线程添加回调函数
发布时间:2024年01月23日
1. 说明
有些场景下,我们需要在任务执行完成后进行一些例如通信的操作。除了在任务主体call或者run末尾添加外,我们还可以使用guava定义回调。本文主要包括以下内容:
- guava添加线程回调示例
- 回调对应源码解析
- 自定义类实现回调
2. guava回调代码示例
2.1 依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>23.0</version>
</dependency>2.2 代码示例
import com.google.common.util.concurrent.*;
import org.jetbrains.annotations.Nullable;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @author pp_lan
* @date 2024/1/22
*/
public class V2ThreadControlTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FutureCallback<Integer> callback = new FutureCallback<Integer>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(@Nullable Integer aBoolean) {
System.out.println("节点执行成功" + aBoolean);
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable throwable) {
System.out.println("节点执行失败");
}
};
ListeningExecutorService pool = MoreExecutors.listeningDecorator(Executors.newFixedThreadPool(128));
try {
ListenableFuture<Integer> future = pool.submit(() -> {
System.out.println("节点1执行");
return 1;
});
ListenableFuture<Integer> future2 = pool.submit(() -> {
System.out.println("节点2执行");
return 2;
});
Futures.addCallback(future, callback);
Futures.addCallback(future2, callback);
List<ListenableFuture<Integer>> futures = Arrays.asList(future, future2);
ListenableFuture<List<Integer>> task = Futures.allAsList(futures);
try {
List<Integer> booleans = task.get();
System.out.println(booleans);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} finally {
pool.shutdown();
try {
if (!pool.awaitTermination(10, TimeUnit.MINUTES)) {
pool.shutdownNow();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}2.3 运行结果
Connected to the target VM, address: '127.0.0.1:56043', transport: 'socket'
节点1执行
节点2执行
节点执行成功1
节点执行成功2
[1, 2]
Disconnected from the target VM, address: '127.0.0.1:56043', transport: 'socket'
Process finished with exit code 0
3. guava对应源码解析
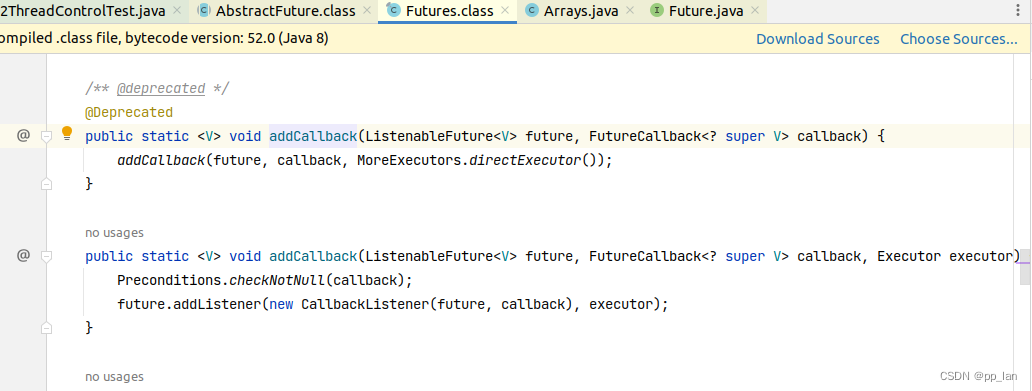
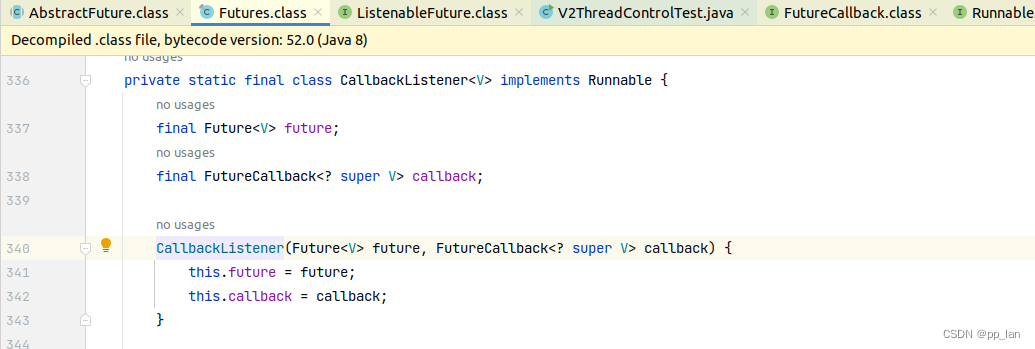
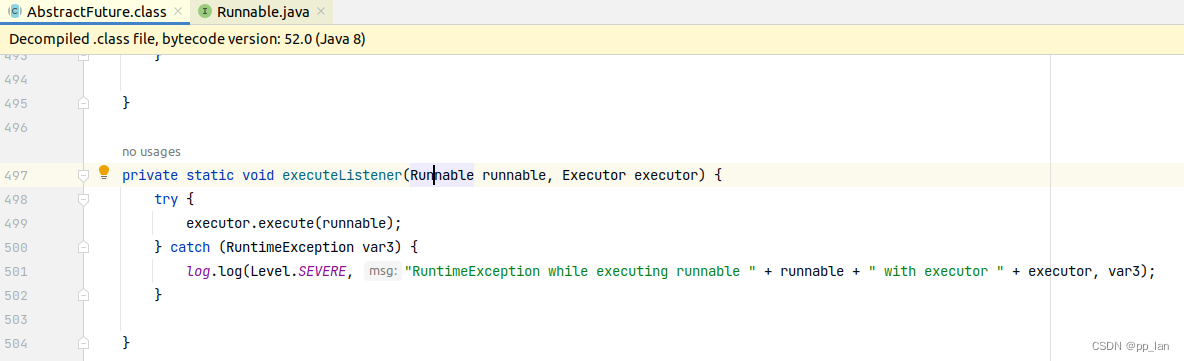
3.1 添加监听方法
????????addListener方法中添加CallbackListener对象,该对象为一个多线程对象。添加回调监听的本质为添加一个线程持续运行,查询Future的状态及结果。

4. 模拟实现
????????为了更好理解上述源码,手写了以下代码,用以简单实现其功能,加深理解。此处主要注意以下两个点:
- listener需要创建线程持续监听
- 结果获取时候需要创建去获取然后合并,避免阻塞
4.1 类描述
| 类名 | 说明 |
| ListenableFuture | 回调接口 |
| PackageFuture | ListenableFuture的实现类 |
| ListeningThreadPool | 线程池包装工具,包含带回调的执行方法invokeAll |
| V3ThreadTest | 调用示例 |
4.2 源码
4.2.1 ListenableFuture
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
/**
* @author pp_lan
* @date 2024/1/22
*/
public interface ListenableFuture<T> {
void addListener(Runnable var1, Executor var2);
}4.2.2 PackageFuture
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
/**
* @author pp_lan
* @date 2024/1/22
*/
public class PackageFuture<V> implements ListenableFuture {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(PackageFuture.class);
private Runnable listener;
private Future<V> future;
public PackageFuture(Runnable listener, Future<V> future) {
this.listener = listener;
this.future = future;
}
@Override
public void addListener(Runnable listener, Executor executor) {
Assert.notNull(listener, "listener不可以为空");
Assert.notNull(executor, "executor不可以为空");
this.listener = listener;
try {
executor.execute(() -> {
while (true) {
if (future.isDone()) {
this.listener.run();
return;
}
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("runnable listener execute error.", e);
}
}
public Future<V> getFuture() {
return future;
}
}4.2.3?ListeningThreadPool
import com.hz.common.bean.TimeoutException;
import com.hz.utils.thread.future.PackageFuture;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.TreeMap;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* @Author: pp_lan
* @Date: 2023/12/15
*/
public class ListeningThreadPool {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ListeningThreadPool.class);
private static volatile ListeningThreadPool instance;
/**
* queueSize设置不需要太大,不然线程数会一直为10
*/
private ThreadPoolExecutor pool;
private ListeningThreadPool(int parallel) {
this.pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(parallel, parallel, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(1));
}
public <T> T submit(Callable<T> callable) {
try {
Future<T> future = this.pool.submit(callable);
return future.get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
LOGGER.error("线程执行异常", e);
}
return null;
}
public <T> T submit(Callable<T> callable, Runnable listener) {
PackageFuture<T> future = buildListenFuture(callable, listener, this.pool);
try {
T t = future.getFuture().get();
return t;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
LOGGER.error("线程执行异常", e);
}
return null;
}
public <T> PackageFuture<T> buildListenFuture(Callable<T> callable, Runnable listener, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
Future<T> future = executor.submit(callable);
PackageFuture<T> baseFuture = new PackageFuture<>(listener, future);
baseFuture.addListener(listener, executor);
return baseFuture;
}
/**
* 批量执行任务
*
* @param callables 任务
* @param listeners 回调
* @param timeout 单位秒
* @return
* @param <T>
*/
public <T> List<T> invokeAll(List<Callable<T>> callables, List<Runnable> listeners, long timeout) {
Assert.notEmpty(callables);
Assert.notEmpty(listeners);
Assert.isTrue(callables.size() == listeners.size(), "任务和回调数量需要一致");
int taskNumber = callables.size();
// 构建任务
List<PackageFuture> futureList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < taskNumber; i++) {
futureList.add(buildListenFuture(callables.get(i), listeners.get(i), this.pool));
}
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Map<Integer, T> result = new TreeMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < taskNumber; i++) {
int index = i;
this.pool.execute(() -> {
PackageFuture<T> packageFuture = futureList.get(index);
Future<T> f = packageFuture.getFuture();
while (true) {
if (!result.containsKey(index)) {
if (f.isDone()) {
try {
System.out.format("[%s]获取值\n", System.currentTimeMillis()/1000);
synchronized (this) {
result.put(index, f.get());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("获取结果异常", e);
}
}
}
}
});
}
while (true) {
if (result.size() >= taskNumber) {
return new ArrayList<>(result.values());
}
if (System.currentTimeMillis() - start >= timeout * 1000) {
for (PackageFuture packageFuture : futureList) {
Future f = packageFuture.getFuture();
if (!f.isCancelled()) {
f.cancel(true);
LOGGER.info("取消任务");
}
}
throw new TimeoutException("取值超时");
}
}
}
public static ListeningThreadPool getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
synchronized (ListeningThreadPool.class) {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new ListeningThreadPool(128);
}
}
}
return instance;
}
public void shutdownGracefully() {
try {
this.pool.shutdown();
if (!this.pool.awaitTermination(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
this.pool.shutdownNow();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
instance = null;
}
}
}4.2.4?V3ThreadTest
import com.hz.utils.thread.pool.ListeningThreadPool;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @author pp_lan
* @date 2024/1/23
*/
public class V3ThreadTest {
@Test
public void test01() {
ListeningThreadPool pool = ListeningThreadPool.getInstance();
try {
Callable<Integer> task = () -> {
System.out.format("[%s]程序1运行\n", System.currentTimeMillis() / 1000);
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
System.out.format("[%s]程序1结束\n", System.currentTimeMillis() / 1000);
return 1;
};
Callable<Integer> task2 = () -> {
System.out.format("[%s]程序2运行\n", System.currentTimeMillis() / 1000);
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.format("[%s]程序2结束\n", System.currentTimeMillis() / 1000);
return 2;
};
Runnable listener = () -> System.out.format("[%s]任务执行完毕\n", System.currentTimeMillis() / 1000);
List<Integer> results = pool.invokeAll(Arrays.asList(task, task2), Arrays.asList(listener, listener), 4);
System.out.format("[%s]%s", System.currentTimeMillis() / 1000, results);
} finally {
pool.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}4.3 运行结果
[1705980753]程序1运行
[1705980753]程序2运行
[1705980754]程序2结束
[1705980754]任务执行完毕
[1705980754]获取值
[1705980755]程序1结束
[1705980755]获取值
[1705980755]任务执行完毕
[1705980766][1, 2]
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/pp_lan/article/details/135766108
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Android Notification 以及 通知铃音使用
- mysql高级使用教程
- 3 Windows多线程
- [Android自定义View]实现一个环形进度条控件
- 图像分割实战-系列教程1:语义分割与实例分割概述
- Linux中禁用SELinux
- 学习Java API(二):基础知识点一文通?
- 【算法与数据结构】63、LeetCode不同路径 II
- leetcode 454 四数之和
- 谷歌浏览器最新chrome94版本CORS跨域问题