快速排序算法
发布时间:2024年01月17日
?一、结构体赋值知识点
 结构体变量的三种赋值方式以及三种常见错误的赋值方式-云社区-华为云 (huaweicloud.com)
结构体变量的三种赋值方式以及三种常见错误的赋值方式-云社区-华为云 (huaweicloud.com)![]() https://bbs.huaweicloud.com/blogs/281765正确的赋值:
https://bbs.huaweicloud.com/blogs/281765正确的赋值:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
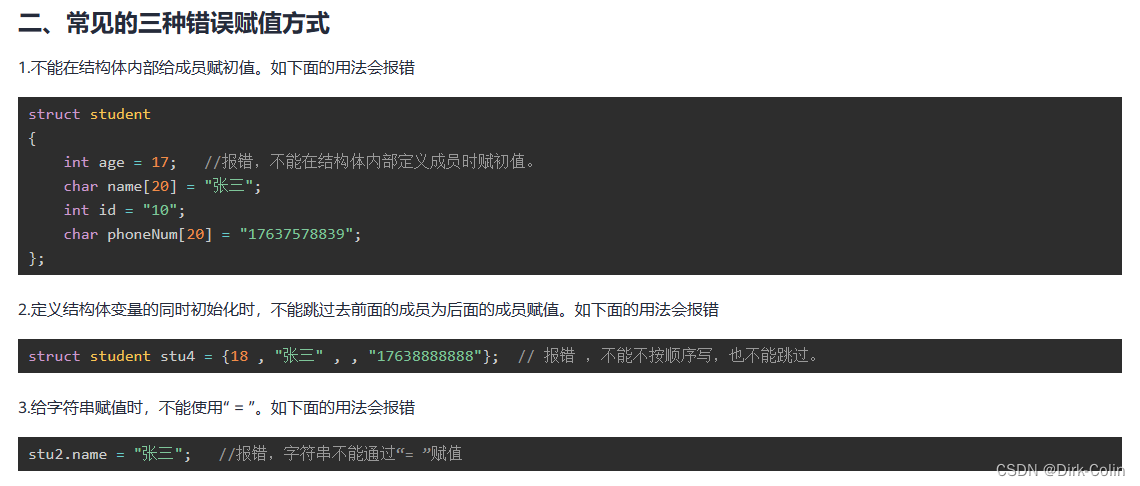
struct student
{
int age; //年龄
char name[20]; //姓名
int id; //学号
char phoneNum[20]; //手机号
// int test = 16; //报错 ,不能在结构体内部赋值
// id = 1; //报错 ,不能在结构体内部赋值
};
int main()
{
printf("年龄\t姓名\t学号\t手机号");
printf("\n=================================\n");
//一、定义变量的同时初始化为stu1赋值
struct student stu1 = {18 , "张三", 17 , "17638888888"}; //类似于数组,必须严格按照定义结构体类型时的成员顺序填写
// struct student stu4 = {18 , "张三" , , "17638888888"}; // 报错 ,不能不按顺序写,也不能跳过。
printf("%d\t%s\t%d\t%s\n",stu1.age,stu1.name,stu1.id,stu1.phoneNum);
//二、利用赋值语句逐条为stu2赋值
struct student stu2;
stu2.age = 19;
// stu2.name = "张三"; //报错,字符串不能通过“= ”赋值
strcpy(stu2.name,"李四");
stu2.id = 18;
strcpy(stu2.phoneNum,"19334533534");
printf("%d\t%s\t%d\t%s\n",stu2.age,stu2.name,stu2.id,stu2.phoneNum);
//三、通过scanf()函数为stu3赋值
struct student stu3;
scanf("%d%s%d%s",&stu3.age,stu3.name,&stu3.id,stu3.phoneNum);
printf("%d\t%s\t%d\t%s\n",stu3.age,stu3.name,stu3.id,stu3.phoneNum);
return 0;
} 

二、快速排序算法
【数据结构】八大排序(超详解+附动图+源码)_数据结构排序-CSDN博客![]() https://blog.csdn.net/Edward_Asia/article/details/121419975
https://blog.csdn.net/Edward_Asia/article/details/121419975
?利用快速排序对以下数据进行排序1,5,7,8,3,5,9,4,1,0
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
void swap(int* a, int* b)
{
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
int search_key(int* parr, int begin, int end)
{
int key = parr[end];
//比key小的在左边,比key大的在右边
int i = (begin - 1);
int j = 0;
for (j = begin; j < end; j++)
{
//这里begin不能是0,就是不能是j = 0;j<end;j++
//不然就死了,调了老久
if (parr[j] <= key)
{
i++;
swap(&parr[i], &parr[j]);
}
}
swap(&parr[i + 1], &parr[end]);
return i + 1;
}
void quick_sort(int* parr, int begin, int end)
{
if(begin < end)
{
int index = search_key(parr, begin, end);
quick_sort(parr, begin, index - 1);
quick_sort(parr, index + 1, end);
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1,5,7,8,3,5,9,4,1,0 };
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int i = 0;
printf("排序前的数组:");
for (i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
printf("%d ", *(arr + i));
}
quick_sort(arr, 0, sz - 1);
printf("\n");
printf("排序后的数组:");
for (i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
printf("%d ", *(arr + i));
}
return 0;
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_57604904/article/details/135370136
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 专业课130+,总分390+四川大学951信号与系统考研通信,电子信息经验分享
- 1、分布式系统的一致性与共识性
- YOLOv5改进 | 主干篇 | 12月最新成果UniRepLknet特征提取网络(附对比试验效果图)
- 甜美、有气质、淑女感十足的衬衫&马甲
- vue3 实现el-date-picker日期筛选过程
- 【Stress-ng】CentOS 7 离线安装Stress-ng
- MySQL视图索引
- [Python] scikit-learn - accuracy_score(准确率分数)函数介绍和使用场景(案例)
- Git学习笔记(第5章):Git团队协作机制
- IP多播多播多播