【阅读笔记】LoRAHub:Efficient Cross-Task Generalization via Dynamic LoRA Composition
一、论文信息
1 论文标题
LoRAHub:Efficient Cross-Task Generalization via Dynamic LoRA Composition
2 发表刊物
NIPS2023_WorkShop
3 作者团队
Sea AI Lab, Singapore
4 关键词
LLMs、LoRA
二、文章结构
1 引言
1.1 研究动机
Investigation into the inherent modularity and composability of LoRA modules. To verify is it feasbile to compose LoRA modules for efficiently generalizing towards unseen tasks?
1.2 任务背景
Intro-P1:
LLM->issues->LoRA->efficiency->inherent modularity and composability
Intro-P2:
generalization of LoRA->automatic assembling without human design->few-shot->auto orchestrate->LoRAHub、LoRAHub Learning
Intro-P3:
Experiments:Flan-T5->BBH benchmark->与few-shot ICL相比效果相当->减少了推理时间->gradient free减少计算开销
Intro-P4:
can work on CPU-only machine->LoRA modules can share, access, apply and reuse
1.3 问题陈述
LLM
- pre-trained Transformer / have been fine-tuned with instruction-following datasets
- encoder-decoder / decoder-only
Cross-Task Generalization
- zero-shot learing
- few-shot learing
当新任务的含标签数据太少时,直接fine-tune效率和效果都不能保证。理想的方式是直接让模型能够基于这少部分数据直接适应新任务场景。
LoRA Tuning
traditional LoRA methods primarily concentrate on training and testing within the same tasks, rather than venturing into few-shot cross-task generalization.
2 创新方法
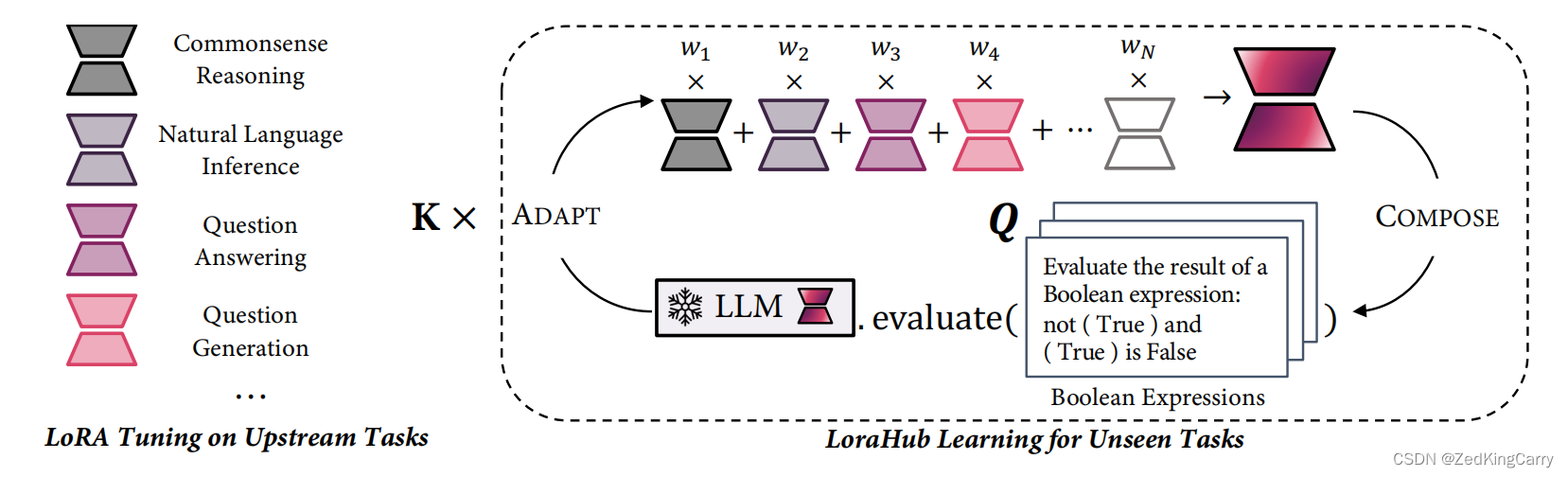
LoraHub learning
- Compose Stage:
existing LoRA modules are integrated into one unified module, employing a set of weights, denoted as w w w, as coefficients. 【加权合并】 - Adapt Stage:
the amalgamated (合并的) LoRA module is evaluated on a few examples from the unseen task.
Subsequently, a gradient-free algorithm is applied to refine w. After executing K iterations, a highly adapted LoRA module is produced, which can be incorporated with the LLM to perform the intended task.
Gradient-free methodology
- Shiwa:CMA-ES (Covariance Matrix Adaptive Evolution Strategies)
- For our case, we deploy this algorithm to shape the search space of w, and eventually select the best weights based on their performance on the few-shot examples from the unseen task.
其它
无
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- C++ 二叉搜索树(BST)的实现(非递归版本与递归版本)与应用
- 精品基于Uniapp+springboot农产品安全领域的信息采集系统App
- 飞天使-docker知识点13-查找docker run 启动时候命令与升级docker版本
- 代码随想录算法训练营第三十八天| 509.斐波那契数、70.爬楼梯、746.使用最小花费爬楼梯
- Kotlin/JS工程构建及编译运行到浏览器
- 五粮液“老二”不好当,业绩增速不及均值
- 基于深度学习的垃圾检测与分类系统(含UI界面、yolov5、Python代码、数据集)
- 我与编程的不解之缘:从Basic到大数据的漫漫探索之旅
- unity C#中使用ref、out区别和使用案例
- 在程序中链接静态库 和 动态库