Java并发编程: 并发编程中的ExecutionException异常
发布时间:2024年01月18日
一、什么是ExecutionException
在并发编程中在执行java.util.concurrent.Future实现类的get方法时,需要捕获java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException这个异常。Future.get()方法通常是要获取任务的执行结果,当执行任务的过程中抛出了异常,就会产生ExecutionException异常。
二、如何处理ExecutionException
案例分析:
package threadpool;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class ExecutorCompletionServiceDemo {
@Test
public void TestExecutorCompletionService () throws InterruptedException {
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(10, 20, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(50));
Collection<Callable<String>> tasks = new ArrayList<>();
tasks.add(() -> {return "1";});
tasks.add(() -> {return "2";});
tasks.add(() -> {return "3";});
tasks.add(() -> {return "4";});
tasks.add(() -> {return "5";});
tasks.add(() -> {return "6";});
tasks.add(() -> {return "7";});
tasks.add(() -> {return "8";});
tasks.add(() -> {throw new UnsupportedOperationException("暂不支持该操作");});
tasks.add(() -> {throw new NullPointerException("NullPointerException occurred");});
execute(executor, tasks);
}
private static void execute(ThreadPoolExecutor executor, Collection<Callable<String>> tasks) {
CompletionService<String> completionService = new ExecutorCompletionService<>(executor);
List<Future<String>> futures = new ArrayList<>(tasks.size());
for (Callable<String> task : tasks) {
futures.add(completionService.submit(task));
}
for (int i = 0; i < futures.size(); i++) {
try {
Future<String> take = completionService.take();
String s = take.get();
System.out.println(s);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
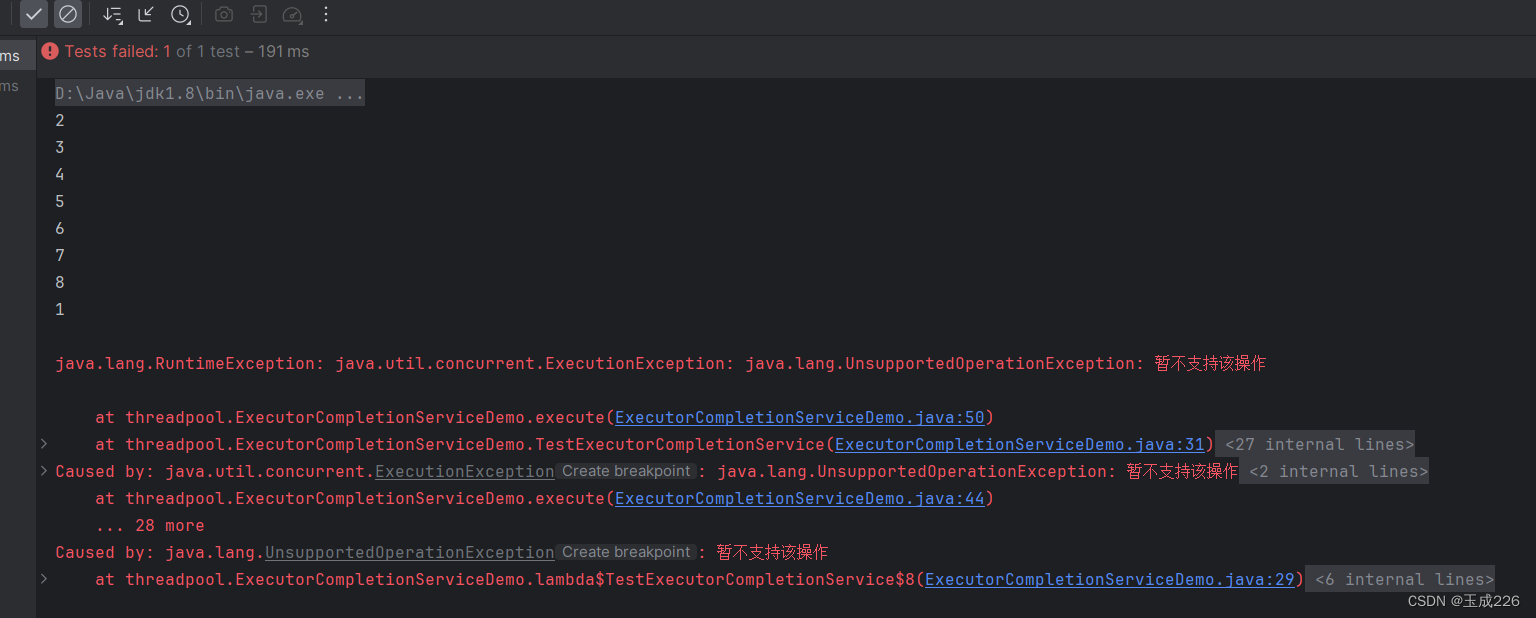
在execute方法中对于对ExecutionExcetion异常可以做一下处理:
引入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>21.0</version>
</dependency>
private static void execute(ThreadPoolExecutor executor, Collection<Callable<String>> tasks) {
CompletionService<String> completionService = new ExecutorCompletionService<>(executor);
List<Future<String>> futures = new ArrayList<>(tasks.size());
for (Callable<String> task : tasks) {
futures.add(completionService.submit(task));
}
for (int i = 0; i < futures.size(); i++) {
try {
Future<String> take = completionService.take();
String s = take.get();
System.out.println(s);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
Throwable cause = e.getCause() == null ? e : e.getCause();
Throwables.propagateIfPossible(cause, RuntimeException.class);
throw new RuntimeException(cause);
}
}
}

可以看出异常信息清晰了很多,便于开发人员分析。在上面的代码中通过getCause方法获取了来获取真实的异常。接下来使用了Google Guava提供的Throwable类来进行错误的转播与检查,当异常类型为RunTimeException进行抛出,最后使用Throw new RuntimeException(cause)进行兜底。
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/yuming226/article/details/135682200
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 41.常用shell之 alias - 创建命令别名 的用法及衍生用法
- C语言编译器(C语言编程软件)完全攻略(第十部分:VS2022下载和安装教程(图解版))
- 如何在Python中执行点分类任务
- IMX6LL|class:设备的大管家
- AttributeError: module ‘edge_tts‘ has no attribute ‘Communicate‘解决方案
- 关于http url带有特殊符号(get请求参数组类型传送)解决传特殊字符。
- Linux对于软件的管理
- python毕设选题 - 基于时间序列的股票预测于分析
- FPGA 查找表的用途和内部功能
- 数模学习day06-主成分分析