2023.12.18 制作py,shell脚本进行数据库操作与定时任务
发布时间:2023年12月20日
目录
1.在pycharm中,使用pymysql,连接数据库进行增删改查操作
3.1 在linux_mysql中进行建库建表操作,编写插入数据等sql语句.
3.2 将插入数据等操作的sql语句,复制到python文件中,使用python来进行数据库的操作
3.4 使用linux命令,定时执行shell脚本文件 crontab -e
虚拟机中已有的两个库: bi_db和shopnc_db?
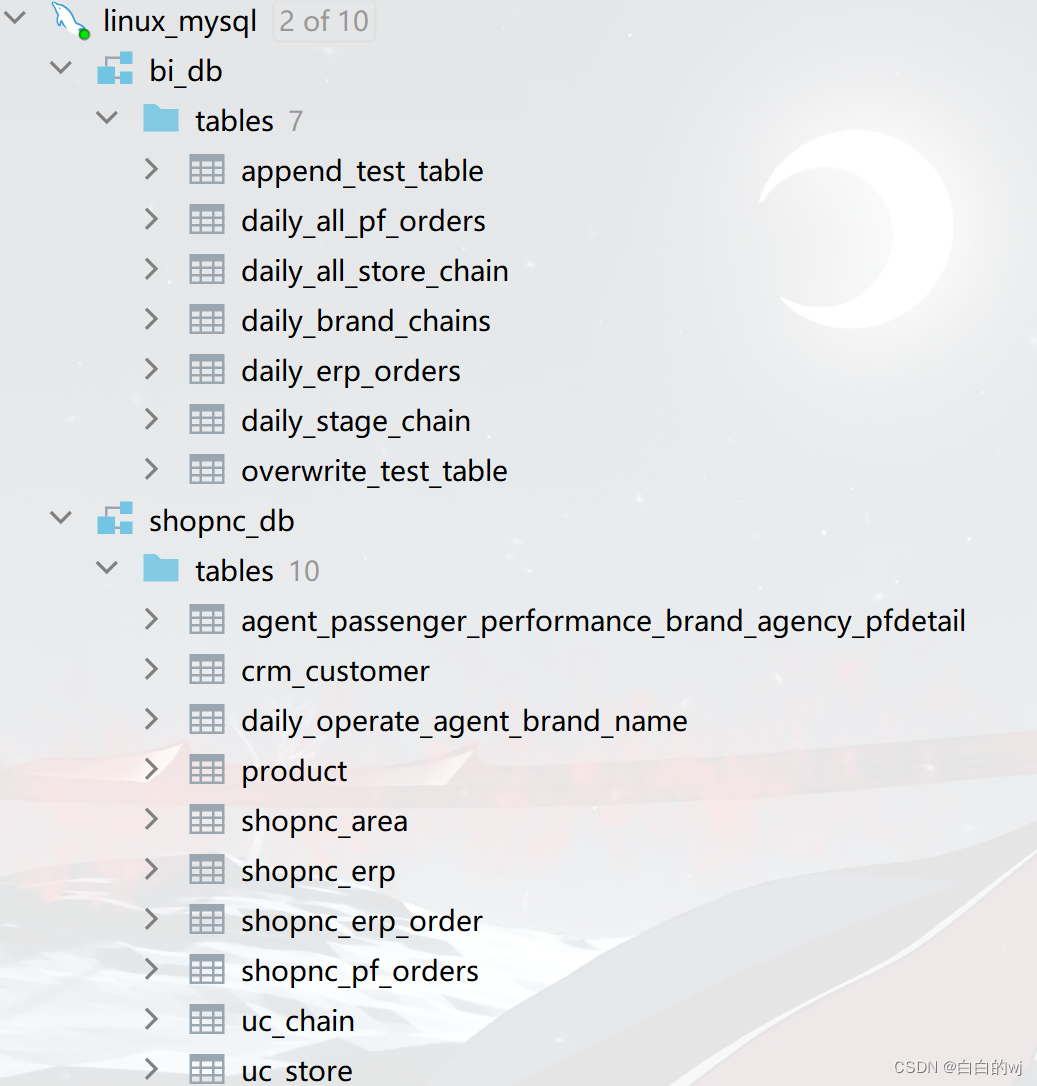
product表:
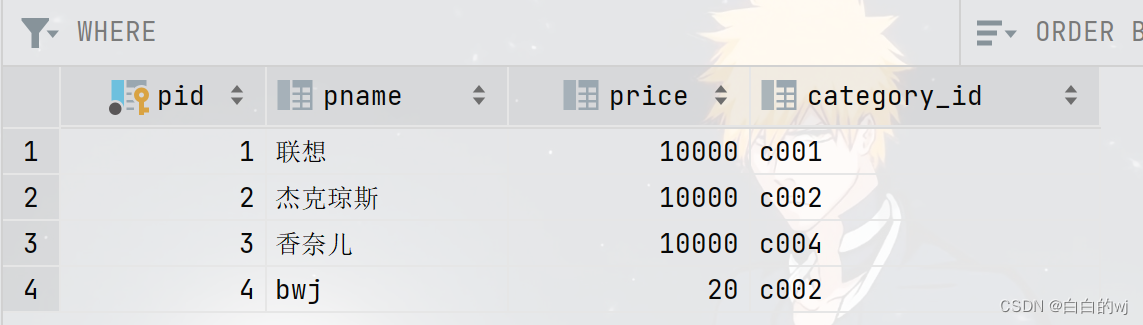
1.在pycharm中,使用pymysql,连接数据库进行增删改查操作
1.1 查询
import pymysql
# 建立与数据库的连接
conn1 = pymysql.connect(
host='192.168.88.100',
port=3306,
user='root',
password='123456',
db='shopnc_db'
)
conn2 = pymysql.connect(
host='192.168.88.100',
port=3306,
user='root',
password='123456',
db='bi_db'
)
# 2.创建游标对象
c1 = conn1.cursor()
# 3.编写sql语句
sql = "select * from shopnc_db.product"
# 4.执行sql语句
c1.execute(sql)
# 5.获取结果集
result = c1.fetchall() #获取所有结果集
print(result)
# 6.关闭连接
conn1.close() # 关闭连接
1.2 修改
import pymysql
# 建立与数据库的连接
conn1 = pymysql.connect(
host='192.168.88.100',
port=3306,
user='root',
password='123456',
db='shopnc_db'
)
conn2 = pymysql.connect(
host='192.168.88.100',
port=3306,
user='root',
password='123456',
db='bi_db'
)
# 2.创建游标对象
c1 = conn1.cursor()
# 3.编写sql语句
sql = "update product set price = 20 where pname = 'bwj'"
# 修改全部的价格都变为10000
# 4.执行sql语句
result = c1.execute(sql)
conn1.commit() # 提交事务
# 5.获取结果集
if result != 0:
print("修改成功")
else:
print("修改失败")
# 6.关闭连接
conn1.close() # 关闭连接
1.3 删除
import pymysql
# 建立与数据库的连接
conn1 = pymysql.connect(
host='192.168.88.100',
port=3306,
user='root',
password='123456',
db='shopnc_db'
)
# 2.创建游标对象
c1 = conn1.cursor()
# 3.编写sql语句
sql = "delete from product where pname = 'hwj' "
# 4.执行sql语句
result = c1.execute(sql)
conn1.commit() # 提交事务
# 5.获取结果集
if result != 0:
print("删除成功")
else:
print("删除失败")
# 6.关闭连接
conn1.close() # 关闭连接
1.4 增加
import pymysql
# 建立与数据库的连接
conn1 = pymysql.connect(
host='192.168.88.100',
port=3306,
user='root',
password='123456',
db='shopnc_db'
)
conn2 = pymysql.connect(
host='192.168.88.100',
port=3306,
user='root',
password='123456',
db='bi_db'
)
# 2.创建游标对象
c1 = conn1.cursor()
# 3.编写sql语句
sql = "insert into product value (0,'hwj',9900,'c001')"
# 4.执行sql语句
result = c1.execute(sql)
conn1.commit() # 提交事务
# 5.获取结果集
if result != 0:
print("插入成功")
else:
print("插入失败")
# 6.关闭连接
conn1.close() # 关闭连接
?
?2.使用pandas,操作pycharm对数据库进行操作
2.1 对mysql进行覆盖写入
将查询到的表的数据,写入到另一个表中
import pandas as pd
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
# 创建与mysql数据库的连接
shopnc_engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:123456@192.168.88.100:3306/shopnc_db')
bi_engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:123456@192.168.88.100:3306/bi_db')
# mysql://用户名:密码@ip地址:端口号/数据库
# 获取所有表中数据
df = pd.read_sql("select * from product",con=shopnc_engine)
print('读取数据成功')
# 将上面获取到的内容,写入另一个库中,写入的模式是覆盖
# 假如没有这个表,pandas会帮你自动新建,但类型不一定一样
df.to_sql('overwrite_test_table',con=bi_engine,if_exists = 'replace',index = False)
print('覆盖写入数据成功')

2.2 对mysql进行追加写入
将查询到的表的数据,写入到另一个表中
import pandas as pd
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
# 创建与mysql数据库的连接
shopnc_engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:123456@192.168.88.100:3306/shopnc_db')
bi_engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:123456@192.168.88.100:3306/bi_db')
# mysql://用户名:密码@ip地址:端口号/数据库
# 获取所有表中数据
df = pd.read_sql("select * from product",con=shopnc_engine)
print('读取数据成功')
# 写入模式是追加
# 假如没有这个表,pandas会帮你自动新建,但类型不一定一样
df.to_sql('append_test_table',con=bi_engine,if_exists = 'append',index = False)
print('追加写入数据成功')

3.在linux中,进行自动化定时调度脚本

3.1 在linux_mysql中进行建库建表操作,编写插入数据等sql语句.
两个库,shopnc_db作为数据源, 在数据源中查询到的结果放到bi_db库中
3.2 将插入数据等操作的sql语句,复制到python文件中,使用python来进行数据库的操作
连接库的语句
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
import pandas as pd
# 忽略警告
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
# 创建mysql数据库链接
# 生产库shopnc_db链接
shopnc_engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:123456@192.168.88.100:3306/shopnc_db')
# BI库bi_db链接
bi_engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:123456@192.168.88.100:3306/bi_db')
中间的sql
# sql语句
daily_all_store_chain_sql = """
select
area.province, -- 省份名称
chains.chain_num, -- 门店数量
store.store_num, -- 店铺数量
curdate() collect_time -- 统计时间
from (
select
area_id,
area_name as province
from shopnc_db.shopnc_area
where area_id < 32
) area
left join (
select
areaid_1,
count(distinct chain_id) as chain_num
from shopnc_db.uc_chain
where is_auth = 1
and chain_name not like '%%test%%'
and chain_name not like '%%测试%%'
and add_time < unix_timestamp(curdate())
group by areaid_1
) chains on chains.areaid_1 = area.area_id
left join (
select
areaid_1,
count(distinct store_id) as store_num
from shopnc_db.uc_store
where is_auth = 1
and store_name not like '%%test%%'
and store_name not like '%%测试%%'
and add_time < unix_timestamp(curdate())
group by areaid_1
) store on store.areaid_1 = area.area_id
"""?输出数据的语句
# 读取mysql数据库中的数据
daily_all_store_chain_data = pd.read_sql(daily_all_store_chain_sql, con=shopnc_engine)
# 将读取的数据保存到mysql数据库中
# name: 表名
# con: 数据库链接
# if_exists: 数据保存方式 replace->覆盖保存 append:追加保存
# index: 是否保留索引序号列, True保留, False保留
daily_all_store_chain_data.to_sql(name="daily_all_store_chain", con=bi_engine, if_exists="append", index=False)3.3 创建shell脚本文件,去调用python文件

前面是python的软件路径? ,中间是要调用执行文件 , 右边是日志记录
3.4 使用linux命令,定时执行shell脚本文件 crontab -e
[root@node1 finereport_file]# crontab -e
linux里的Crontab,定时任务命令
时间格式 : * * * * *
分 时 日 月 周
命令 第1列表示分钟1~59 每分钟用*或者 */1表示
第2列表示小时1~23(0表示0点)
第3列表示日期1~31
第4列表示月份1~12
第5列标识号星期0~6(0表示星期天)
第6列要运行的命令
4. 五个python脚本中的细节
脚本运行失败的主要原因都是SQL语句的细节,先在本地pycharm进行运行,确认无误了,再将.py文件拖入虚拟机的linux中,再在linux里使用脚本调用,最后确认结果
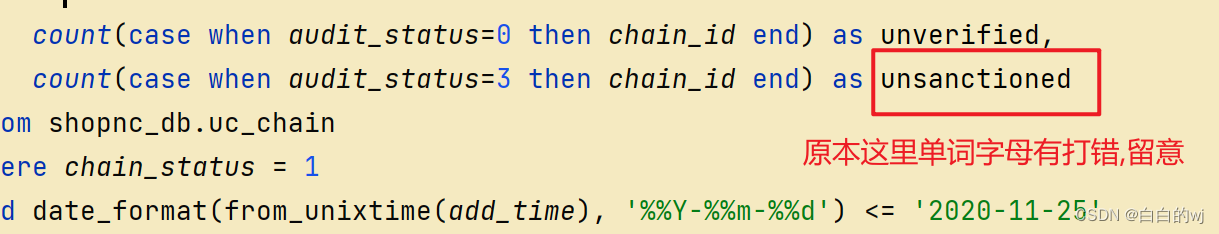
表中id主键字段设置了auto_increment后,null和0都代表自动使用自增?
daily_all pf orders.py :没有问题
daily_all store_chain.py:
语句中只有一个%的,都需要变为两个;因为%在python里是占位符,%% 在有%拼接的的字符串里,如果要打印百分号,用两个百分号表示%%

daily_brand_chains.py:

daily_erp_orders.py:
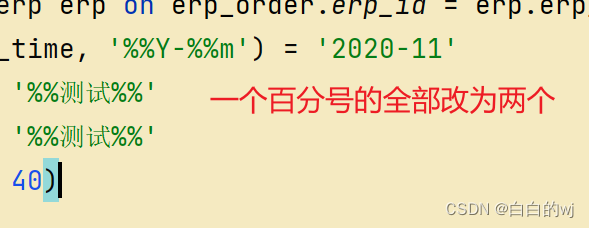
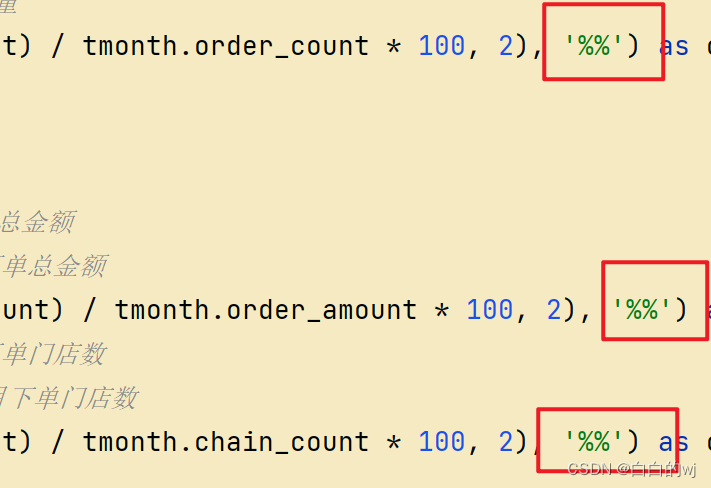

daily stage_chain.py:
同上,百分号,字段名字的问题
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_49956154/article/details/135081271
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- [ComfyUI进阶教程] Controlnet预处理器节点安装和使用教程
- C++异常处理机制
- 大数据开发之Spark(累加器、广播变量、Top10热门品类实战)
- 基于ssm航空信息管理系统论文
- echarts实现点击不同的柱子实现类目的不同名字
- Linux VMware安装及本地网络配置
- 为什么西拉和设拉子的味道如此不同?
- 【科普】家长们:如何早期发现孩子的听力问题?
- 云手机引领社交平台运营新潮流
- 从零开始训练神经网络