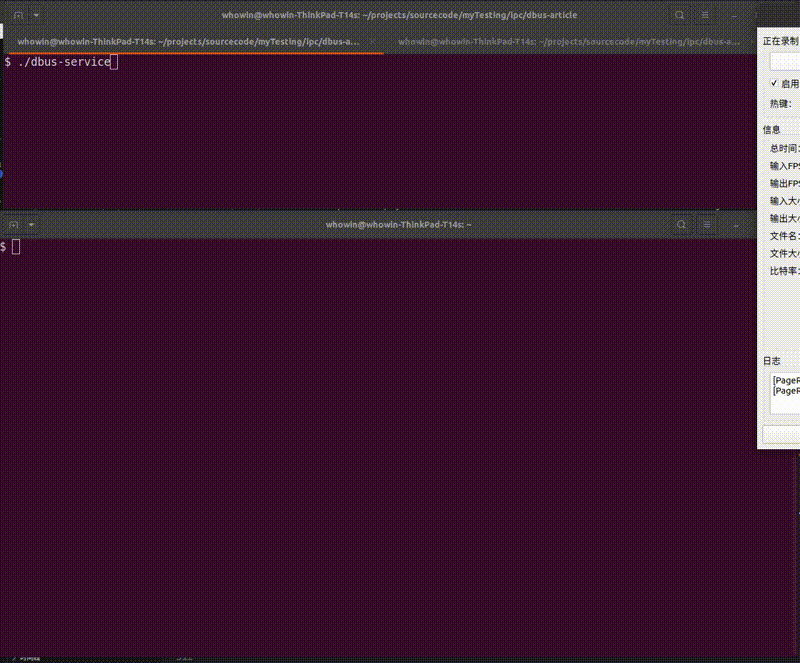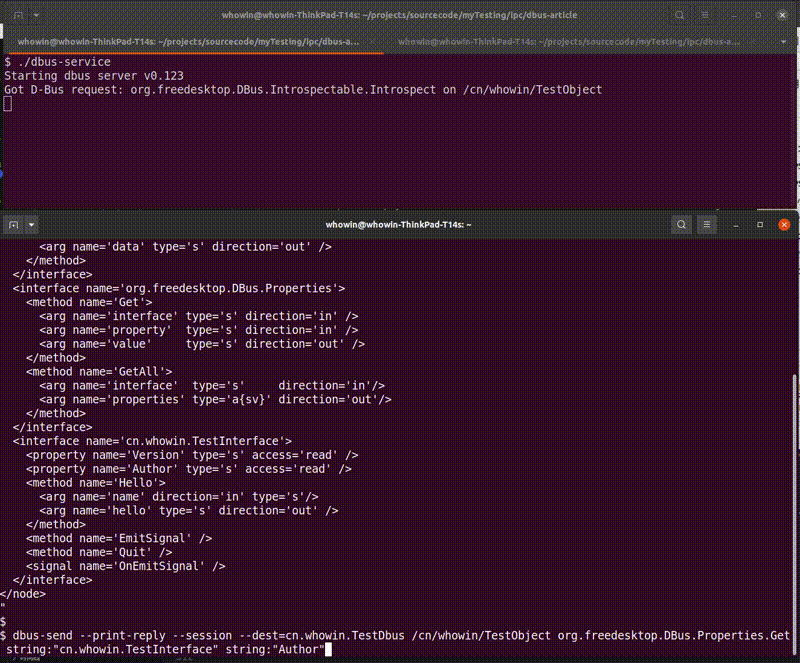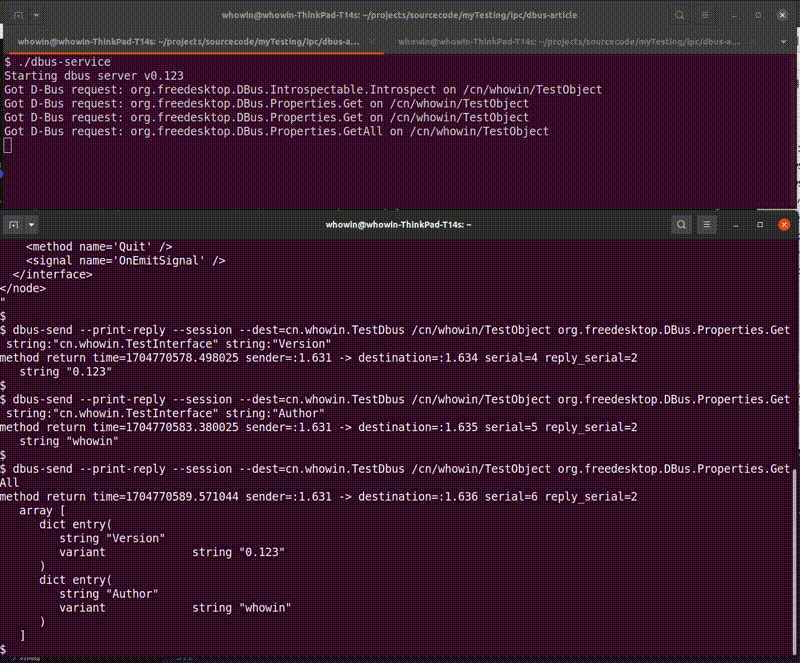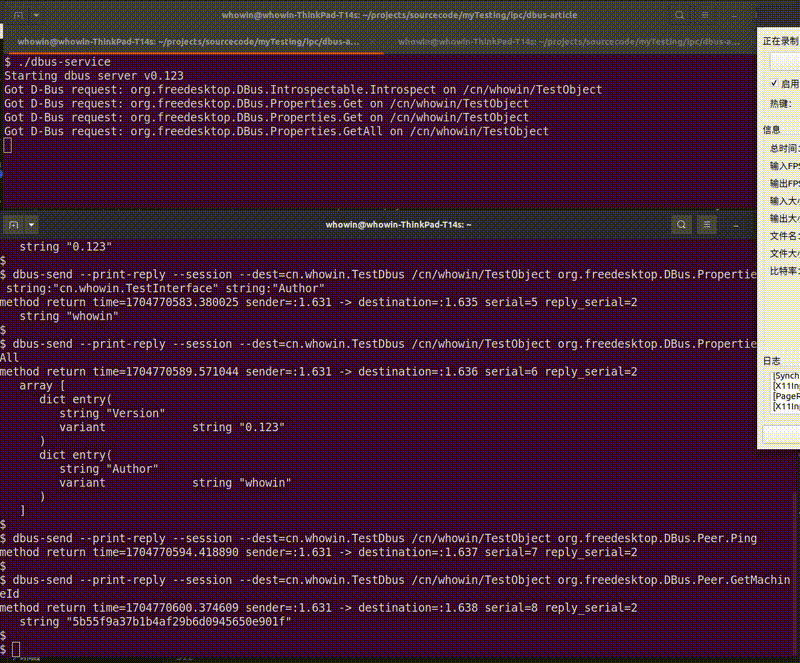
dbus-service程序,在另一个终端上输入如下命令可以测试本程序的各个方法和属性:- 标准接口测试:
$ dbus-send --print-reply --session --dest=cn.whowin.TestDbus /cn/whowin/TestObject org.freedesktop.DBus.Introspectable.Introspect $ dbus-send --print-reply --session --dest=cn.whowin.TestDbus /cn/whowin/TestObject org.freedesktop.DBus.Properties.Get string:"cn.whowin.TestInterface" string:"Version" $ dbus-send --print-reply --session --dest=cn.whowin.TestDbus /cn/whowin/TestObject org.freedesktop.DBus.Properties.Get string:"cn.whowin.TestInterface" string:"Author" $ dbus-send --print-reply --session --dest=cn.whowin.TestDbus /cn/whowin/TestObject org.freedesktop.DBus.Properties.GetAll $ dbus-send --print-reply --session --dest=cn.whowin.TestDbus /cn/whowin/TestObject org.freedesktop.DBus.Peer.Ping $ dbus-send --print-reply --session --dest=cn.whowin.TestDbus /cn/whowin/TestObject org.freedesktop.DBus.Peer.GetMachineId - 自定义接口测试:
$ dbus-send --print-reply --session --dest=cn.whowin.TestDbus /cn/whowin/TestObject cn.whowin.TestInterface.Hello string:"whowin" $ dbus-send --print-reply --session --dest=cn.whowin.TestDbus /cn/whowin/TestObject cn.whowin.TestInterface.EmitSignal $ dbus-send --print-reply --session --dest=cn.whowin.TestDbus /cn/whowin/TestObject cn.whowin.TestInterface.Quit
- 标准接口测试:
-
在自定义接口中,有一个
EmitSignal方法,服务端收到该方法的请求时,会广播出一个OnEmitSignal信号,测试方法如下:- 在 1 号终端上运行服务端程序:
$ ./dbus-service - 在 2 号终端上订阅自定义接口上的信号:
$ dbus-monitor "type='signal',sender='cn.whowin.TestDbus',interface='cn.whowin.TestInterface'" - 在 3 号终端上请求服务端的
EmitSignal方法:$ dbus-send --print-reply --session --dest=cn.whowin.TestDbus /cn/whowin/TestObject cn.whowin.TestInterface.EmitSignal - 在 2 号终端上可以看到收到了
OnEmitSignal信号;
- 在 1 号终端上运行服务端程序:
-
使用
gdbus命令测试内省(Introspection)机制$ gdbus introspect --session --dest cn.whowin.TestDbus --object-path /cn/whowin/TestObject -
标准接口测试运行动图:
欢迎订阅 『进程间通信专栏』
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 【C语言】ipoib驱动 - ipoib_cm_post_receive_srq_rss函数
- linux远程连接finalshell始终失败解决方法
- 【模拟通信】AM、FM等的调制解调
- App Inventor 2 接入短信服务,实现短信验证码功能
- 【接口测试】Postman中接口断言方式!
- 认识Linux指令之 “ head tail ” 命令
- 如何在Docker本地搭建流程图绘制神器draw.io并实现公网远程访问
- SwiftUI 打造一款收缩自如的 HStack(三):“魔镜魔镜,我爱你”
- 【JavaWeb学习-第二章】JavaScript事件
- 7.评价预测模型——C指数,NRI,IDI计算