代码随想录算法训练营Day14 | 257. 二叉树的所有路径、110.平衡二叉树、404.左叶子之和
发布时间:2023年12月29日
LeetCode 257 二叉树的所有路径
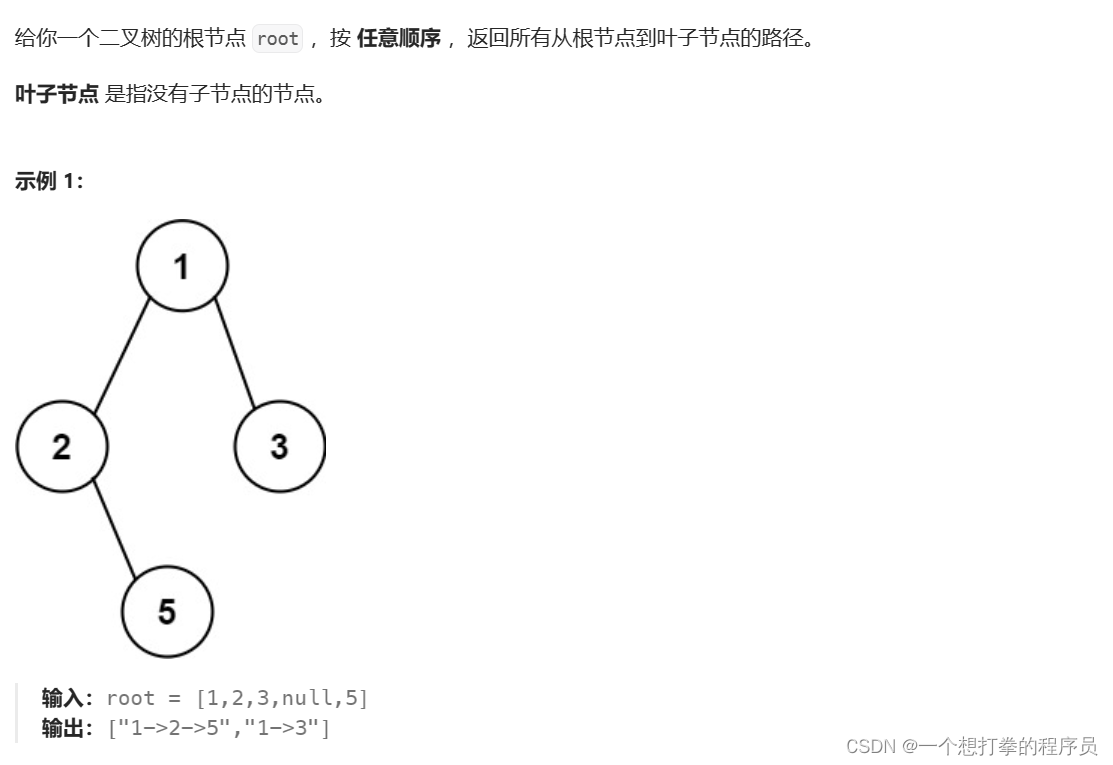
本题思路:利用前序遍历的思想。用递归来解决。
- 首先找到递归的出口:如果该节点的左右孩子为空,说明已经到了叶子节点,那么就保存这条路径上的所有元素。然后添加到总结果中
- 如果左孩子不为空,就把当左孩子上的往左走的路径全部保存,保存完后, 节点回溯到这个左孩子上
- 如果右孩子不为空。再把右孩子上的往右走的路径全部保存,保存完后,节点回溯到这个右孩子上。
class Solution {
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
List<String> res = new LinkedList();
if(root == null){
return res;
}
List<Integer> paths = new LinkedList();
travel(root,paths,res);
return res;
}
public void travel(TreeNode root, List<Integer> paths, List<String> res){
// 先把根节点放入Paths中
paths.add(root.val);
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for(int i = 0; i < paths.size() - 1; i++){
sb.append(paths.get(i) + "->");
}
sb.append(paths.get(paths.size() - 1));
res.add(sb.toString());
return;
}
if(root.left != null){
travel(root.left,paths,res);
paths.remove(paths.size()-1);
}
if(root.right != null){
travel(root.right,paths,res);
paths.remove(paths.size()-1);
}
}
}
LeetCode 110 平衡二叉树
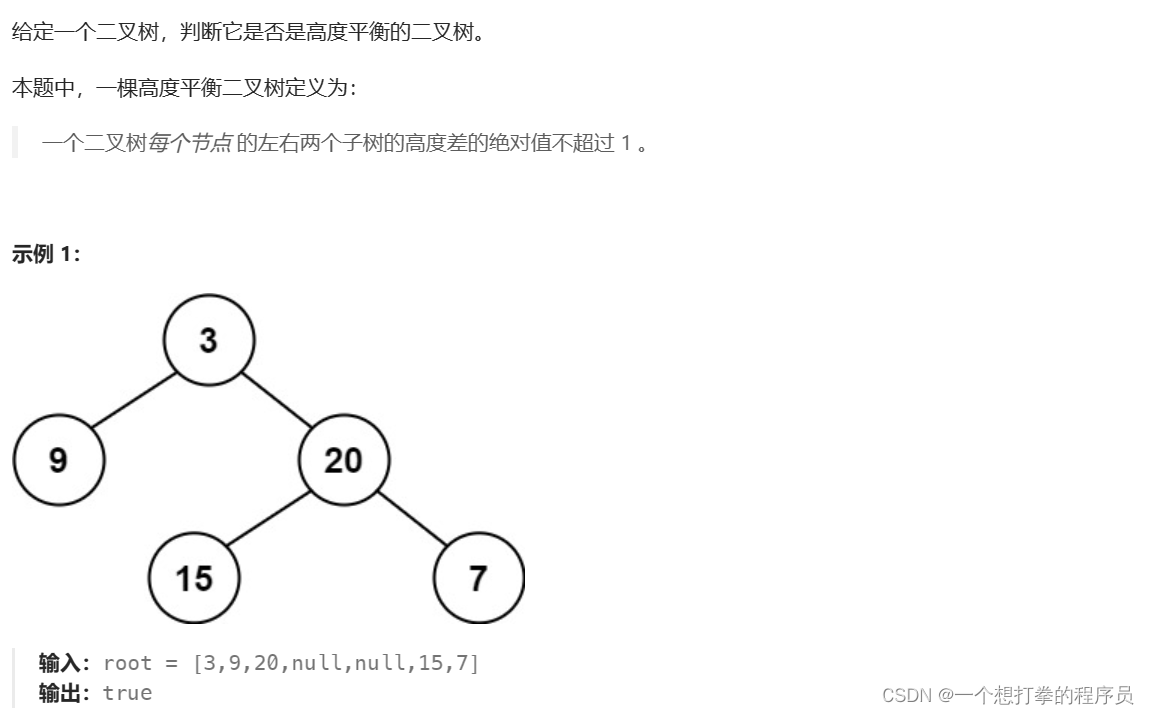
本题思路: 递归思想。
- 先找出口,root == null,返回 true。
- ①先以根节点分为左右子树,如果左子树和右子树高度差绝对值小于1,说明左右子树平衡
- ②然后再递归判断,左孩子为根节点的左右子树是否平衡。
- ③然后再递归判断 ,右孩子为根节点的左右子树是否平衡
- 最后如果①②③都为true,说明平衡
class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return true;
}
int l = height(root.left);
int r = height(root.right);
boolean res = Math.abs(l-r)<=1?true:false;
boolean left = isBalanced(root.left);
boolean right = isBalanced(root.right);
return res && left && right;
}
public int height(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int left = height(root.left);
int right = height(root.right);
return Math.max(left,right) + 1;
}
}
LeetCode 404 左叶子之和
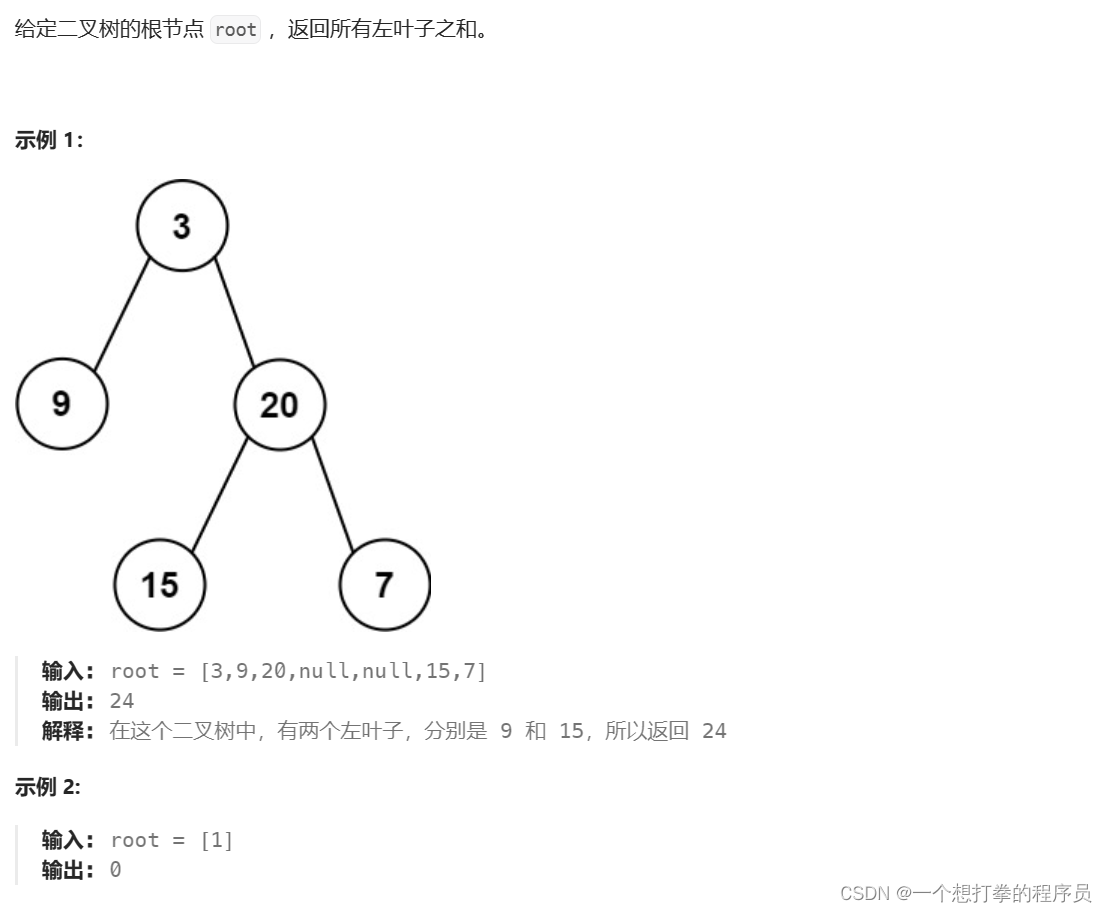
本题思路: 递归思想
- 先找到出口 root == null,返回 0
- ①单层判断逻辑:该节点的左孩子不为空,并且该节点的左孩子的左右孩子都为空,就 记录 root.left.val 值
- ②然后递归遍历 root 的左子树得到和
- ③然后递归遍历 root 的右子树得到和
- 最后累加 ①②③
class Solution {
public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
// 用来记录当前节点的直接左叶子节点的值
int res = (root.left != null && root.left.left == null && root.left.right == null) == true?root.left.val:0;
int l = sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left);
int r = sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right);
return l + r + res;
}
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/hero_jy/article/details/135298183
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- node.js项目express的初始化
- Build .NET MAUI Apps on Mac
- DA14531-外设驱动篇-UART收发通信应用
- 挖矿木马应急响应-案例分析
- 代码随想录刷题题Day17
- FISCO BCOS(十六)多机部署及相关操作
- 局部阈值 local_threshold
- Dockerfile中CMD命令的用法,你了解几个?
- Maven Scope 取值含义
- 终端(命令提示符或Windows PowerShell或Azure Cloud Shell)概述