Java多线程技术7——线程组(备份)
?1 概述
? ? ? ? 为了方便对某些相同功能的线程进行管理,我们可以把线程归属到某一个线程组。线程组中可以有线程对象、线程,类似树的形式,效果如下图:
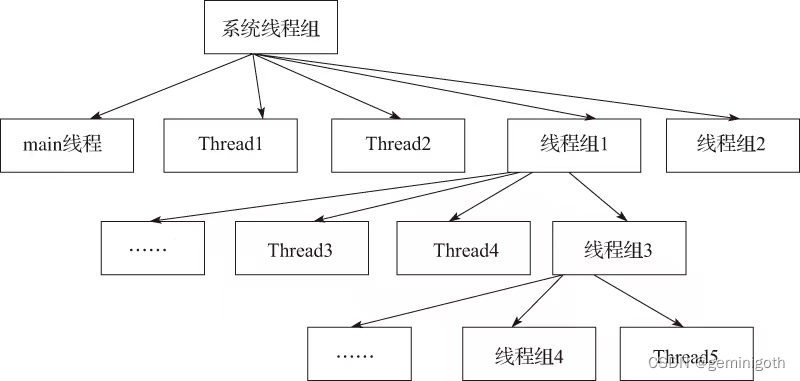
? ? ? ? 线程组的作用是可以批量地管理线程或线程对象,有效地对线程或线程对象进行组织。
2 线程对象关联线程组:一级关联
? ? ? ? 所谓的一级关联就是父对象中有子对象,但并不创建子孙对象,这种情况经常出现在开发中。
public class ThreadA extends Thread{
@Override
public void run(){
try {
while(!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()){
System.out.println("线程名称 = " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
Thread.sleep(3000);
}
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}public class ThreadB extends Thread{
@Override
public void run(){
try {
while(!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()){
System.out.println("线程名称 = " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
Thread.sleep(3000);
}
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}public class Run1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadA a = new ThreadA();
ThreadB b = new ThreadB();
ThreadGroup threadGroup = new ThreadGroup("线程组1");
Thread t1 = new Thread(threadGroup, a);
Thread t2 = new Thread(threadGroup, b);
t1.setName("t1");
t1.start();
t2.setName("t2");
t2.start();
System.out.println("活动的线程数为:" + threadGroup.activeCount());
System.out.println("线程组的名称为:" + threadGroup.getName());
}
}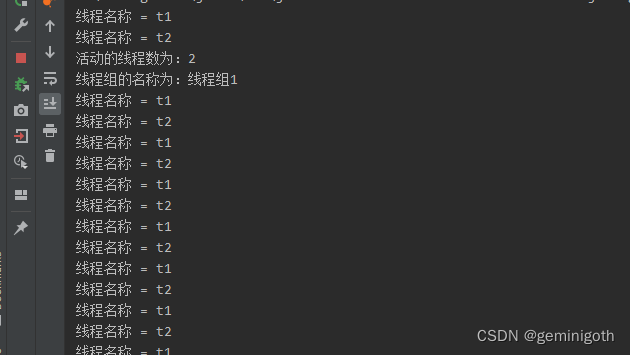
? ? ? ? 在代码中,将a和b对象与线程组threadgroup关联,然后对t1和t2对象执行start方法,之后执行ThreadA和ThreadB中的run方法。
? ? ? ? 控制条打印出线程组中的2个线程,以及线程组的名称。另外,两个线程一直运行,并且每隔3秒打印日志。
3 线程对象关联线程组:多级关联
? ? ? ? 多级关联就是父对象中有子对象,子对象中在创建子对象,也就是出现了子孙对象。但是,此种写法在开发中不常见。设计非常复杂的线程树结构不利于线程对象的管理,但JDK支持多级关联的线程树结构。实现多级关联的关键是ThreadGroup类的构造方法。
public ThreadGroup(ThreadGroup parent, String name) {
this(checkParentAccess(parent), parent, name);
}public class Run1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//在main方法线程组添加线程组A,然后在线程组A中添加线程对象B
ThreadGroup mainGroup = Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
//获取main主线程所在的线程组
ThreadGroup group = new ThreadGroup(mainGroup,"A");
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("runMethod");
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
Thread newThread = new Thread(group, runnable);
newThread.setName("B");
newThread.start();
//线程必须是程序启动后才归到线程组A中,因为在调用start方法时会调用group.add(this)
ThreadGroup[] listGroup = new ThreadGroup[Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup().activeCount()];
Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup().enumerate(listGroup);
System.out.println("main线程中有多少个子线程组:" + listGroup.length + ";名字为:" + listGroup[0].getName());
Thread[] listThread = new Thread[listGroup[0].activeCount()];
listGroup[0].enumerate(listThread);
System.out.println(listThread[0].getName());
}
}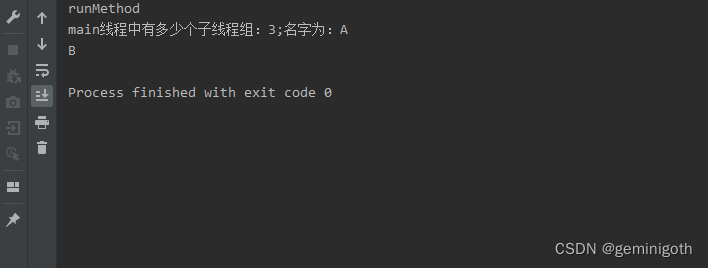
? ? ? ? 本程序代码的结构是在main组中创建一个新组,然后在新组中添加了线程,并取得相关信息。
4 线程组自动归属特性
? ? ? ? 自动归属就是自动归到当前线程组中。
public class Run1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("A处线程 :" + Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup()
+ " ,所属的线程组名为 " + Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup().getName()
+ ",中有线程组数量 " + Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup().activeGroupCount());
//自动加入main组中
ThreadGroup group = new ThreadGroup("新的组");
System.out.println("B处线程 :" + Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup()
+ " ,所属的线程组名为 " + Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup().getName()
+ ",中有线程组数量 " + Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup().activeGroupCount());
ThreadGroup[] threadGroups = new ThreadGroup[Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup().activeGroupCount()];
Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup().enumerate(threadGroups);
for (int i = 0; i < threadGroups.length; i++) {
System.out.println("第一个线程组名称为:" + threadGroups[i].getName());
}
}
}
?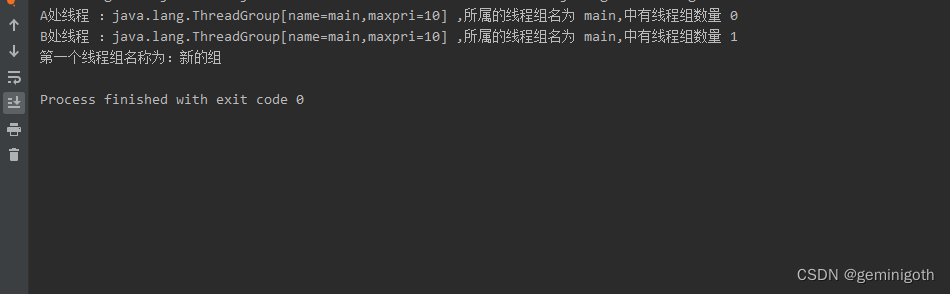
? ? ? ? 本实验?要证明的是,在实例化1个ThreadGroup线程组x时,如果不指定所属的线程组,线程组x会自动归到当前线程对象所属的线程组中,也就是隐式地在线程组中添加一个子线程组,所以控制台打印的线程组数量值由0变成了1。
5 组内的线程批量停止
? ? ? ? 使用线程组ThreadGroup的优点是可以批量处理本组内线程对象,比如可以批量中断组中的线程。
public class MyThread extends Thread{
public MyThread(ThreadGroup group, String name) {
super(group, name);
}
@Override
public void run(){
System.out.println("ThreadName = " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",开始准备死循环");
while(!this.isInterrupted()){
}
System.out.println("ThreadName = " +Thread.currentThread().getName() + "结束");
}
}
public class Run1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
ThreadGroup group= new ThreadGroup("我的线程组");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
MyThread thread = new MyThread(group,"线程"+(i+1));
thread.start();
}
Thread.sleep(5000);
group.interrupt();
System.out.println("调用了interrupt方法");
}catch (InterruptedException e){
System.out.println("停止了");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}? ? ? ? 通过将线程归属到线程组,可以实现当调用线程组ThreadGroup的interrupt()方法时中断该组中所有正在运行的线程。
6 Thread.activeCount()方法的使用
public static int activeCount()方法的作用是返回当前线程所在的线程组中活动线程的数目。
public class Run1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Thread.activeCount());
}
}
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 【C】const 关键字 xTaskCreate(const char * const pcName)
- 寒假刷题-递归与递推
- 房间里有网口但没有Wifi信号,把网口利用起来,让你房间也有Wifi信号!
- 卡码网 16 set集合
- 持续集成交付CICD:Jira 发布流水线
- redis-exporter监控部署(k8s内)tensuns专用
- 二、算法与复杂度
- JAVA版鸿鹄云商B2B2C:解析多商家入驻直播带货商城系统的实现与应用
- solidity 特性导致的漏洞
- Hive-SQL语法大全