netty-daxin-4(http&websocket)
学习链接
Netty源码分析-Websocket之WebSocket08FrameDecoder
Netty源码分析-Websocket之WebSocket08FrameEncoder
http
服务端
NettyHttpServer
可参考:GitHub上netty项目中的example包中的代码
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpObjectAggregator;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpRequestDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpResponseEncoder;
public class NettyHttpServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(16);
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast("http-decoder", new HttpRequestDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast("http-encoder", new HttpResponseEncoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast("aggregator", new HttpObjectAggregator(65536));
ch.pipeline().addLast("serverHandler", new HelloWorldServerHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8080).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
HelloWorldServerHandler
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFutureListener;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.*;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import static io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpHeaderNames.CONNECTION;
import static io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_LENGTH;
import static io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_TYPE;
import static io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpHeaderValues.CLOSE;
import static io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpHeaderValues.KEEP_ALIVE;
import static io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpHeaderValues.TEXT_PLAIN;
import static io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpResponseStatus.OK;
@Slf4j
public class HelloWorldServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<HttpObject> {
private static final byte[] CONTENT = { 'H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', ' ', 'W', 'o', 'r', 'l', 'd' };
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, HttpObject msg) throws Exception {
log.info("来了Http消息了");
if (msg instanceof HttpRequest) {
HttpRequest req = (FullHttpRequest) msg;
boolean keepAlive = HttpUtil.isKeepAlive(req);
FullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(req.protocolVersion(), OK,
Unpooled.wrappedBuffer(CONTENT));
response.headers()
.set(CONTENT_TYPE, TEXT_PLAIN)
.setInt(CONTENT_LENGTH, response.content().readableBytes());
if (keepAlive) {
if (!req.protocolVersion().isKeepAliveDefault()) {
response.headers().set(CONNECTION, KEEP_ALIVE);
}
} else {
// Tell the client we're going to close the connection.
response.headers().set(CONNECTION, CLOSE);
}
ChannelFuture f = ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
if (!keepAlive) {
f.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
}
}
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
log.info("active===>");
}
@Override
public void channelRegistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
log.info("register===>");
}
@Override
public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
log.info("断开连接===>");
}
@Override
public void channelUnregistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
log.info("取消注册===>");
}
}
客户端
ApiPost
使用ApiPost接口测试工具发送请求,测试如下
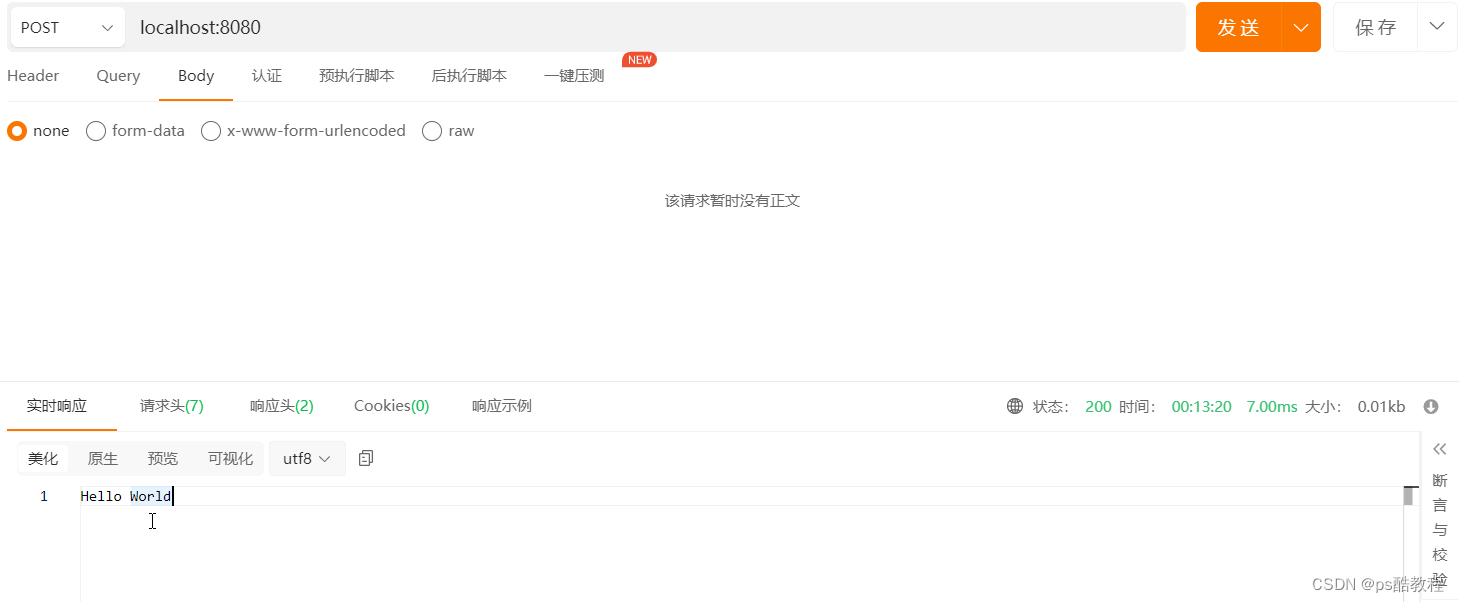
服务端日志输出
register===>
active===>
来了Http消息了
断开连接===>
取消注册===>
websocket
初步了解
为什么需要 WebSocket
在http协议中,客户端向服务器发出请求,服务器返回查询结果。HTTP 协议做不到服务器主动向客户端推送信息。
这种单向请求的特点,注定了如果服务器有连续的状态变化,客户端要获知就非常麻烦。我们只能使用"轮询":每隔一段时候,就发出一个询问,了解服务器有没有新的信息。最典型的场景就是聊天室。
轮询的效率低,非常浪费资源(因为必须不停连接,或者 HTTP 连接始终打开)。因此,工程师们一直在思考,有没有更好的方法。WebSocket 就是这样发明的。
简介
WebSocket 协议在2008年诞生,2011年成为国际标准。所有浏览器都已经支持了。
它的最大特点就是,服务器可以主动向客户端推送信息,客户端也可以主动向服务器发送信息,是真正的双向平等对话,属于服务器推送技术的一种。
WebSocket与http协议一样都是基于TCP的,所以他们都是可靠的协议,调用的WebSocket的send函数在实现中最终都是通过TCP的系统接口进行传输的。
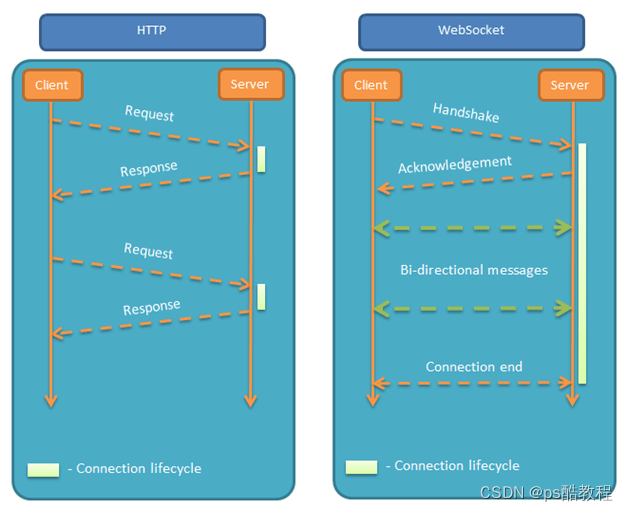
其他特点包括:
(1)建立在 TCP 协议之上,服务器端的实现比较容易。
(2)与 HTTP 协议有着良好的兼容性。默认端口也是80和443,并且握手阶段采用 HTTP 协议,因此握手时不容易屏蔽,能通过各种 HTTP 代理服务器。
(3)数据格式比较轻量,性能开销小,通信高效。
(4)可以发送文本,也可以发送二进制数据。
(5)没有同源限制,客户端可以与任意服务器通信。
(6)协议标识符是ws(如果加密,则为wss),服务器网址就是 URL。
浏览器的WebSocket客户端
客户端的简单示例
WebSocket 的用法相当简单。
var ws = new WebSocket("wss://echo.websocket.org");
ws.onopen = function(evt) {
console.log("Connection open ...");
ws.send("Hello WebSockets!");
};
ws.onmessage = function(evt) {
console.log( "Received Message: " + evt.data);
ws.close();
};
ws.onclose = function(evt) {
console.log("Connection closed.");
};
客户端的 API
WebSocket 构造函数
WebSocket 对象作为一个构造函数,用于新建 WebSocket 实例。
var ws = new WebSocket('ws://localhost:8080');
执行上面语句之后,客户端就会与服务器进行连接。
实例对象的所有属性和方法清单,参见 mozilla-WebSocket介绍。
webSocket.readyState
readyState属性返回实例对象的当前状态(只读),共有四种。
- CONNECTING:值为0,表示正在连接。
- OPEN:值为1,表示连接成功,可以通信了。
- CLOSING:值为2,表示连接正在关闭。
- CLOSED:值为3,表示连接已经关闭,或者打开连接失败。
下面是一个示例。
switch (ws.readyState) {
case WebSocket.CONNECTING:
// do something
break;
case WebSocket.OPEN:
// do something
break;
case WebSocket.CLOSING:
// do something
break;
case WebSocket.CLOSED:
// do something
break;
default:
// this never happens
break;
}
webSocket.onopen
实例对象的onopen属性,用于指定连接成功后的回调函数。
ws.onopen = function () {
ws.send('Hello Server!');
}
如果要指定多个回调函数,可以使用addEventListener方法。
ws.addEventListener('open', function (event) {
ws.send('Hello Server!');
});
webSocket.onclose
实例对象的onclose属性,用于指定连接关闭后的回调函数。
ws.onclose = function(event) {
var code = event.code;
var reason = event.reason;
var wasClean = event.wasClean;
// handle close event
};
ws.addEventListener("close", function(event) {
var code = event.code;
var reason = event.reason;
var wasClean = event.wasClean;
// handle close event
});
webSocket.onerror
实例对象的onerror属性,用于指定报错时的回调函数。
socket.onerror = function(event) {
// handle error event
};
socket.addEventListener("error", function(event) {
// handle error event
});
webSocket.onmessage
实例对象的onmessage属性,用于指定收到服务器数据后的回调函数。
ws.onmessage = function(event) {
var data = event.data;
// 处理数据
};
ws.addEventListener("message", function(event) {
var data = event.data;
// 处理数据
});
注意,服务器数据可能是文本,也可能是二进制数据(blob对象或Arraybuffer对象)。
ws.onmessage = function(event){
if(typeof event.data === String) {
console.log("Received data string");
}
if(event.data instanceof ArrayBuffer){
var buffer = event.data;
console.log("Received arraybuffer");
}
}
除了动态判断收到的数据类型,也可以使用binaryType属性,显式指定收到的二进制数据类型。
// 收到的是 blob 数据
ws.binaryType = "blob";
ws.onmessage = function(e) {
console.log(e.data.size);
};
// 收到的是 ArrayBuffer 数据
ws.binaryType = "arraybuffer";
ws.onmessage = function(e) {
console.log(e.data.byteLength);
};
webSocket.send()
实例对象的send()方法用于向服务器发送数据。
发送文本的例子。
ws.send('your message');
发送 Blob 对象的例子。
var file = document.querySelector('input[type="file"]').files[0];
ws.send(file);
发送 ArrayBuffer 对象的例子。
// Sending canvas ImageData as ArrayBuffer
var img = canvas_context.getImageData(0, 0, 400, 320);
var binary = new Uint8Array(img.data.length);
for (var i = 0; i < img.data.length; i++) {
binary[i] = img.data[i];
}
ws.send(binary.buffer);
webSocket.bufferedAmount
实例对象的bufferedAmount属性,表示还有多少字节的二进制数据没有发送出去。它可以用来判断发送是否结束。
var data = new ArrayBuffer(10000000);
socket.send(data);
if (socket.bufferedAmount === 0) {
// 发送完毕
} else {
// 发送还没结束
}
交互过程
搭建环境
NettyWsServer
@Slf4j
public class NettyWsServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(16);
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast("http-decoder", new HttpRequestDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast("http-encoder", new HttpResponseEncoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast("aggregator", new HttpObjectAggregator(655360));
WebSocketServerProtocolConfig wsServerConfig = WebSocketServerProtocolConfig
.newBuilder()
.websocketPath("/websocket")
.maxFramePayloadLength(Integer.MAX_VALUE)
.checkStartsWith(true).build();
ch.pipeline().addLast("websocketHandler", new WebSocketServerProtocolHandler(wsServerConfig));
ch.pipeline().addLast("wsTextHandler", new WsTextHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8080).sync();
log.info("=========ws服务器启动成功==========");
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
WsTextHandler
注意:如果这个Handler需要定义成单例,那么必须加上@Sharable注解哦,否则,当第二个客户端连接上来时,netty就会检测到它会添加了多次,却没有添加@Sharable注解而报错
@Slf4j
public class WsTextHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<TextWebSocketFrame> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, TextWebSocketFrame msg) throws Exception {
log.info("收到Ws客户端消息: {}", msg.text());
}
}
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
发送内容: <input type="text" id="content">
<button id="sendBtn">发送</button>
</body>
<script>
var ws = new WebSocket('ws://127.0.0.1:8080/websocket')
ws.onopen = function(evt) {
console.log('ws连接建立');
}
ws.onclose = function(evt) {
console.log('ws连接断开');
}
ws.onerror = function(evt) {
console.log('ws连接发生错误');
}
ws.onmessage = function(msg) {
console.log('收到消息: ' + JSON.stringify(msg));
}
const contentIpt = document.querySelector('#content')
const sendBtn = document.querySelector('#sendBtn')
sendBtn.addEventListener('click', function() {
console.log(contentIpt.value);
ws.send(contentIpt.value)
})
</script>
</html>
Postman测试websocket连接
也可以vscocde使用live server直接启动index.html 或者 如下使用postman来测试
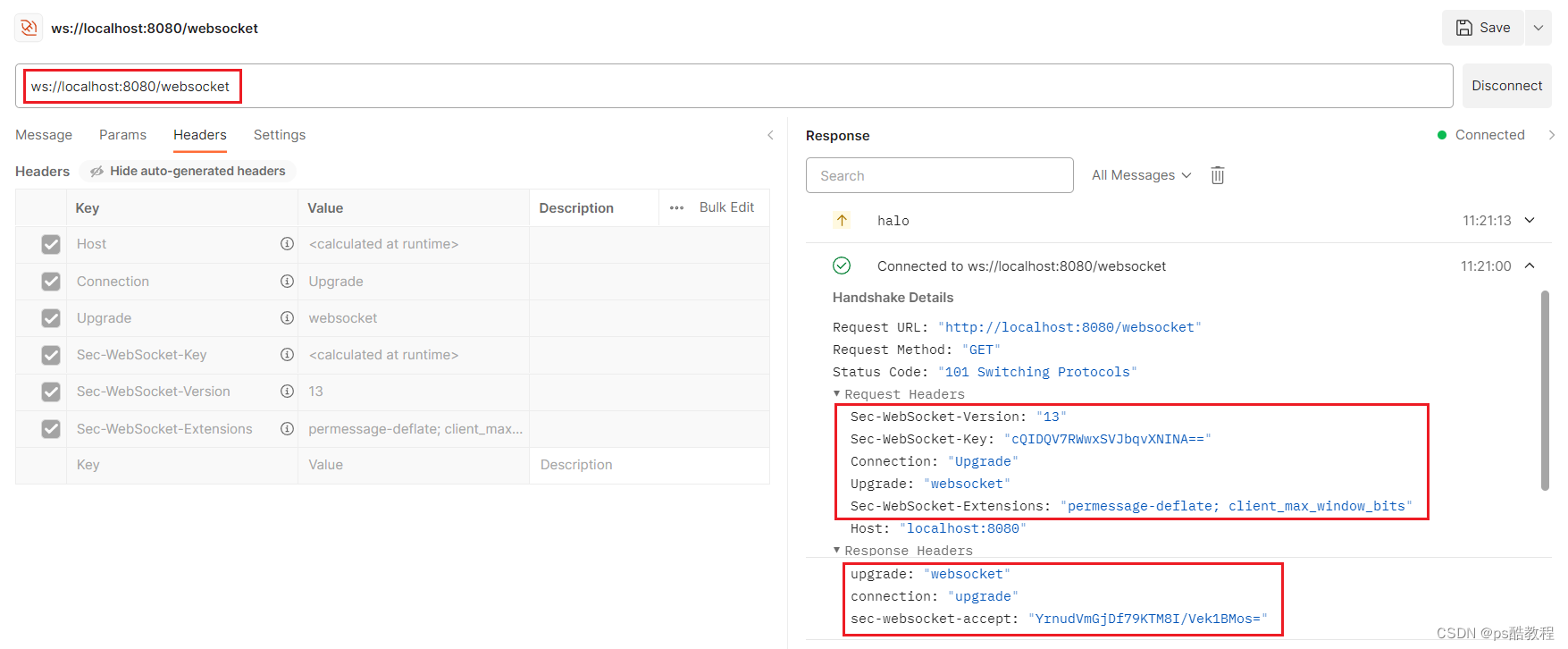
建立连接过程(握手)
前面提到,WebSocket复用了HTTP的握手通道。具体指的是,客户端通过HTTP请求与WebSocket服务端协商升级协议。协议升级完成后,后续的数据交换则遵照WebSocket的协议。
Http协议和WebSocket协议都是建立在Tcp连接之上的,Tcp连接本身就支持双向通信,只不过WebSocket的握手过程这个阶段须借助Http,一旦建立连接之后,就按照WebSocket协议定义的数据帧进行数据交互。
1、客户端:申请协议升级
首先,客户端发起协议升级请求。可以看到,采用的是标准的HTTP报文格式,且只支持GET方法。
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: localhost:8080
Origin: http://127.0.0.1:3000
Connection: Upgrade
Upgrade: websocket
Sec-WebSocket-Version: 13
Sec-WebSocket-Key: w4v7O6xFTi36lq3RNcgctw==
重点请求首部意义如下:
Connection: Upgrade:表示要升级协议Upgrade: websocket:表示要升级到websocket协议。Sec-WebSocket-Version: 13:表示websocket的版本。如果服务端不支持该版本,需要返回一个Sec-WebSocket-Versionheader,里面包含服务端支持的版本号。Sec-WebSocket-Key:与后面服务端响应首部的Sec-WebSocket-Accept是配套的,提供基本的防护,比如恶意的连接,或者无意的连接。
注意,上面请求省略了部分非重点请求首部。由于是标准的HTTP请求,类似Host、Origin、Cookie等请求首部会照常发送。在握手阶段,可以通过相关请求首部进行 安全限制、权限校验等。
2、服务端:响应协议升级
服务端返回内容如下,状态代码101表示协议切换。到此完成协议升级,后续的数据交互都按照新的协议来。
HTTP/1.1 101 Switching Protocols
Connection:Upgrade
Upgrade: websocket
Sec-WebSocket-Accept: Oy4NRAQ13jhfONC7bP8dTKb4PTU=
备注:每个header都以\r\n结尾,并且最后一行加上一个额外的空行\r\n。此外,服务端回应的HTTP状态码只能在握手阶段使用。过了握手阶段后,就只能采用特定的错误码。
3、Sec-WebSocket-Accept的计算
Sec-WebSocket-Key/Sec-WebSocket-Accept在主要作用在于提供基础的防护,减少恶意连接、意外连接。Sec-WebSocket-Key主要目的并不是确保数据的安全性,因为Sec-WebSocket-Key、Sec-WebSocket-Accept的转换计算公式是公开的,而且非常简单,最主要的作用是预防一些常见的意外情况(非故意的)
Sec-WebSocket-Accept根据客户端请求首部的Sec-WebSocket-Key计算出来。
计算公式为:
- 将Sec-WebSocket-Key跟258EAFA5-E914-47DA-95CA-C5AB0DC85B11拼接。
- 通过SHA1计算出摘要,并转成base64字符串。
伪代码如下:
>toBase64( sha1( Sec-WebSocket-Key + 258EAFA5-E914-47DA-95CA-C5AB0DC85B11 ) )
验证下前面的返回结果:
const crypto = require('crypto');
const magic = '258EAFA5-E914-47DA-95CA-C5AB0DC85B11';
const secWebSocketKey = 'w4v7O6xFTi36lq3RNcgctw==';
let secWebSocketAccept = crypto.createHash('sha1')
.update(secWebSocketKey + magic)
.digest('base64');
console.log(secWebSocketAccept);
// Oy4NRAQ13jhfONC7bP8dTKb4PTU=
WireShark抓包图示

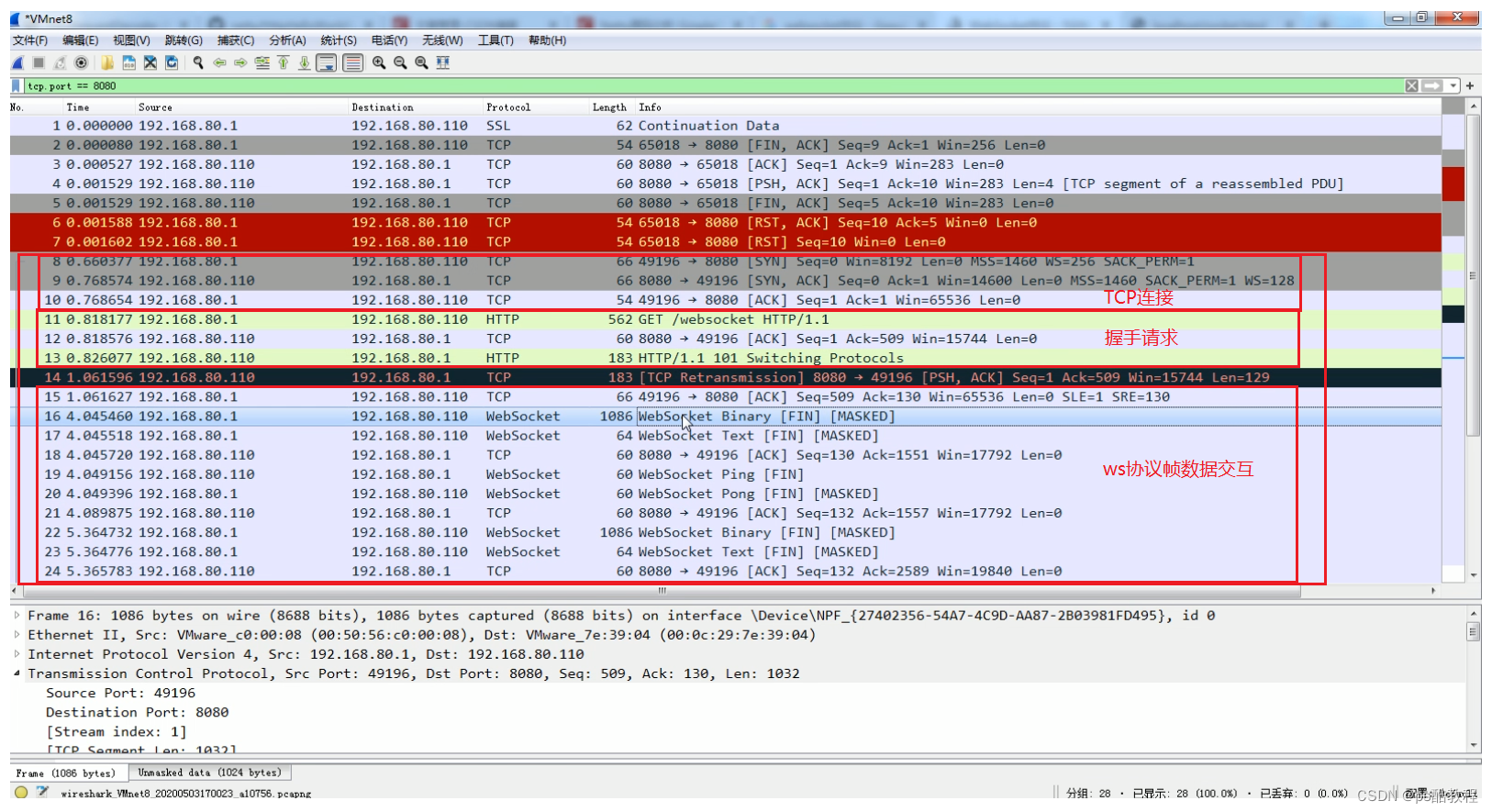
ws协议数据交互
客户端、服务端数据的交换,离不开数据帧格式的定义。因此,在实际讲解数据交换之前,我们先来看下WebSocket的数据帧格式。
WebSocket客户端、服务端通信的最小单位是帧(frame),由1个或多个帧组成一条完整的消息(message)。
- 发送端:将消息切割成多个帧,并发送给服务端;
- 接收端:接收消息帧,并将关联的帧重新组装成完整的消息;
本节的重点,就是讲解数据帧的格式。详细定义可参考 RFC6455 5.2节 。
1、数据帧格式概览
下面给出了WebSocket数据帧的统一格式。熟悉TCP/IP协议的同学对这样的图应该不陌生。
- 从左到右,单位是比特。比如FIN、RSV1各占据1比特,opcode占据4比特。
- 内容包括了标识、操作代码、掩码、数据、数据长度等。(下一小节会展开)
0 1 2 3
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1
+-+-+-+-+-------+-+-------------+-------------------------------+
|F|R|R|R| opcode|M| Payload len | Extended payload length |
|I|S|S|S| (4) |A| (7) | (16/64) |
|N|V|V|V| |S| | (if payload len==126/127) |
| |1|2|3| |K| | |
+-+-+-+-+-------+-+-------------+ - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - +
| Extended payload length continued, if payload len == 127 |
+ - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - +-------------------------------+
| |Masking-key, if MASK set to 1 |
+-------------------------------+-------------------------------+
| Masking-key (continued) | Payload Data |
+-------------------------------- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - +
: Payload Data continued ... :
+ - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - +
| Payload Data continued ... |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
2、数据帧格式详解
针对前面的格式概览图,这里逐个字段进行讲解,如有不清楚之处,可参考协议规范,或留言交流。
FIN:1个比特。
如果是1,表示这是消息(message)的最后一个分片(fragment),如果是0,表示不是是消息(message)的最后一个分片(fragment)。
RSV1, RSV2, RSV3:各占1个比特。
一般情况下全为0。当客户端、服务端协商采用WebSocket扩展时,这三个标志位可以非0,且值的含义由扩展进行定义。如果出现非零的值,且并没有采用WebSocket扩展,连接出错。
Opcode: 4个比特。
操作代码,Opcode的值决定了应该如何解析后续的数据载荷(data payload)。如果操作代码是不认识的,那么接收端应该断开连接(fail the connection)。可选的操作代码如下:
- %x0:表示一个延续帧。当Opcode为0时,表示本次数据传输采用了数据分片,当前收到的数据帧为其中一个数据分片。
- %x1:表示这是一个文本帧(frame)
- %x2:表示这是一个二进制帧(frame)
- %x3-7:保留的操作代码,用于后续定义的非控制帧。
- %x8:表示连接断开。
- %x9:表示这是一个ping操作。
- %xA:表示这是一个pong操作。
- %xB-F:保留的操作代码,用于后续定义的控制帧。
Mask: 1个比特。
表示是否要对数据载荷进行掩码操作。从客户端向服务端发送数据时,需要对数据进行掩码操作;从服务端向客户端发送数据时,不需要对数据进行掩码操作。
如果服务端接收到的数据没有进行过掩码操作,服务端需要断开连接。
如果Mask是1,那么在Masking-key中会定义一个掩码键(masking key),并用这个掩码键来对数据载荷进行反掩码。所有客户端发送到服务端的数据帧,Mask都是1。
掩码的算法、用途在下一小节讲解。
Payload length:数据载荷的长度,单位是字节。为7位,或7+16位,或1+64位。
假设数Payload length === x,如果
- x为0~126:数据的长度为x字节。
- x为126:后续2个字节代表一个16位的无符号整数,该无符号整数的值为数据的长度。
- x为127:后续8个字节代表一个64位的无符号整数(最高位为0),该无符号整数的值为数据的长度。
此外,如果payload length占用了多个字节的话,payload length的二进制表达采用网络序(big endian,重要的位在前)。
Masking-key:0或4字节(32位)
所有从客户端传送到服务端的数据帧,数据载荷都进行了掩码操作,Mask为1,且携带了4字节的Masking-key。如果Mask为0,则没有Masking-key。
备注:载荷数据的长度,不包括mask key的长度。
Payload data:(x+y) 字节
载荷数据:包括了扩展数据、应用数据。其中,扩展数据x字节,应用数据y字节。
扩展数据:如果没有协商使用扩展的话,扩展数据数据为0字节。所有的扩展都必须声明扩展数据的长度,或者可以如何计算出扩展数据的长度。此外,扩展如何使用必须在握手阶段就协商好。如果扩展数据存在,那么载荷数据长度必须将扩展数据的长度包含在内。
应用数据:任意的应用数据,在扩展数据之后(如果存在扩展数据),占据了数据帧剩余的位置。载荷数据长度 减去 扩展数据长度,就得到应用数据的长度。
3、数据传递
一旦WebSocket客户端、服务端建立连接后,后续的操作都是基于数据帧的传递。
WebSocket根据opcode来区分操作的类型。比如0x8表示断开连接,0x0-0x2表示数据交互。
1、数据分片
WebSocket的每条消息可能被切分成多个数据帧。当WebSocket的接收方收到一个数据帧时,会根据FIN的值来判断,是否已经收到消息的最后一个数据帧。
FIN=1表示当前数据帧为消息的最后一个数据帧,此时接收方已经收到完整的消息,可以对消息进行处理。FIN=0,则接收方还需要继续监听接收其余的数据帧。
此外,opcode在数据交换的场景下,表示的是数据的类型。0x01表示文本,0x02表示二进制。而0x00比较特殊,表示延续帧(continuation frame),顾名思义,就是完整消息对应的数据帧还没接收完。
2、数据分片例子
直接看例子更形象些。下面例子来自MDN,可以很好地演示数据的分片。客户端向服务端两次发送消息,服务端收到消息后回应客户端,这里主要看客户端往服务端发送的消息。
第一条消息
FIN=1, 表示是当前消息的最后一个数据帧。服务端收到当前数据帧后,可以处理消息。opcode=0x1,表示客户端发送的是文本类型。
第二条消息
FIN=0,opcode=0x1,表示发送的是文本类型,且消息还没发送完成,还有后续的数据帧。
FIN=0,opcode=0x0,表示消息还没发送完成,还有后续的数据帧,当前的数据帧需要接在上一条数据帧之后。
FIN=1,opcode=0x0,表示消息已经发送完成,没有后续的数据帧,当前的数据帧需要接在上一条数据帧之后。服务端可以将关联的数据帧组装成完整的消息。
Client: FIN=1, opcode=0x1, msg="hello"
Server: (process complete message immediately) Hi.
Client: FIN=0, opcode=0x1, msg="and a"
Server: (listening, new message containing text started)
Client: FIN=0, opcode=0x0, msg="happy new"
Server: (listening, payload concatenated to previous message)
Client: FIN=1, opcode=0x0, msg="year!"
Server: (process complete message) Happy new year to you too!
4、连接保持+心跳
WebSocket为了保持客户端、服务端的实时双向通信,需要确保客户端、服务端之间的TCP通道保持连接没有断开。然而,对于长时间没有数据往来的连接,如果依旧长时间保持着,可能会浪费包括的连接资源。
但不排除有些场景,客户端、服务端虽然长时间没有数据往来,但仍需要保持连接。这个时候,可以采用心跳来实现。
- 发送方->接收方:ping
- 接收方->发送方:pong
ping、pong的操作,对应的是WebSocket的两个控制帧,opcode分别是0x9、0xA。
举例,WebSocket服务端向客户端发送ping,只需要如下代码(采用ws模块)
ws.ping('', false, true);
WebSocket握手源码分析
动态编解码:通过wireShark抓包,我们知道客户端先与服务端经过TCP三次握手之后,建立TCP连接,紧接着,客户端就通过HTTP协议发送了握手请求,在收到服务端协同意协议升级的响应后。客户端和服务端就可以使用websocket协议进行数据交互了。这也就意味着,刚开始服务端先用http解码器和http编码器处理握手请求与响应,在握手完成之后,就不能再使用http编解码器了(因为后续的数据是按照websocket协议帧发送的),这涉及到动态编解码,因此需要在握手完成之后,此时切换成websocket的编解码器。
WebSocketServerProtocolHandler
在上面搭建环境中,我们在客户端连接服务端时,指定了如下的ChannelHandler,依次是:HttpRequestDecoder -> HttpResponseEncoder -> HttpObjectAggregator -> WebSocketServerProtocolHandler -> WsTextHandler
我们先看下WebSocketServerProtocolHandler的handlerAdded方法,它在handler添加到pipeline时,会创建1个WebSocketServerProtocolHandshakeHandler 的ws协议握手处理器,并把它添加到当前channelHandler处理器的前面,即现在的顺序是:HttpRequestDecoder -> HttpResponseEncoder -> HttpObjectAggregator -> WebSocketServerProtocolHandshakeHandler -> WebSocketServerProtocolHandler -> WsTextHandler
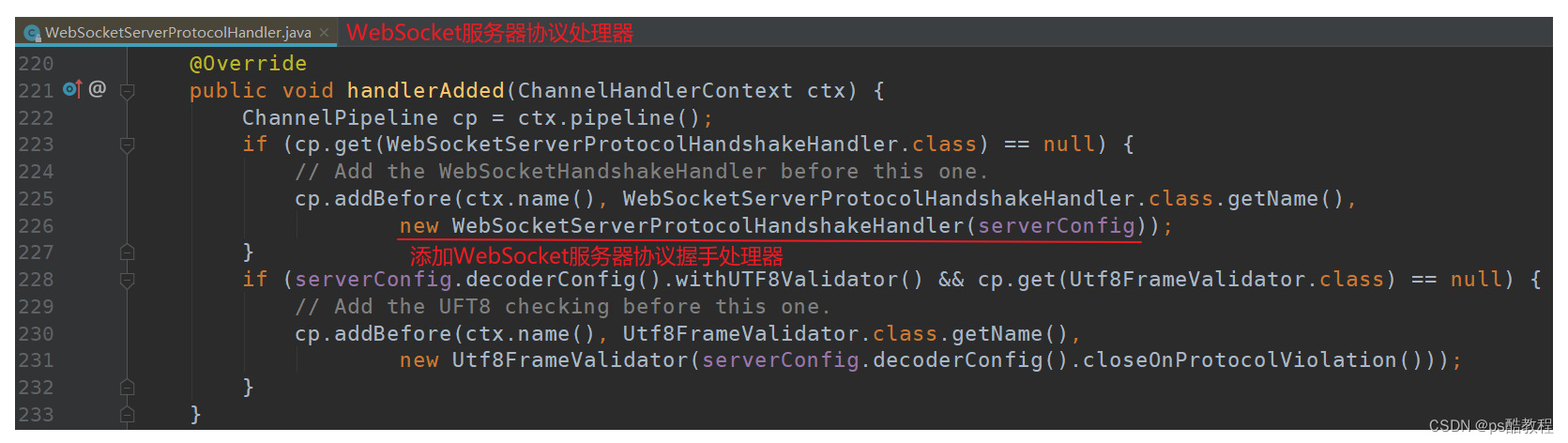
现在客户端完成与服务端的TCP的3次握手之后,就会发送1个Http协议的握手请求,因此这个时候,是要用到pipeline中的HttpRequestDecoder和HttpObjectAggregator 的,握手成功之后把握手响应给到客户端,是要用到HttpResponseEncoder 的。
WebSocketServerProtocolHandshakeHandler
然后,我们在WebSocketServerProtocolHandshakeHandler 中看下握手的过程,
@Override
public void channelRead(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg){
final HttpObject httpObject = (HttpObject) msg;
// 由前面的HttpRequestDecoder解码,并使用HttpObjectAggregator聚合
if (httpObject instanceof HttpRequest) {
final HttpRequest req = (HttpRequest) httpObject;
// 判断websocket的连接路径是否正确
isWebSocketPath = isWebSocketPath(req);
if (!isWebSocketPath) {
// 如果不是websocket的连接路径,就传递给到下1个处理器
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
return;
}
// 到这里,证明是websocket的连接路径
try {
// 必须是get请求,如果不是,则返回403
if (!GET.equals(req.method())) {
sendHttpResponse(ctx, req, new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HTTP_1_1, FORBIDDEN, ctx.alloc().buffer(0)));
return;
}
// 创建WebSocketServerHandshakerFactory
final WebSocketServerHandshakerFactory wsFactory = new WebSocketServerHandshakerFactory(
getWebSocketLocation(ctx.pipeline(), req, serverConfig.websocketPath()),
serverConfig.subprotocols(), serverConfig.decoderConfig());
// 使用WebSocketServerHandshakerFactory根据请求中的sec-websocket-version指定的websocket协议版本,选择具体的websocket握手器
final WebSocketServerHandshaker handshaker = wsFactory.newHandshaker(req);
final ChannelPromise localHandshakePromise = handshakePromise;
if (handshaker == null) {
// 如果未根据客户端请求的ws协议版本找到对应的握手器,则不支持该版本
WebSocketServerHandshakerFactory.sendUnsupportedVersionResponse(ctx.channel());
} else {
WebSocketServerProtocolHandler.setHandshaker(ctx.channel(), handshaker);
// 从pipeline上移除当前WebSocketServerProtocolHandshakeHandler
//(因为后面用不到它了,它的作用就是用来根据协议版本找到对应的握手器,然后 交给握手处理器去完成握手)
// 现在的顺序是:【HttpRequestDecoder -> HttpResponseEncoder -> HttpObjectAggregator-> WebSocketServerProtocolHandler -> WsTextHandler】
ctx.pipeline().remove(this);
// 交给握手处理器去完成握手
final ChannelFuture handshakeFuture = handshaker.handshake(ctx.channel(), req);
// 给握手完成后的Future添加监听器
handshakeFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) {
// 如果握手失败,
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
localHandshakePromise.tryFailure(future.cause());
// 则fire异常往下面传递
ctx.fireExceptionCaught(future.cause());
} else {
// 至此,握手成功
localHandshakePromise.trySuccess();
// 则把fire用户自定义事件
// (也即握手成功之后,我们可以通过重写userEventTriggered方法接收到WebSocketServerProtocolHandler.ServerHandshakeStateEvent.HANDSHAKE_COMPLETE事件)
// (但是,注意一下,它触发了2次,是为了兼容以前的版本,第二个事件可以拿到更多的信息)
ctx.fireUserEventTriggered(WebSocketServerProtocolHandler.ServerHandshakeStateEvent.HANDSHAKE_COMPLETE);
ctx.fireUserEventTriggered(new WebSocketServerProtocolHandler.HandshakeComplete(req.uri(), req.headers(), handshaker.selectedSubprotocol()));
}
}
});
applyHandshakeTimeout();
}
} finally {
ReferenceCountUtil.release(req);
}
} else if (!isWebSocketPath) {
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
} else {
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
}
}
WebSocketServerHandshaker
接下来,就看下具体是怎么握手的,因此来看WebSocketServerHandshaker抽象类
public final ChannelFuture handshake(final Channel channel, HttpRequest req,
final HttpHeaders responseHeaders, final ChannelPromise promise) {
// 只看这个if,进去看握手过程
if (req instanceof FullHttpRequest) {
return handshake(channel, (FullHttpRequest) req, responseHeaders, promise);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("{} WebSocket version {} server handshake", channel, version());
}
ChannelPipeline p = channel.pipeline();
ChannelHandlerContext ctx = p.context(HttpRequestDecoder.class);
if (ctx == null) {
// this means the user use an HttpServerCodec
ctx = p.context(HttpServerCodec.class);
if (ctx == null) {
promise.setFailure( new IllegalStateException("No HttpDecoder and no HttpServerCodec in the pipeline"));
return promise;
}
}
String aggregatorCtx = ctx.name();
if (HttpUtil.isContentLengthSet(req) || HttpUtil.isTransferEncodingChunked(req) ||
version == WebSocketVersion.V00) {
// Add aggregator and ensure we feed the HttpRequest so it is aggregated. A limit of 8192 should be
// more then enough for the websockets handshake payload.
aggregatorCtx = "httpAggregator";
p.addAfter(ctx.name(), aggregatorCtx, new HttpObjectAggregator(8192));
}
p.addAfter(aggregatorCtx, "handshaker", new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
private FullHttpRequest fullHttpRequest;
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
if (msg instanceof HttpObject) {
try {
handleHandshakeRequest(ctx, (HttpObject) msg);
} finally {
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
}
} else {
super.channelRead(ctx, msg);
}
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
// Remove ourself and fail the handshake promise.
ctx.pipeline().remove(this);
promise.tryFailure(cause);
ctx.fireExceptionCaught(cause);
}
@Override
public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
try {
// Fail promise if Channel was closed
if (!promise.isDone()) {
promise.tryFailure(new ClosedChannelException());
}
ctx.fireChannelInactive();
} finally {
releaseFullHttpRequest();
}
}
@Override
public void handlerRemoved(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
releaseFullHttpRequest();
}
private void handleHandshakeRequest(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, HttpObject httpObject) {
if (httpObject instanceof FullHttpRequest) {
ctx.pipeline().remove(this);
handshake(channel, (FullHttpRequest) httpObject, responseHeaders, promise);
return;
}
if (httpObject instanceof LastHttpContent) {
assert fullHttpRequest != null;
FullHttpRequest handshakeRequest = fullHttpRequest;
fullHttpRequest = null;
try {
ctx.pipeline().remove(this);
handshake(channel, handshakeRequest, responseHeaders, promise);
} finally {
handshakeRequest.release();
}
return;
}
if (httpObject instanceof HttpRequest) {
HttpRequest httpRequest = (HttpRequest) httpObject;
fullHttpRequest = new DefaultFullHttpRequest(httpRequest.protocolVersion(), httpRequest.method(),
httpRequest.uri(), Unpooled.EMPTY_BUFFER, httpRequest.headers(), EmptyHttpHeaders.INSTANCE);
if (httpRequest.decoderResult().isFailure()) {
fullHttpRequest.setDecoderResult(httpRequest.decoderResult());
}
}
}
private void releaseFullHttpRequest() {
if (fullHttpRequest != null) {
fullHttpRequest.release();
fullHttpRequest = null;
}
}
});
try {
ctx.fireChannelRead(ReferenceCountUtil.retain(req));
} catch (Throwable cause) {
promise.setFailure(cause);
}
return promise;
}
接下来作握手处理,截至此时,当前的pipeline中的处理器顺序为:【HttpRequestDecoder -> HttpResponseEncoder -> HttpObjectAggregator-> WebSocketServerProtocolHandler -> WsTextHandler】(因为上面移除了WebSocketServerProtocolHandshakeHandler,WebSocketServerProtocolHandshakeHandler的作用就是在客户端发送的是握手请求时,根据客户端请求的ws协议版本获取到对应的WebSocketServerHandshaker)
public final ChannelFuture handshake(Channel channel, FullHttpRequest req,
HttpHeaders responseHeaders, final ChannelPromise promise) {
// 构建握手响应对象,由具体的子类实现,如:WebSocketServerHandshaker13
//(比如:根据sec-websocket-key握手请求头计算得到sec-websocket-accept响应头、
// 根据sec-websocket-protocol子协议头返回支持的子协议)
FullHttpResponse response = newHandshakeResponse(req, responseHeaders);
// 拿到pipeline
ChannelPipeline p = channel.pipeline();
// 移除掉pipeline中的聚合器
if (p.get(HttpObjectAggregator.class) != null) {
p.remove(HttpObjectAggregator.class);
}
// 移除掉pipeline中的内容压缩器
if (p.get(HttpContentCompressor.class) != null) {
p.remove(HttpContentCompressor.class);
}
// 拿到pipeline中的http请求解码器
ChannelHandlerContext ctx = p.context(HttpRequestDecoder.class);
final String encoderName;
if (ctx == null) {
// 如果pipeline中的http请求解码器为空,那么用户肯定是用的是HttpServerCodec的http编解码器
ctx = p.context(HttpServerCodec.class);
// 如果http编解码器也没设置,就直接是失败了
if (ctx == null) {
promise.setFailure(new IllegalStateException("No HttpDecoder and no HttpServerCodec in the pipeline"));
return promise;
}
// 添加wsencoder的ws编码器、wsdecoder的ws解码器
p.addBefore(ctx.name(), "wsencoder", newWebSocketEncoder());
p.addBefore(ctx.name(), "wsdecoder", newWebsocketDecoder());
encoderName = ctx.name();
} else {
// 显然,我们走的是这里的逻辑
// 将Http解码器替换为wsdecoder解码器
p.replace(ctx.name(), "wsdecoder", newWebsocketDecoder());
// 拿到http编码器的名字(等握手响应发给客户端之后,须移除它)
encoderName = p.context(HttpResponseEncoder.class).name();
// 在http编码器前面添加wsencoder编码器
p.addBefore(encoderName, "wsencoder", newWebSocketEncoder());
// 此时,pipeline中的channelHandler顺序如下:
//【WebSocketFrameDecoder(HttpRequestDecoder被替换为WebSocketFrameDecoder) -> WebSocketFrameEncoder(在htt编码器的前面加上WebSocketFrameEncoder) -> HttpResponseEncoder -> HttpObjectAggregator -> WebSocketServerProtocolHandler -> WsTextHandler】
}
// 将握手响应写给客户端
channel.writeAndFlush(response).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
// 握手响应成功写回给客户端之后,移除掉pipeline中的http编码器
if (future.isSuccess()) {
ChannelPipeline p = future.channel().pipeline();
p.remove(encoderName);
promise.setSuccess();
} else {
promise.setFailure(future.cause());
}
}
});
return promise;
}
经过握手处理后,channel的pipeline中的channelHandler处理器链如下:
即握手完成后完整的链是:WebSocketFrameDecoder -> WebSocketFrameEncoder -> WebSocketServerProtocolHandler -> WsTextHandler(这里就先不考虑Head和Tail了,实际上都有头和尾)。
握手完成之后,客户端就是按照websocket协议帧发送数据给服务端,因此,channle的pipeline上维护了ws的解码器,以及当需发送消息给客户端所要使用的ws的编码器。
WebSocket08FrameDecoder解码器
- 它继承自ByteToMessageDecoder
- 读取客户端传过来的字节数据,当字节数不够时,直接return,等待下次将足够的数据传递过来后,再接着往下处理
- 通过枚举类来标识当前读取到了当前websocket帧的哪个阶段,等下次数据传过来之后,接着原来的阶段去处理
- 处理中用到了位运算取出特定的比特位,再根据websocket协议解析这些比特位的含义,等解析完了1个完整的websocket帧,再把这个解析出来的对象传给后面的业务handler处理
- 解析出来的结果类型有:PingWebSocketFrame、PongWebSocketFrame、CloseWebSocketFrame、TextWebSocketFrame、BinaryWebSocketFrame、ContinuationWebSocketFrame
public class WebSocket08FrameDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder
implements WebSocketFrameDecoder {
//当前解码器状态枚举
enum State {
READING_FIRST,
READING_SECOND,
READING_SIZE,
MASKING_KEY,
PAYLOAD,
CORRUPT
}
//定义opcode
private static final byte OPCODE_CONT = 0x0;
private static final byte OPCODE_TEXT = 0x1;
private static final byte OPCODE_BINARY = 0x2;
private static final byte OPCODE_CLOSE = 0x8;
private static final byte OPCODE_PING = 0x9;
private static final byte OPCODE_PONG = 0xA;
//Websocket最大荷载数据长度,超过该值抛出异常
private final long maxFramePayloadLength;
//是否允许WS扩展
private final boolean allowExtensions;
//是否期望对荷载数据进行掩码-客户端发送的数据必须要掩码
private final boolean expectMaskedFrames;
//是否允许掩码缺失
private final boolean allowMaskMismatch;
//分片发送的数量
private int fragmentedFramesCount;
//当前ws帧是否是完整的
private boolean frameFinalFlag;
//当前ws荷载数据是否已经掩码
private boolean frameMasked;
//RSV1 RSV2 RSV3
private int frameRsv;
//ws帧内 opocde的值
private int frameOpcode;
//荷载数据的长度
private long framePayloadLength;
//掩码
private byte[] maskingKey;
//ws协议PayloadLength表示的长度
private int framePayloadLen1;
//是否收到关闭帧
private boolean receivedClosingHandshake;
//初始状态
private State state = State.READING_FIRST;
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
// Discard all data received if closing handshake was received before.
//如果已经收到关闭帧,则丢弃说有字节
if (receivedClosingHandshake) {
in.skipBytes(actualReadableBytes());
return;
}
switch (state) {
case READING_FIRST:
if (!in.isReadable()) {
return;
}
//把荷载数据长度设置为0
framePayloadLength = 0;
// FIN, RSV, OPCODE
//读取ws帧的第一个字节,解析出FIN RSV OPCODE
byte b = in.readByte();
frameFinalFlag = (b & 0x80) != 0; //b & 10000000 得到FIN
frameRsv = (b & 0x70) >> 4; //b & 01110000 完了右移4位 得到RSV
frameOpcode = b & 0x0F; // b & 00001111 得到opcode
//改变状态
state = State.READING_SECOND;
case READING_SECOND:
if (!in.isReadable()) {
return;
}
//读取ws帧的第二个字节
// MASK, PAYLOAD LEN 1
b = in.readByte();
//计算是否需要掩码
frameMasked = (b & 0x80) != 0;
//ws协议PayloadLength表示的长度
framePayloadLen1 = b & 0x7F;
//如果RSV不为0说明使用了WS扩展协议,allowExtensions如果设置为不允许扩展则报错
//目前RSV都为0,还没有扩展协议
if (frameRsv != 0 && !allowExtensions) {
protocolViolation(ctx, "RSV != 0 and no extension negotiated, RSV:" + frameRsv);
return;
}
//如果不允许缺失掩码 并且 客户端又没有掩码 则报错
if (!allowMaskMismatch && expectMaskedFrames != frameMasked) {
protocolViolation(ctx, "received a frame that is not masked as expected");
return;
}
//如果opcpde为一个控制帧 如果 ping pong close
if (frameOpcode > 7) { // control frame (have MSB in opcode set)
// control frames MUST NOT be fragmented
//控制帧必须是一个完整的帧,所有frameFinalFlag必须为true
if (!frameFinalFlag) {
protocolViolation(ctx, "fragmented control frame");
return;
}
//控制帧framePayload必须小于等于125
// control frames MUST have payload 125 octets or less
if (framePayloadLen1 > 125) {
protocolViolation(ctx, "control frame with payload length > 125 octets");
return;
}
//控制帧目前只能是close ping pong,其它目前ws还未定义,出现则报错
// check for reserved control frame opcodes
if (!(frameOpcode == OPCODE_CLOSE || frameOpcode == OPCODE_PING
|| frameOpcode == OPCODE_PONG)) {
protocolViolation(ctx, "control frame using reserved opcode " + frameOpcode);
return;
}
// close frame : if there is a body, the first two bytes of the
// body MUST be a 2-byte unsigned integer (in network byte
// order) representing a getStatus code
//关闭帧framePayloadLen1必为0,不能携带数据
if (frameOpcode == 8 && framePayloadLen1 == 1) {
protocolViolation(ctx, "received close control frame with payload len 1");
return;
}
} else { // data frame
//小于7的都是数据帧
//%x0:表示一个延续帧。当Opcode为0时,表示本次数据传输采用了数据分片,当前收到的数据帧为其中一个数据分片。
//%x1:表示这是一个文本帧(frame)
//%x2:表示这是一个二进制帧(frame)
// check for reserved data frame opcodes
//目前只支持这三种帧,其它抛出异常
if (!(frameOpcode == OPCODE_CONT || frameOpcode == OPCODE_TEXT
|| frameOpcode == OPCODE_BINARY)) {
protocolViolation(ctx, "data frame using reserved opcode " + frameOpcode);
return;
}
//如果是延续帧,那前面必须有一个Text或Binary帧,通过fragmentedFramesCount>0来判断
// check opcode vs message fragmentation state 1/2
if (fragmentedFramesCount == 0 && frameOpcode == OPCODE_CONT) {
protocolViolation(ctx, "received continuation data frame outside fragmented message");
return;
}
//如果fragmentedFramesCount != 0 说明前面出现了text或binary帧,并且fin为false 指示后续还有数据
//但是frameOpcode又不是一个延续帧,说明出现混乱情况报错
//我觉得frameOpcode != OPCODE_PING是一个无效的判断
// check opcode vs message fragmentation state 2/2
if (fragmentedFramesCount != 0 && frameOpcode != OPCODE_CONT && frameOpcode != OPCODE_PING) {
protocolViolation(ctx,
"received non-continuation data frame while inside fragmented message");
return;
}
}
//修改状态
state = State.READING_SIZE;
case READING_SIZE:
// Read frame payload length
//如果payload length=126 后续2个字节是荷载数据的长度
if (framePayloadLen1 == 126) {
if (in.readableBytes() < 2) {
return;
}
//读2个字节,按无符号处理
framePayloadLength = in.readUnsignedShort();
if (framePayloadLength < 126) {
protocolViolation(ctx, "invalid data frame length (not using minimal length encoding)");
return;
}
//127 后续8个字节是何在数据的长度
} else if (framePayloadLen1 == 127) {
if (in.readableBytes() < 8) {
return;
}
//读取8个字节为数据长度
framePayloadLength = in.readLong();
// TODO: check if it's bigger than 0x7FFFFFFFFFFFFFFF, Maybe
// just check if it's negative?
if (framePayloadLength < 65536) {
protocolViolation(ctx, "invalid data frame length (not using minimal length encoding)");
return;
}
} else {
//payload length<125 说明framePayloadLen1本身就表示数据长度
framePayloadLength = framePayloadLen1;
}
//如果荷载数据的长度 大于阈值,抛出异常
if (framePayloadLength > maxFramePayloadLength) {
protocolViolation(ctx, "Max frame length of " + maxFramePayloadLength + " has been exceeded.");
return;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Decoding WebSocket Frame length={}", framePayloadLength);
}
//转换状态
state = State.MASKING_KEY;
case MASKING_KEY:
//是否有掩码
if (frameMasked) {
if (in.readableBytes() < 4) {
return;
}
//读取4个字节,读取掩码
if (maskingKey == null) {
maskingKey = new byte[4];
}
in.readBytes(maskingKey);
}
//转换状态
state = State.PAYLOAD;
case PAYLOAD:
//可读数据达不到荷载数据长度则等待下一轮事件
if (in.readableBytes() < framePayloadLength) {
return;
}
ByteBuf payloadBuffer = null;
try {
//将荷载数据读到新的缓冲区中
payloadBuffer = readBytes(ctx.alloc(), in, toFrameLength(framePayloadLength));
//切换状态为初始状态,进行下一轮读取。
state = State.READING_FIRST;
//如果有掩码,需要进行XOR二次计算还原出原文
// Unmask data if needed
if (frameMasked) {
unmask(payloadBuffer);
}
// Processing ping/pong/close frames because they cannot be
// fragmented
//根据情况封装不同数据帧
if (frameOpcode == OPCODE_PING) {
out.add(new PingWebSocketFrame(frameFinalFlag, frameRsv, payloadBuffer));
payloadBuffer = null;
return;
}
if (frameOpcode == OPCODE_PONG) {
out.add(new PongWebSocketFrame(frameFinalFlag, frameRsv, payloadBuffer));
payloadBuffer = null;
return;
}
if (frameOpcode == OPCODE_CLOSE) {
//如果是对方发的Close帧则关闭socket
receivedClosingHandshake = true;
checkCloseFrameBody(ctx, payloadBuffer);
out.add(new CloseWebSocketFrame(frameFinalFlag, frameRsv, payloadBuffer));
payloadBuffer = null;
return;
}
// Processing for possible fragmented messages for text and binary
// frames
if (frameFinalFlag) {
//如果是最终的分片则fragmentedFramesCount=0
// Final frame of the sequence. Apparently ping frames are
// allowed in the middle of a fragmented message
if (frameOpcode != OPCODE_PING) {
fragmentedFramesCount = 0;
}
} else {
// Increment counter
//否则fragmentedFramesCount++
fragmentedFramesCount++;
}
// 返回各种帧
if (frameOpcode == OPCODE_TEXT) {
out.add(new TextWebSocketFrame(frameFinalFlag, frameRsv, payloadBuffer));
payloadBuffer = null;
return;
} else if (frameOpcode == OPCODE_BINARY) {
out.add(new BinaryWebSocketFrame(frameFinalFlag, frameRsv, payloadBuffer));
payloadBuffer = null;
return;
} else if (frameOpcode == OPCODE_CONT) {
out.add(new ContinuationWebSocketFrame(frameFinalFlag, frameRsv,
payloadBuffer));
payloadBuffer = null;
return;
} else {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Cannot decode web socket frame with opcode: "
+ frameOpcode);
}
} finally {
//释放缓冲区,如果payloadBuffer!=null 说明没有成功返回数据帧
if (payloadBuffer != null) {
payloadBuffer.release();
}
}
case CORRUPT:
if (in.isReadable()) {
// If we don't keep reading Netty will throw an exception saying
// we can't return null if no bytes read and state not changed.
in.readByte();
}
return;
default:
throw new Error("Shouldn't reach here.");
}
}
private void unmask(ByteBuf frame) {
int i = frame.readerIndex();
int end = frame.writerIndex();
ByteOrder order = frame.order();
//把掩码二进制数组转换为int
int intMask = ((maskingKey[0] & 0xFF) << 24)
| ((maskingKey[1] & 0xFF) << 16)
| ((maskingKey[2] & 0xFF) << 8)
| (maskingKey[3] & 0xFF);
//如果是小端序,需要把INT类型的掩码反转
if (order == ByteOrder.LITTLE_ENDIAN) {
intMask = Integer.reverseBytes(intMask);
}
//XOR运算,还原原始值
for (; i + 3 < end; i += 4) {
int unmasked = frame.getInt(i) ^ intMask;
frame.setInt(i, unmasked);
}
for (; i < end; i++) {
frame.setByte(i, frame.getByte(i) ^ maskingKey[i % 4]);
}
}
//抛出异常
private void protocolViolation(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String reason) {
protocolViolation(ctx, new CorruptedFrameException(reason));
}
//抛出异常,关闭socket
private void protocolViolation(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, CorruptedFrameException ex) {
state = State.CORRUPT;
if (ctx.channel().isActive()) {
Object closeMessage;
if (receivedClosingHandshake) {
closeMessage = Unpooled.EMPTY_BUFFER;
} else {
closeMessage = new CloseWebSocketFrame(1002, null);
}
ctx.writeAndFlush(closeMessage).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
}
throw ex;
}
}
WebSocket08FrameEncoder编码器
- 它继承自MessageToMessageEncoder<WebSocketFrame>,因此该编码器可以处理的是WebSocketFrame类型的对象
- 当ws服务端发送数据给客户端时,需要按照websocket协议将待发送的数据封装成websocket帧,发送给客户端,这就是websocket编码器需要做的事
package io.netty.handler.codec.http.websocketx;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.handler.codec.MessageToMessageEncoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.TooLongFrameException;
import io.netty.util.internal.logging.InternalLogger;
import io.netty.util.internal.logging.InternalLoggerFactory;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.ByteOrder;
import java.util.List;
//WebSocketFrame编码器,负责把WebSocketFrame的子类转换为bytebuf
public class WebSocket08FrameEncoder extends MessageToMessageEncoder<WebSocketFrame> implements WebSocketFrameEncoder {
private static final InternalLogger logger = InternalLoggerFactory.getInstance(WebSocket08FrameEncoder.class);
private static final byte OPCODE_CONT = 0x0; //延续帧 0000 0000
private static final byte OPCODE_TEXT = 0x1; //文本帧 0000 0001
private static final byte OPCODE_BINARY = 0x2; //二进制帧 0000 0010
private static final byte OPCODE_CLOSE = 0x8; //关闭 0000 1000
private static final byte OPCODE_PING = 0x9; //心跳检测帧 0000 1001
private static final byte OPCODE_PONG = 0xA; //心跳应答帧 0000 1010
//阈值,发送的字节超过此长度将不会合并到一个bytebuf中
private static final int GATHERING_WRITE_THRESHOLD = 1024;
//表示websocket是否需要对数据进行掩码运算
//掩码运算也叫XOR加密,详情可以在http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2017/05/xor.html了解。
//那么websocket客户端发送到服务器端的数据需要进行XOR运算是为了防止攻击
//因为websocket发送的数据,黑客很有可能在数据字节码中加入http请求的关键字,比如getxx \r\n,
//如果不加以限制,那么某些代理服务器会以为这是一个http请求导致错误转发。
//那么通过对原生字节进行XOP计算后,http关键字会被转化为其它字节,从而避免攻击。
private final boolean maskPayload;
public WebSocket08FrameEncoder(boolean maskPayload) {
this.maskPayload = maskPayload;
}
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, WebSocketFrame msg, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
//要发送的数据
final ByteBuf data = msg.content();
//掩码XOR计算需要的KEY
byte[] mask;
//根据帧的类型确定opcode的值
byte opcode;
if (msg instanceof TextWebSocketFrame) {
opcode = OPCODE_TEXT;
} else if (msg instanceof PingWebSocketFrame) {
opcode = OPCODE_PING;
} else if (msg instanceof PongWebSocketFrame) {
opcode = OPCODE_PONG;
} else if (msg instanceof CloseWebSocketFrame) {
opcode = OPCODE_CLOSE;
} else if (msg instanceof BinaryWebSocketFrame) {
opcode = OPCODE_BINARY;
} else if (msg instanceof ContinuationWebSocketFrame) {
opcode = OPCODE_CONT;
} else {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Cannot encode frame of type: " + msg.getClass().getName());
}
//要发送数据的长度
int length = data.readableBytes();
int b0 = 0;
//判断消息是否是最后一个分片,如果是最后一个分片 那么FIN要设置为1
if (msg.isFinalFragment()) {
//1 << 7 左移7位 1000 0000 把FIN比特为设为1
//bo = 0 | 128 (当两边操作数的位有一边为1时,结果为1,否则为0),值不变。
b0 |= 1 << 7;
//计算完 b0=128 【1000 0000】
}
//RSV1, RSV2, RSV3:各占1个比特 正常全为0,属于扩展字段
//msg.rsv() % 8 任何int摸8都返回小于8的数 二进制位<=[0000 0111]
//<< 4 左移4位得到 [0111 0000],这里假设的是rsv不为0的情况。
//实际情况rsv是0,那么得到【0000 0000]
b0 |= msg.rsv() % 8 << 4; //b0 |= 0 值没变还是128[1000 0000]
//opcode % 128 值不变
//我们假设opcode= 0x1; //文本帧 0000 0001
b0 |= opcode % 128; //那么 bo |= 0x1 得到 [1000 0001]
// Fin RSV opcode
//所以websocket第一个比特位已经得到 = 【 1 000 0001 】
if (opcode == OPCODE_PING && length > 125) {
throw new TooLongFrameException("invalid payload for PING (payload length must be <= 125, was "
+ length);
}
//是否释放bytebuf的标记位
boolean release = true;
ByteBuf buf = null;
try {
//是否需要掩码,如果需要则需要4个字节的位置
int maskLength = maskPayload ? 4 : 0;
//数据的长度125之内
if (length <= 125) {
//size= 2+掩码的长度(如果有掩码,没有为0)
//数据长度<=125,ws头2个字节+掩码长度即可
int size = 2 + maskLength;
//如果需要掩码 或者length<=1024
if (maskPayload || length <= GATHERING_WRITE_THRESHOLD) {
//把size的值增大
size += length;
}
//分配缓冲区(如果maskPayload=true或length<=125,那么size就是websocket的头部长度+数据长度)
buf = ctx.alloc().buffer(size);
//写入websocket头的第一个字节:假设[10000001]
buf.writeByte(b0);
//websocket头第二个字节: 需要掩码为0x80 | (byte) length,假设长度120,那么得到 [1(需要掩码) 111 1000]
//如果不需要掩码则得到 [0(不需要掩码)111 1000], 8个比特第一位表示是否需要掩码,其余7位表示长度。
byte b = (byte) (maskPayload ? 0x80 | (byte) length : (byte) length);
//写入第二个字节
buf.writeByte(b);
//数据长度65535之内
} else if (length <= 0xFFFF) {
//size= 4+掩码的长度(如果有掩码,没有为0)
//数据长度 x>125 ,x<=65535,ws头需要4个字节+掩码长度
int size = 4 + maskLength;
//需要掩码 或 长度小于1024
if (maskPayload || length <= GATHERING_WRITE_THRESHOLD) {
size += length;
}
//分配缓冲区
buf = ctx.alloc().buffer(size);
//写入第一个字节
buf.writeByte(b0);
//需要掩码写入【1111 1110】,不需要掩码写入【0111 1110】
//第一个比特代表掩码,后面7个字节代表长度,写死126表示后续俩个字节为数据的真实长度。
buf.writeByte(maskPayload ? 0xFE : 126);
//假设length=3520 二进制为【00000000 00000000 00001101 11000000】
//length分为俩个字节写入,先右移8位,把高位写入
//右移8位:length >>> 8 = [00000000 00000000 00000000 00001101] & [11111111] = [00001101]
buf.writeByte(length >>> 8 & 0xFF);
//length & 0xFF = [00000000 00000000 00001101 11000000] & [11111111] = [11000000]
//写入低8位
buf.writeByte(length & 0xFF);
} else {
//size= 10+掩码的长度(如果有掩码,没有为0)
//数据长度x>65535,ws头需要10个字节+掩码长度
int size = 10 + maskLength;
if (maskPayload || length <= GATHERING_WRITE_THRESHOLD) {
size += length;
}
//分配缓冲区
buf = ctx.alloc().buffer(size);
//写入第一个ws头字节
buf.writeByte(b0);
//写入第二个ws头字节
//如果需要掩码为[1 1111111],否则为[0 1111111]
//第一个比特表示掩码,后续7个字全都是1=127固定,表示后续8个字节为数据长度
buf.writeByte(maskPayload ? 0xFF : 127);
//写入8个字节为数据长度
buf.writeLong(length);
}
// 需要掩码的逻辑
if (maskPayload) {
//生成随机数作为XOR的KEY
int random = (int) (Math.random() * Integer.MAX_VALUE);
//返回字节数组
mask = ByteBuffer.allocate(4).putInt(random).array();
//把掩码写入到buf中
buf.writeBytes(mask);
//获得字符序列
ByteOrder srcOrder = data.order();
ByteOrder dstOrder = buf.order();
int counter = 0;
int i = data.readerIndex();
int end = data.writerIndex();
//如果字符序列相同
if (srcOrder == dstOrder) {
//把数组拼接为32位的int形式
int intMask = ((mask[0] & 0xFF) << 24)
| ((mask[1] & 0xFF) << 16)
| ((mask[2] & 0xFF) << 8)
| (mask[3] & 0xFF);
//小端序列转换掩码
if (srcOrder == ByteOrder.LITTLE_ENDIAN) {
intMask = Integer.reverseBytes(intMask);
}
//每4个字节一组与掩码Key进行XOR运算
for (; i + 3 < end; i += 4) {
int intData = data.getInt(i);
//将结果写入buf
buf.writeInt(intData ^ intMask);
}
}
//不需要掩码才会走这个循环,如果上面需要掩码i的值已经被增加,这里不会循环
for (; i < end; i++) {
//XOR计算
byte byteData = data.getByte(i);
buf.writeByte(byteData ^ mask[counter++ % 4]);
}
//返回buf到底层channel中输出
out.add(buf);
}
//不需要掩码的逻辑
else {
//如果buf缓冲区可写的空间 >=data数据可读的长度,说明buf在创建时size已经包括了length
if (buf.writableBytes() >= data.readableBytes()) {
//把data写入到buf中
buf.writeBytes(data);
//返回buf写入到底channel中
out.add(buf);
} else {
//返回buf写入到底channel中
out.add(buf);
//返回data写入到底层channel中
//计数器必须要增加+,因为在父类中对data进行了释放ReferenceCountUtil.release(cast);
//计数器+1后,相当于变成了2,那么在父类中释放一次,在channel用完后会在释放一次。
out.add(data.retain());
}
}
//正在情况不释放
release = false;
} finally {
//不出异常的情况不释放buf,由底层使用完毕后释放
if (release && buf != null) {
buf.release();
}
}
}
}
HandShakeComplete握手成功事件
在上面的WebSocketServerProtocolHandshakeHandler#channelRead方法中,在完成握手时,会fire用户事件,我们可以重写userEventTriggered方法,来获得这个事件,从而拿到握手请求时的数据。
比如:握手成功之后,直接从uri上拿到当前用户名,并绑定对应的channel
import io.netty.channel.Channel;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpHeaders;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.websocketx.TextWebSocketFrame;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.websocketx.WebSocketServerProtocolHandler;
import io.netty.util.AttributeKey;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.net.URI;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArraySet;
@Slf4j
public class WsTextHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<TextWebSocketFrame> {
private static ConcurrentHashMap<String, Channel> channels = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private static ConcurrentHashMap<String, Set<String>> userChannelIds = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private static AttributeKey<String> attrKey = AttributeKey.valueOf("uname");
public static void print() {
for (Map.Entry<String, Set<String>> userChannelEntry : userChannelIds.entrySet()) {
log.info("unameOwner: {}, channelId集合: {}", userChannelEntry.getKey(), Arrays.toString(userChannelEntry.getValue().toArray()));
}
System.out.println();
}
// 群发
public static void sendToAll(String fromChannelId, String msg) {
channels.forEach((cid, channel)->{
if (!cid.equals(fromChannelId)) {
channel.writeAndFlush(new TextWebSocketFrame(msg));
}
});
}
// 私发
public static void sendToOne(String toUname, String msg) {
Set<String> targetChannelIdSet = userChannelIds.get(toUname);
if (!targetChannelIdSet.isEmpty()) {
targetChannelIdSet.stream().forEach(targetChannelId->{
Optional.ofNullable(channels.get(targetChannelId)).ifPresent(ch->{
ch.writeAndFlush(new TextWebSocketFrame(msg));
});
});
}
}
@Override
public void channelRegistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
log.info("channelRegistered...");
super.channelRegistered(ctx);
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
log.info("channelActive...");
super.channelActive(ctx);
}
@Override
public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
String uname = ctx.channel().attr(attrKey).get();
userChannelIds.computeIfPresent(uname, (name, channelIdSet) -> {
channelIdSet.remove(ctx.channel().id().toString());
if (channelIdSet.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
return channelIdSet;
});
channels.remove(ctx.channel().id().toString());
log.info("用户: {} 下线", uname);
print();
sendToAll(null, uname + "走了~");
}
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, TextWebSocketFrame msg) throws Exception {
log.info("收到Ws客户端消息: {}", msg.text());
}
@Override
public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception {
log.info("触发用户事件...");
if (evt instanceof WebSocketServerProtocolHandler.HandshakeComplete) {
WebSocketServerProtocolHandler.HandshakeComplete handshakeComplete = (WebSocketServerProtocolHandler.HandshakeComplete) evt;
String requestUri = handshakeComplete.requestUri();
String selectedSubprotocol = handshakeComplete.selectedSubprotocol();
HttpHeaders requestHeaders = handshakeComplete.requestHeaders();
log.info("握手完成...{}, {}, {}", requestUri, selectedSubprotocol, requestHeaders);
URI uri = new URI(requestUri);
String query = uri.getQuery();
Map<String, String> queryParams = new HashMap<>();
if (query != null) {
String[] params = query.split("&");
for (String param : params) {
String[] keyValue = param.split("=");
String key = keyValue[0];
String value = keyValue.length > 1 ? keyValue[1] : "";
queryParams.put(key, value);
}
}
if (queryParams.get("uname") == null) {
ctx.channel().close();
log.error("未携带用户标识, 直接下线该用户");
print();
return;
}
String uname = String.valueOf(queryParams.get("uname"));
log.info("当前的用户是: {}", uname);
// 将用户名设置到channel中
ctx.channel().attr(attrKey).set(uname);
channels.put(ctx.channel().id().toString(), ctx.channel());
userChannelIds.compute(uname, (name, channelIds) -> {
if (channelIds != null) {
log.info("添加新的用户: {} 啦~", name);
channelIds.add(ctx.channel().id().toString());
return channelIds;
}
log.info("用户: {}, 又加channel啦~", name);
CopyOnWriteArraySet<String> set = new CopyOnWriteArraySet<>();
set.add(ctx.channel().id().toString());
return set;
});
print();
sendToAll(ctx.channel().id().toString(), "halo, I'm " + uname);
} else {
ctx.fireUserEventTriggered(evt);
}
}
}
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 捍卫中华数学产权系列4.中华级数
- 【LeetCode 面试经典150题】238. Product of Array Except Self 除自身以外数组的乘积
- 运维工程师的出路到底在哪里?
- SSM共享汽车租赁平台----计算机毕业设计
- 训练营四十五天 | ● 70. 爬楼梯 (进阶)● 322. 零钱兑换 ● 279.完全平方数
- 基于springboot+vue的家教预约管理系统
- 安卓学习笔记
- Python—使用LangCahin调用千帆大模型
- 千万不要在方法上打断点!千万不要!
- 你对自己的努力满意吗?回复10-100分