VIT代码解析 (bubbliiiing版本)
1.代码流程
以VIT-B/16为例,模型结构下图所示
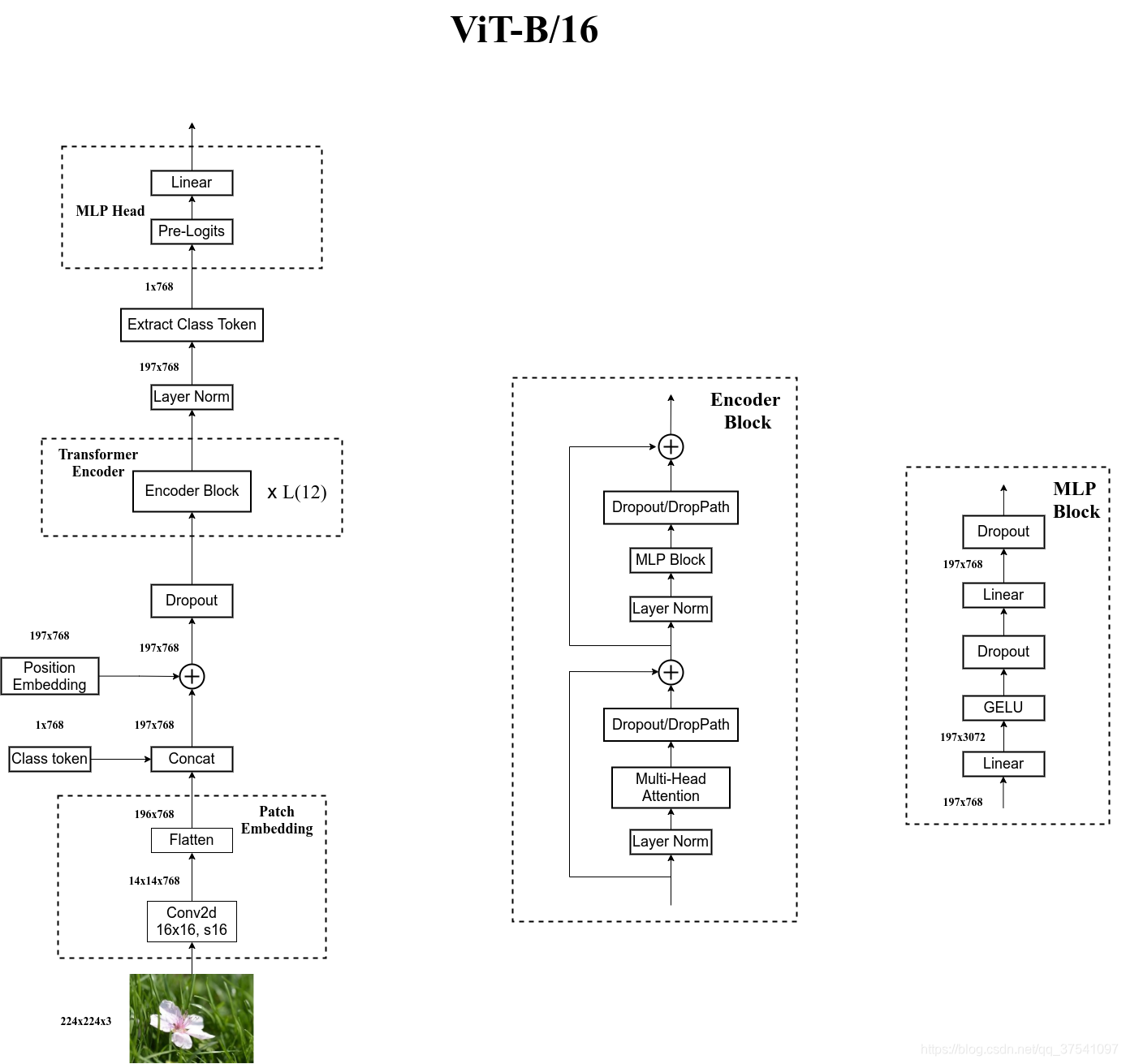
将以下列顺序进行解析
1.PatchEmbed
2.Class token
3.Position Embeding
4.Dropout
5.Encoder Block
6.MLP block
7.Layer Norm
8.Extract Class Token
9.MLP Head
2.代码块
2.1?PatchEmbed
对应网络结构图的这一块,输入为224*224*3的图片,经过Conv2d(k=16,s=16)得到768个大小为14*14的分割块,再经过展平和维度变换得到768*196,即768个序列长度为196的图像特征。
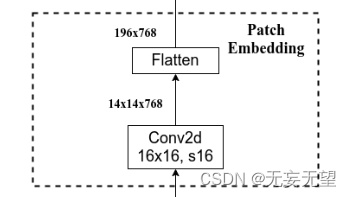
class PatchEmbed(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_shape=[224, 224], patch_size=16, in_chans=3, num_features=768, norm_layer=None, flatten=True):
super().__init__()
self.num_patches = (input_shape[0] // patch_size) * (input_shape[1] // patch_size)
self.flatten = flatten
self.proj = nn.Conv2d(in_chans, num_features, kernel_size=patch_size, stride=patch_size)
self.norm = norm_layer(num_features) if norm_layer else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.proj(x)
if self.flatten:
x = x.flatten(2).transpose(1, 2) # BCHW -> BNC
x = self.norm(x)
return x2.2 Class token
对应这一块
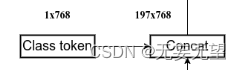
classtoken部分是transformer的分类特征。用于堆叠到序列化后的图片特征中,作为一个单位的序列特征进行特征提取。? ?在利用步长为16x16的卷积将输入图片划分成14x14的部分后,将14x14部分的特征平铺,一幅图片会存在序列长度为196的特征。
此时生成一个classtoken,将classtoken堆叠到序列长度为196的特征上,获得一个序列长度为197的特征。在特征提取的过程中,classtoken会与图片特征进行特征的交互。最终分类时,我们取出classtoken的特征,利用全连接分类。
num_features就是patchembed的输出结果
self.cls_token = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, 1, num_features))2.3Position Embeding?
对应这一块
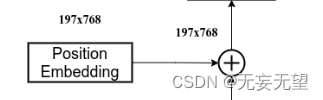
为网络提取到的特征添加上位置信息。
以输入图片为224, 224, 3为例,我们获得的序列化后的图片特征为196, 768。加上classtoken后就是197, 768
此时生成的pos_Embedding的shape也为197, 768,代表每一个特征的位置信息。
?
self.pos_embed = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, num_patches + 1, num_features))?2.4 Dropout
对应这一块
def drop_path(x, drop_prob: float = 0., training: bool = False):
if drop_prob == 0. or not training:
return x
keep_prob = 1 - drop_prob
shape = (x.shape[0],) + (1,) * (x.ndim - 1)
random_tensor = keep_prob + torch.rand(shape, dtype=x.dtype, device=x.device)
random_tensor.floor_()
output = x.div(keep_prob) * random_tensor
return output
class DropPath(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, drop_prob=None):
super(DropPath, self).__init__()
self.drop_prob = drop_prob
def forward(self, x):
return drop_path(x, self.drop_prob, self.training)?2.5 Encoder Block
对应这一块
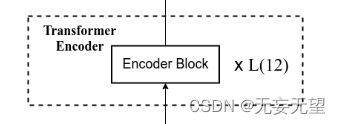
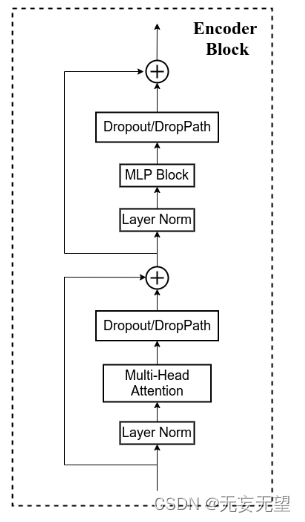
Encoder Block的作用是将输入序列进行编码,生成对应的语义向量。它由多个子层组成,包括自注意力机制(Self-Attention)和前馈神经网络(Feed-Forward Neural Network)。自注意力机制用于捕捉输入序列中不同位置之间的依赖关系,而前馈神经网络则用于对每个位置的特征进行非线性变换。通过多个Encoder Block的堆叠,可以逐步提取输入序列的语义信息,并生成对应的语义向量c,用于后续的解码工作。?
class Block(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, num_heads, mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=False, drop=0., attn_drop=0.,
drop_path=0., act_layer=GELU, norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm):
super().__init__()
self.norm1 = norm_layer(dim)
self.attn = Attention(dim, num_heads=num_heads, qkv_bias=qkv_bias, attn_drop=attn_drop, proj_drop=drop)
self.norm2 = norm_layer(dim)
self.mlp = Mlp(in_features=dim, hidden_features=int(dim * mlp_ratio), act_layer=act_layer, drop=drop)
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x):
x = x + self.drop_path(self.attn(self.norm1(x)))
x = x + self.drop_path(self.mlp(self.norm2(x)))
return x2.5.1Multi-Head Attention
对应这一块
# ? Attention机制
# ? 将输入的特征qkv特征进行划分,首先生成query, key, value。query是查询向量、key是键向量、v是值向量。
# ? 然后利用 查询向量query 点乘 转置后的键向量key,这一步可以通俗的理解为,利用查询向量去查询序列的特征,获得序列每个部分的重要程度score。
# ? 然后利用 score 点乘 value,这一步可以通俗的理解为,将序列每个部分的重要程度重新施加到序列的值上去。?
class Attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, num_heads=8, qkv_bias=False, attn_drop=0., proj_drop=0.):
super().__init__()
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.scale = (dim // num_heads) ** -0.5
self.qkv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 3, bias=qkv_bias)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop)
def forward(self, x):
B, N, C = x.shape
qkv = self.qkv(x).reshape(B, N, 3, self.num_heads, C // self.num_heads).permute(2, 0, 3, 1, 4)
q, k, v = qkv[0], qkv[1], qkv[2]
attn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1)) * self.scale
attn = attn.softmax(dim=-1)
attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
x = (attn @ v).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B, N, C)
x = self.proj(x)
x = self.proj_drop(x)
return x
2.6 MLP block
对应这一块
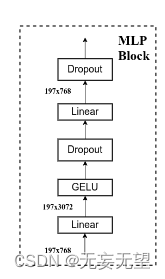
MLP在ViT(Vision Transformer)中的作用是替代self-attention机制,用于实现特征的混合和整合。在ViT中,首先将输入图像分割成一系列的小块,然后通过patch embedding将每个小块映射为一个向量表示。接下来,这些向量会经过多个Mixer Layer进行处理。
每个Mixer Layer由两个部分组成:channel-mixing MLPs和token-mixing MLPs。channel-mixing MLPs用于在每个小块的通道维度上进行特征混合,以捕捉不同通道之间的关系。而token-mixing MLPs则用于在每个小块的位置维度上进行特征混合,以捕捉不同位置之间的关系。
与传统的self-attention机制相比,MLP在ViT中的作用是通过全连接层来建模特征之间的关系,而不是通过注意力权重来计算特征的重要性。这种替代方式使得ViT在处理图像任务时能够取得和传统的self-attention机制相媲美的结果。
因为token-mixing MLPs对输入tokens的顺序非常敏感,所以在Mixer中不适用positional encoding。这意味着Mixer不会考虑输入图像的位置信息,而仅仅关注特征之间的关系。这种设计选择使得Mixer在处理图像时更加高效,并且能够取得很好的性能。
?
class Mlp(nn.Module):
""" MLP as used in Vision Transformer, MLP-Mixer and related networks
"""
def __init__(self, in_features, hidden_features=None, out_features=None, act_layer=GELU, drop=0.):
super().__init__()
out_features = out_features or in_features
hidden_features = hidden_features or in_features
drop_probs = (drop, drop)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(in_features, hidden_features)
self.act = act_layer()
self.drop1 = nn.Dropout(drop_probs[0])
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_features, out_features)
self.drop2 = nn.Dropout(drop_probs[1])
def forward(self, x):
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.act(x)
x = self.drop1(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.drop2(x)
return x2.6.1GELU
对应这一块
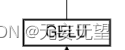
class GELU(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(GELU, self).__init__()
def forward(self, x):
return 0.5 * x * (1 + F.tanh(np.sqrt(2 / np.pi) * (x + 0.044715 * torch.pow(x,3))))2.7 Layer Norm
对应这一块
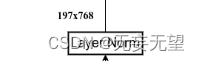
self.norm = norm_layer(num_features)?
2.8 Extract Class Token
对应这一块

return x[:, 0]?
2.9MLP Head
对应这一块
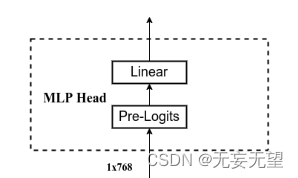
self.head = nn.Linear(num_features, num_classes) if num_classes > 0 else nn.Identity()3.完整代码
from functools import partial
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
#--------------------------------------#
# Gelu激活函数的实现
# 利用近似的数学公式
#--------------------------------------#
class GELU(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(GELU, self).__init__()
def forward(self, x):
return 0.5 * x * (1 + F.tanh(np.sqrt(2 / np.pi) * (x + 0.044715 * torch.pow(x,3))))
def drop_path(x, drop_prob: float = 0., training: bool = False):
if drop_prob == 0. or not training:
return x
keep_prob = 1 - drop_prob
shape = (x.shape[0],) + (1,) * (x.ndim - 1)
random_tensor = keep_prob + torch.rand(shape, dtype=x.dtype, device=x.device)
random_tensor.floor_()
output = x.div(keep_prob) * random_tensor
return output
class DropPath(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, drop_prob=None):
super(DropPath, self).__init__()
self.drop_prob = drop_prob
def forward(self, x):
return drop_path(x, self.drop_prob, self.training)
class PatchEmbed(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_shape=[224, 224], patch_size=16, in_chans=3, num_features=768, norm_layer=None, flatten=True):
super().__init__()
self.num_patches = (input_shape[0] // patch_size) * (input_shape[1] // patch_size)
self.flatten = flatten
self.proj = nn.Conv2d(in_chans, num_features, kernel_size=patch_size, stride=patch_size)
self.norm = norm_layer(num_features) if norm_layer else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.proj(x)
if self.flatten:
x = x.flatten(2).transpose(1, 2) # BCHW -> BNC
x = self.norm(x)
return x
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# Attention机制
# 将输入的特征qkv特征进行划分,首先生成query, key, value。query是查询向量、key是键向量、v是值向量。
# 然后利用 查询向量query 点乘 转置后的键向量key,这一步可以通俗的理解为,利用查询向量去查询序列的特征,获得序列每个部分的重要程度score。
# 然后利用 score 点乘 value,这一步可以通俗的理解为,将序列每个部分的重要程度重新施加到序列的值上去。
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
class Attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, num_heads=8, qkv_bias=False, attn_drop=0., proj_drop=0.):
super().__init__()
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.scale = (dim // num_heads) ** -0.5
self.qkv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 3, bias=qkv_bias)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop)
def forward(self, x):
B, N, C = x.shape
qkv = self.qkv(x).reshape(B, N, 3, self.num_heads, C // self.num_heads).permute(2, 0, 3, 1, 4)
q, k, v = qkv[0], qkv[1], qkv[2]
attn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1)) * self.scale
attn = attn.softmax(dim=-1)
attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
x = (attn @ v).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B, N, C)
x = self.proj(x)
x = self.proj_drop(x)
return x
class Mlp(nn.Module):
""" MLP as used in Vision Transformer, MLP-Mixer and related networks
"""
def __init__(self, in_features, hidden_features=None, out_features=None, act_layer=GELU, drop=0.):
super().__init__()
out_features = out_features or in_features
hidden_features = hidden_features or in_features
drop_probs = (drop, drop)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(in_features, hidden_features)
self.act = act_layer()
self.drop1 = nn.Dropout(drop_probs[0])
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_features, out_features)
self.drop2 = nn.Dropout(drop_probs[1])
def forward(self, x):
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.act(x)
x = self.drop1(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.drop2(x)
return x
class Block(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, num_heads, mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=False, drop=0., attn_drop=0.,
drop_path=0., act_layer=GELU, norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm):
super().__init__()
self.norm1 = norm_layer(dim)
self.attn = Attention(dim, num_heads=num_heads, qkv_bias=qkv_bias, attn_drop=attn_drop, proj_drop=drop)
self.norm2 = norm_layer(dim)
self.mlp = Mlp(in_features=dim, hidden_features=int(dim * mlp_ratio), act_layer=act_layer, drop=drop)
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x):
x = x + self.drop_path(self.attn(self.norm1(x)))
x = x + self.drop_path(self.mlp(self.norm2(x)))
return x
class VisionTransformer(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self, input_shape=[224, 224], patch_size=16, in_chans=3, num_classes=1000, num_features=768,
depth=12, num_heads=12, mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True, drop_rate=0.1, attn_drop_rate=0.1, drop_path_rate=0.1,
norm_layer=partial(nn.LayerNorm, eps=1e-6), act_layer=GELU
):
super().__init__()
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 224, 224, 3 -> 196, 768
#-----------------------------------------------#
self.patch_embed = PatchEmbed(input_shape=input_shape, patch_size=patch_size, in_chans=in_chans, num_features=num_features)
num_patches = (224 // patch_size) * (224 // patch_size)
self.num_features = num_features
self.new_feature_shape = [int(input_shape[0] // patch_size), int(input_shape[1] // patch_size)]
self.old_feature_shape = [int(224 // patch_size), int(224 // patch_size)]
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# classtoken部分是transformer的分类特征。用于堆叠到序列化后的图片特征中,作为一个单位的序列特征进行特征提取。
#
# 在利用步长为16x16的卷积将输入图片划分成14x14的部分后,将14x14部分的特征平铺,一幅图片会存在序列长度为196的特征。
# 此时生成一个classtoken,将classtoken堆叠到序列长度为196的特征上,获得一个序列长度为197的特征。
# 在特征提取的过程中,classtoken会与图片特征进行特征的交互。最终分类时,我们取出classtoken的特征,利用全连接分类。
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 196, 768 -> 197, 768
self.cls_token = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, 1, num_features))
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 为网络提取到的特征添加上位置信息。
# 以输入图片为224, 224, 3为例,我们获得的序列化后的图片特征为196, 768。加上classtoken后就是197, 768
# 此时生成的pos_Embedding的shape也为197, 768,代表每一个特征的位置信息。
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 197, 768 -> 197, 768
self.pos_embed = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, num_patches + 1, num_features))
self.pos_drop = nn.Dropout(p=drop_rate)
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 197, 768 -> 197, 768 12次
#-----------------------------------------------#
dpr = [x.item() for x in torch.linspace(0, drop_path_rate, depth)]
self.blocks = nn.Sequential(
*[
Block(
dim = num_features,
num_heads = num_heads,
mlp_ratio = mlp_ratio,
qkv_bias = qkv_bias,
drop = drop_rate,
attn_drop = attn_drop_rate,
drop_path = dpr[i],
norm_layer = norm_layer,
act_layer = act_layer
)for i in range(depth)
]
)
self.norm = norm_layer(num_features)
self.head = nn.Linear(num_features, num_classes) if num_classes > 0 else nn.Identity()
def forward_features(self, x):
x = self.patch_embed(x)
cls_token = self.cls_token.expand(x.shape[0], -1, -1)
x = torch.cat((cls_token, x), dim=1)
cls_token_pe = self.pos_embed[:, 0:1, :]
img_token_pe = self.pos_embed[:, 1: , :]
img_token_pe = img_token_pe.view(1, *self.old_feature_shape, -1).permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
img_token_pe = F.interpolate(img_token_pe, size=self.new_feature_shape, mode='bicubic', align_corners=False)
img_token_pe = img_token_pe.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).flatten(1, 2)
pos_embed = torch.cat([cls_token_pe, img_token_pe], dim=1)
x = self.pos_drop(x + pos_embed)
x = self.blocks(x)
x = self.norm(x)
return x[:, 0]
def forward(self, x):
x = self.forward_features(x)
x = self.head(x)
return x
def freeze_backbone(self):
backbone = [self.patch_embed, self.cls_token, self.pos_embed, self.pos_drop, self.blocks[:8]]
for module in backbone:
try:
for param in module.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
except:
module.requires_grad = False
def Unfreeze_backbone(self):
backbone = [self.patch_embed, self.cls_token, self.pos_embed, self.pos_drop, self.blocks[:8]]
for module in backbone:
try:
for param in module.parameters():
param.requires_grad = True
except:
module.requires_grad = True
def vit_b_16(input_shape=[224, 224], pretrained=False, num_classes=1000):
model = VisionTransformer(input_shape)
if pretrained:
model.load_state_dict(torch.load("model_data/vit-patch_16.pth"))
if num_classes!=1000:
model.head = nn.Linear(model.num_features, num_classes)
return model本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 2024年品牌最核心增长路径——不是促销,而是回归客户体验,AI成得力助手
- 系统存储架构升级分享
- 【C语言】联合体与枚举详解
- 【蓝桥杯重点】还不快来学贪心算法!
- Java spring mvc 和 struts 的区别是什么?
- 【力扣题解】P106-从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树-Java题解
- 【深入探索Python库】用于访问与 Python 解释器密切相关变量和函数的sys库(下)
- 【栈与队列专题】滑动窗口的最大值
- Hive文件存储与压缩
- JS中Set、WeakSet、Map 和 WeakMap区别