二叉树的顺序结构,堆的实现
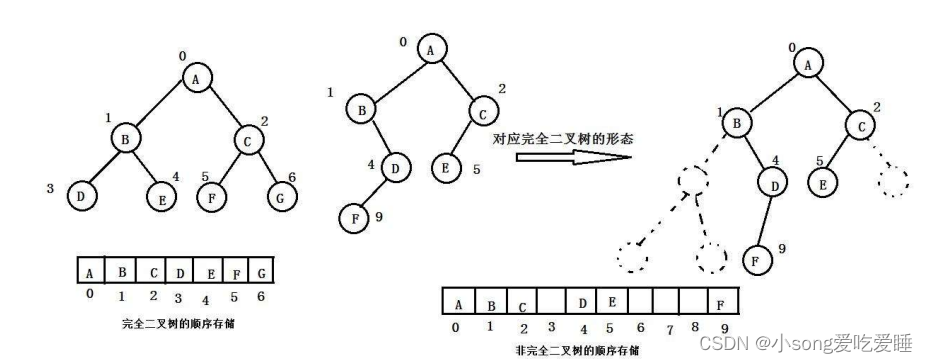
?二叉树的顺序存储
顺序结构存储就是使用数组来存储,因为可能会存在大量的空间浪费。而完全二叉树更适合使用顺序结构存储。现实中我们通常把堆(一种二叉树)使用顺序结构的数组来存储,需要注意的是这里的堆和操作系统虚拟进程地址空间中的堆是两回事,一个是数据结构,一个是操作系统中管理内存的一块区域分段。
堆的概念及结构?
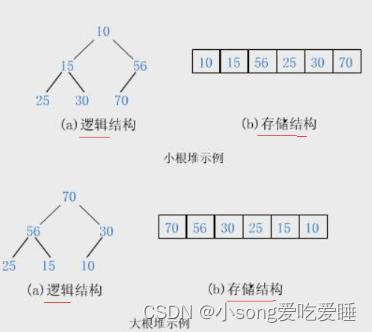
如果有一个关键码的集合K = { k0,k1 ,k2 ,k3…,kn-1 },把它的所有元素按完全二叉树的顺序存储方式存储 在一个一维数组中,并满足:k(i) <=k(2*i+1) 且 k(i)>=k(2*i+2) ?i = 0,1, 2…,则称为小堆(或大堆)。将根节点最大的堆叫做最大堆或大根堆,根节点最小的堆叫做最小堆或小根堆。
堆的性质:
- 堆中某个节点的值总是不大于或不小于其父节点的值;
- 堆总是一棵完全二叉树;
?
堆的实现
堆的创建
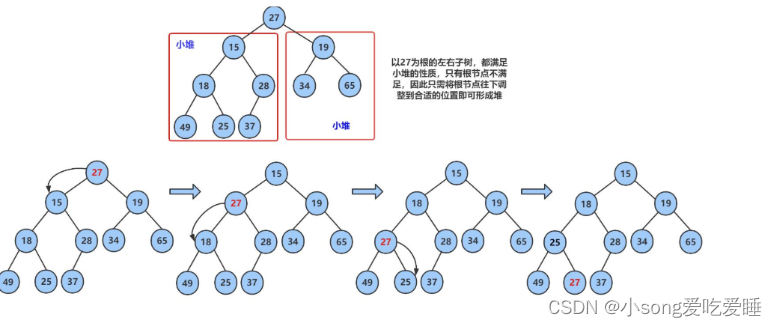
下面我们给出一个数组,这个数组逻辑上可以看做一颗完全二叉树,但是还不是一个堆,现在我们通过算法,把它构建成一个堆。根节点左右子树不是堆,我们怎么调整呢?这里我们从倒数的第一个非叶子节点的 子树开始调整,一直调整到根节点的树,就可以调整成堆。
堆的插入
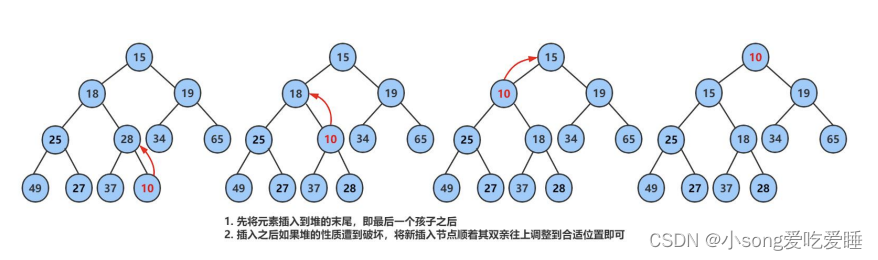
先插入一个数据到数组的尾上,再进行向上调整算法,直到满足堆
堆的向上调整算法
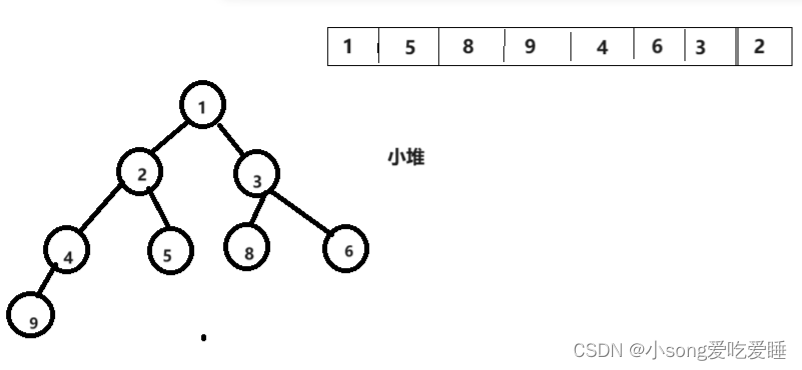
我们通过从叶子节点开始向上Push调整建成一个小堆
//向上调整算法
void AdjustUp(HPDataType*a,int child) //child 孩子
{
//找到父亲节点
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child>0)
{
//孩子节点小于父亲我们就交换
if (a[child] < a[parent])
{
//交换
swap(&a[child],&a[parent]);
//让孩子节点等于父亲节点,父亲节点也往前走
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
//child=(child-1)/2;
//parent=(parent-1)/2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}?我们将数据不断的Push入堆就会变成下面的情况
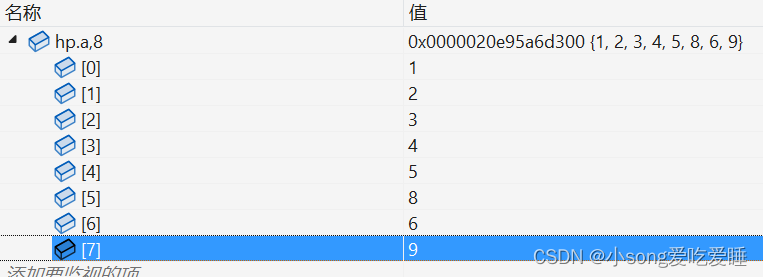
int main()
{
int a[] = { 1,5,8,9,4,6,3,2 };
HP hp;
//初始化
HeapInit(&hp);
for (int i = 0; i <sizeof(a)/sizeof(int); ++i)
{
HeapPush(&hp, a[i]);
}
}
?
?
堆的向下调整算法?
在堆里删除一个Pop掉一个数是将根节点Pop掉,我们在这里如果直接Pop掉的话,会打乱整个堆的结构,所以我们将根节点与最后一个节点交换,交换后再Pop掉,然后我们再通过根节点开始的向下调整算法把他调整成为一个小堆。
前提:左右子树必须是一个堆,才能调整。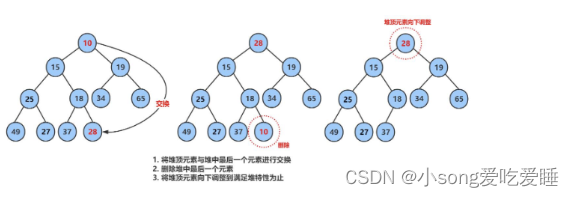
?
//向下调整
void AdjustDown(HPDataType* a,int parent,int size)
{
int child = parent*2+ 1;
while (child<size)
{
//假设法进行交换,找出小的//+1防止越界
if (child+1<size&&a[child] > a[child + 1])
{
++child;
}
if (a[child] < a[parent])
{
swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);
parent = child;
child = child * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}?我们将前三个节点Pop掉
?
我们会发现剩下的节点还是小堆,我们只需要访问的时候去掉k就行了
堆完整版代码的实现
Heap.h? ?函数声明
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
typedef int HPDataType;
typedef struct Heap
{
HPDataType* a;
int size;
int capacity;
}HP;
//初始化
void HeapInit(HP*php);
//堆的销毁
void HeapDestroy(HP*php);
//堆的插入
void HeapPush(HP* php,HPDataType x);
//堆的删除
void HeapPop(HP*php);
//取堆顶的数据
HPDataType HeapTop(HP* php);
//堆的数据个数
int HeapSize(HP* php);
//堆的判空
bool HeapEmpty(HP*php);Heap.c? ?函数定义
?
#include"Heap.h"
//初始化
void HeapInit(HP* php)
{
php->a = NULL;
php->capacity = 0;
php->size = 0;
}
//堆的销毁
void HeapDestroy(HP* php)
{
assert(php);
free(php->a);
php->a = NULL;
php->capacity = php->size = 0;
}
//交换
void swap(HPDataType* p1, HPDataType*p2)
{
HPDataType tmp = *p1;
*p1 = *p2;
*p2 = tmp;
}
//向上调整
void AdjustUp(HPDataType*a,int child) //child 孩子
{
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child>0)
{
if (a[child] < a[parent])
{
swap(&a[child],&a[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
//插入
void HeapPush(HP* php, HPDataType x)
{
assert(php);
if (php->size == php->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = php->capacity == 0 ? 4 : php->capacity * 2;
HPDataType* tmp = (HPDataType*)realloc(php->a, sizeof(HPDataType)* newcapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc feil");
exit;
}
php->a = tmp;
php->capacity = newcapacity;
}
php->a[php->size] = x;
php->size++;
AdjustUp(php->a, php->size - 1);
}
//向下调整
void AdjustDown(HPDataType* a,int parent,int size)
{
int child = parent*2+ 1;
while (child<size)
{
//假设法进行交换,找出小的//+1防止越界
if (child+1<size&&a[child] > a[child + 1])
{
++child;
}
if (a[child] < a[parent])
{
swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);
parent = child;
child = child * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
//堆的删除
void HeapPop(HP* php)
{
assert(php);
assert(php->size > 0);
swap(&php->a[0], &php->a[php->size - 1]);
php->size--;
AdjustDown(php->a,0,php->size);
}
//取堆顶的数据
HPDataType HeapTop(HP* php)
{
assert(php);
assert(php->size > 0);
return php->a[0];
}
//堆的数据个数
int HeapSize(HP* php)
{
assert(php);
return php->size;
}
//堆的判空
bool HeapEmpty(HP* php)
{
assert(php);
return php->size== 0;
}
test.c
?
#include"Heap.h"
int main()
{
int a[] = { 1,5,8,9,4,6,3,2 };
HP hp;
HeapInit(&hp);
for (int i = 0; i <sizeof(a)/sizeof(int); ++i)
{
HeapPush(&hp, a[i]);
}
int k = 3;
while (k--)
{
printf("%d ", HeapTop(&hp));
HeapPop(&hp);
}
/*printf("\n");*/
//while (!HeapEmpty(&hp))
//{
// printf("%d ", HeapTop(&hp));
// HeapPop(&hp);
//}
HeapDestroy(&hp);
return 0;
}堆的应用
堆排序
? ? ? ?堆排序即利用堆的思想来进行排序,总共分为两个步骤:
- 升序:建大堆
- 降序:建小堆
利用堆删除的思想来进行排序?
建堆和堆删除中都用到了向下调整,因此掌握了向下调整,就可以完成堆排序。堆排的本质是一种选择排序
void HeapSort(int*a,int n)
{
//升序建大堆
//降序建小堆
//O(N*logN)
/*for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i)
{
AdjustUp(a,i);
}*/
//O(N)
//防止数组越界,从后向前开始排序
for (int i = (n - 1-1) / 2; i >= 0; --i)
{
AdjustDown(a, i, n);
}
//O(N*logN)
int end = n - 1;
while (end)
{
Swap(&a[0],&a[end]);
AdjustDown(a,0,end);
--end;
}
}
int main()
{
int a[] = { 10,8,4,6,7,9,2,3,1,5 };
HeapSort(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(int));
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(a) / sizeof(int); ++i)
{
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
return 0;
}
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?建堆?

? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ??调整?
以下图为列?
?
?下一篇:我们讲TopK问题:在数据量比较大的情况下求数据前K个最大的元素或者最小的元素。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Blender 萌新学习笔记
- Jmeter压力测试实战分析详解
- torch.from_numpy
- 公章透明png图片怎么弄?一键生成透明图片
- 【LangChain学习之旅】—(2) LangChain系统快速入门
- 12/31
- 大数据从入门到精通(超详细版)之Hive的DML操作,通俗易懂,包看包会!!!
- NTFS权限与文件系统:深入解析与实践指南
- React Native android环境搭建,使用夜神模拟器进行开发(适用于0.73+版本)
- 爬虫工作量由小到大的思维转变---<第二十四章 Scrapy的`统计数据`收集stats collection>
