数据结构实验7:查找的应用
目录
一、实验目的
1.掌握查找的基本概念;
2.掌握并实现以下查找算法:顺序查找、折半查找、二叉树查找。
二、实验原理
1. 顺序查找
原理:
顺序查找是一种逐个检查数据元素的搜索方法。从列表的第一个元素开始,逐个比较目标值和列表中的元素,直到找到匹配的元素或搜索完整个列表。
时间复杂度:
O(n),其中n是数据元素的数量。?
代码:
int sequential_search(int arr[], int size, int target) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (arr[i] == target) {//若找到目标元素,返回第一个出现的索引
return i;
}
}
return -1;//若没有找到目标元素
}2. 折半查找
原理:
折半查找要求数据元素必须有序。它通过反复将搜索范围减半来查找目标值。首先,与中间元素比较,如果目标值小于中间元素,则在左半部分继续查找;如果大于中间元素,则在右半部分继续查找。重复这个过程直到找到目标值或搜索范围缩小到空。?
时间复杂度:
?O(log n),其中n是数据元素的数量。
代码:
int binary_search(int arr[], int size, int target) {
int low = 0, high = size - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
if (arr[mid] == target) {//若找到目标元素,返回出现的索引
return mid;
}
else if (target < arr[mid]) {//如果中间元素较大
high = mid - 1;
}
else {//如果中间元素较小
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return -1;//若没有找到目标元素
}3. 二叉树查找?
原理:
二叉树是一种树形结构,每个节点最多有两个子节点,且左子节点的值小于父节点,右子节点的值大于父节点。二叉树查找利用这个有序性质,通过比较目标值和当前节点的值,决定向左子树或右子树移动,直到找到目标值或达到叶子节点。
时间复杂度:
平均情况下为O(log n),最坏情况下可能为O(n),取决于树的平衡性。
代码:
//定义二叉树结构
struct Treenode {
int value;
struct Treenode* left;
struct Treenode* right;
};
//创建新结点
struct Treenode* Create_node(int num) {
struct Treenode* node = (struct Treenode*)malloc(sizeof(struct Treenode));
node->value = num;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
//二叉树查找
struct Treenode* binary_tree_search(struct Treenode* root,int target) {
if (root->value == target) {//如果找到
return root;
}
else if(root->value<target){//如果目标值小于根,则在其左子树上查找
return binary_tree_search(root->left, target);
}
else {//如果目标值大于根,则在其右子树上查找
return binary_tree_search(root->right, target);
}
}三、实验内容
对同一组数据,试用三种方法查找某一相同数据:
1.建立一个顺序表,用顺序查找的方法对其实施查找;
2.建立一个有序表,用折半查找的方法对其实施查找;
3.建立一个二叉排序树,根据给定值对其实施查找;
实验一
任务
包括的函数有: typedef struct,创建函数 void create(seqlist &L),输出函数 voidprint(seqlist L),顺序查找 int find(seqlist L,intnumber),折半查找 int halffind(seqlist L,int number),主函数 main()。
?代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//定义学生结构
typedef struct Record {
int ID;//学号
string name;//姓名
string sex;//性别
int age;//年龄
}student;
typedef struct seqlist {
student record[10];//这个列表最多有十个学生的记录
int num;//实际学生的数目
};
//对列表进行初始化
void Initial_list(seqlist& list) {
list.num = 0;
return;
}
//创建列表
void create(seqlist& L) {
cout << "请输入学生数目:";
cin >> L.num;
cout << "学号 姓名 性别 年龄" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < L.num; i++) {
cin >> L.record[i].ID;
cin >> L.record[i].name;
cin >> L.record[i].sex;
cin >> L.record[i].age;
}
return;
}
//打印列表
void print(seqlist L) {
cout << "学生的基本信息为:" << endl;
cout << "学号 姓名 性别 年龄" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < L.num; i++) {
cout << L.record[i].ID <<" " <<L.record[i].name<<" " << L.record[i].sex << " "<<L.record[i].age << endl;
}
return;
}
//顺序表查找
int find(seqlist L, int number) {
for (int i = 0; i < L.num; i++) {
if (L.record[i].ID == number) {//若找到目标元素,返回第一个出现的索引
return i;
}
}
return -1;//若目标不在顺序表中
}
//折半查找
int halffind(seqlist L, int number) {
int low = 0, high = L.num - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
if (L.record[mid].ID == number) {//若找到目标元素,返回出现的索引
return mid;
}
else if (number < L.record[mid].ID) {//如果中间元素较大
high = mid - 1;
}
else {//如果中间元素较小
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return -1;//若没有找到目标元素
}
int main() {
seqlist L1;
int id1, id2,index1,index2;
Initial_list(L1);//初始化
create(L1);//输入,由于要求满足折半查找,则表中元素应该有序
print(L1);//输出
cout << "顺序查找" << endl;
cout << "请输入你要查询的学号:";
cin >> id1;
index1 = find(L1, id1);
if (index1 ==-1 ) {
cout << "未找到所需元素" << endl;
}
else {
cout << L1.record[index1].ID << " " << L1.record[index1].name << " " << L1.record[index1].sex << " " << L1.record[index1].age << endl;
}
cout << "折半查找" << endl;
cout << "请输入你要查询的学号:";
cin >> id2;
index2 = halffind(L1, id2);
if (index2 == -1) {
cout << "未找到所需元素" << endl;
}
else {
cout << L1.record[index2].ID << " " << L1.record[index2].name << " " << L1.record[index2].sex << " " << L1.record[index2].age << endl;
}
}截图

实验2
任务
?包括的函数有:结构体 typedef struct, 插入函数 void insert(bnode*& T,bnode * S), void insert1(bnode * & T) , 创 建 函 数 voidcreate(bnode*& T),查找函数:bnode *search (bnode*T. int number),主函数main()。
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
// 定义二叉树结构
struct TreeNode {
int ID;
string name;
string sex;
int age;
struct TreeNode* left;
struct TreeNode* right;
};
// 创建新结点
struct TreeNode* Create_node(int num) {
struct TreeNode* newnode = new TreeNode;
if (newnode == NULL) {
cout << "内存分配失败" << endl;
exit(1); // 或者采取其他处理方式
}
newnode->ID = num;
cout << "输入姓名、性别、年龄:" << endl;
cin >> newnode->name;
cin >> newnode->sex;
cin >> newnode->age;
newnode->left = NULL;
newnode->right = NULL;
return newnode;
}
// 建立二叉树
struct TreeNode* buildTree() {
int elem;
cout << "输入节点的数值(-1代表空节点):";
cin >> elem;
if (elem == -1) {
return NULL;
}
struct TreeNode* root = Create_node(elem);
cout << "输入" << elem << "的左节点" << endl;
root->left = buildTree();
cout << "输入" << elem << "的右节点" << endl;
root->right = buildTree();
return root;
}
// 二叉树查找
struct TreeNode* binary_tree_search(struct TreeNode* root, int target) {
if (root == NULL || root->ID == target) {
return root;
}
if (target < root->ID) {
return binary_tree_search(root->left, target);
}
else {
return binary_tree_search(root->right, target);
}
}
// 插入节点
void insert(struct TreeNode* root, int target) {
if (root == NULL) {//若是空节点,直接插入
root= Create_node(target);
return;
}
if (target < root->ID) {//插入左子树
if (root->left == NULL) {//左子树为空,直接插入
root->left = Create_node(target);
}
else {
insert(root->left, target);
}
}
else {
if (root->right == NULL) {
root->right = Create_node(target);
}
else {
insert(root->right, target);
}
}
return;
}
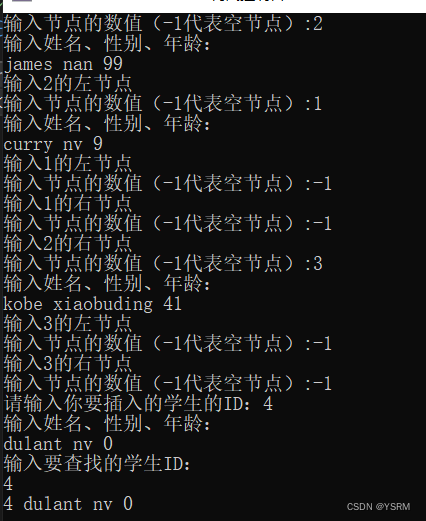
int main() {
struct TreeNode* T = buildTree(); // 建立二叉树
int number;
cout << "请输入你要插入的学生的ID:";
cin >> number;
insert(T, 4);
int targetID;
cout << "输入要查找的学生ID:" << endl;
cin >> targetID;
struct TreeNode* ans = binary_tree_search(T, targetID);
if (ans != NULL) {
cout << ans->ID << " " << ans->name << " " << ans->sex << " " << ans->age << endl;
}
else {
cout << "未找到目标节点" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
截图
?
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- python面试题大全(四)
- 力扣(leetcode)第28题找出字符串中第一个匹配项的下标(Python)
- C# Onnx Yolov8 Detect yolov8n、yolov8s、yolov8m、yolov8l、yolov8x 对比
- 分享一个小妙招,把文档制作成可翻页的电子书
- Flink电商实时数仓(四)
- 微信小程序-textarea组件字数实时更新
- c语言递归写小乐乐走台阶
- echarts通过dataZoom实现单击图像滑动
- LLM之LangChain(二)| LangChain中的Agent
- 子类能继承父类的那些内容