面试算法107:矩阵中的距离
发布时间:2024年01月09日
题目
输入一个由0、1组成的矩阵M,请输出一个大小相同的矩阵D,矩阵D中的每个格子是矩阵M中对应格子离最近的0的距离。水平或竖直方向相邻的两个格子的距离为1。假设矩阵M中至少有一个0。
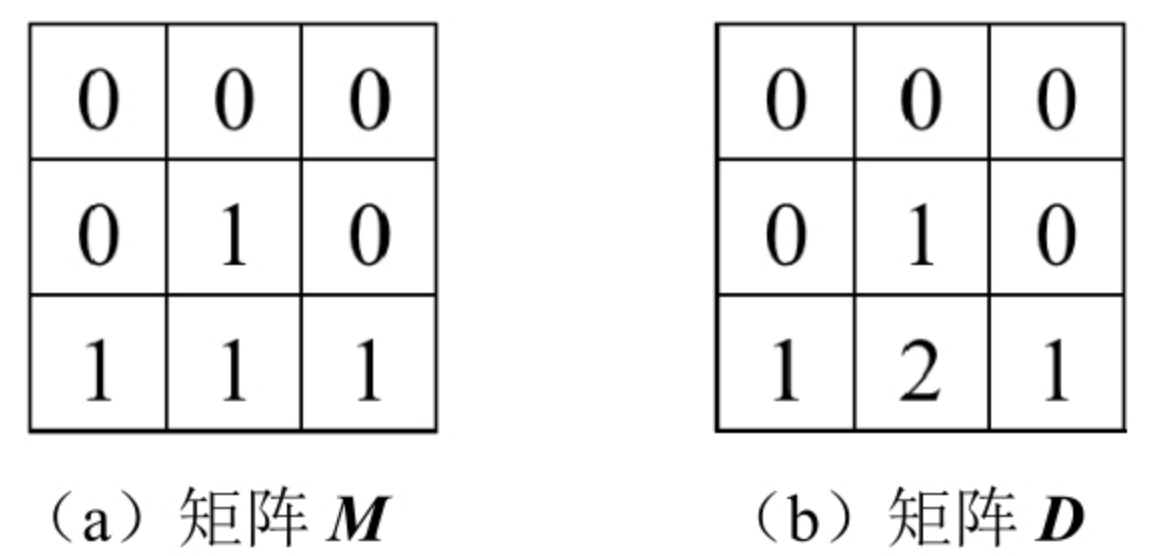
例如,图(a)是一个只包含0、1的矩阵M,它的每个格子离最近的0的距离如(b)的矩阵D所示。M[0][0]等于0,因此它离最近的0的距离是0,所以D[0][0]等于0。M[2][1]等于1,离它最近的0的坐标是(0,1)、(1,0)、(1,2),它们离坐标(2,1)的距离都是2,所以D[2][1]等于2。
分析
这个题目要求计算每个格子离最近的0的距离。根据题目的要求,上、下、左、右相邻的两个格子的距离为1。可以将图看成一个无权图,图中两个节点的距离是连通它们的路径经过的边的数目。由于这个问题与无权图的最近距离相关,因此可以考虑应用广度优先搜索解决。
解
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] matrix = {{0, 0, 0}, {0, 1, 0}, {1, 1, 1}};
int[][] result = updateMatrix(matrix);
for (int[] item : result) {
System.out.println(item[0] + " " + item[1] + " " + item[2]);
}
}
public static int[][] updateMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
int rows = matrix.length;
int cols = matrix[0].length;
int[][] dists = new int[rows][cols];
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if (matrix[i][j] == 0) {
// 先将所有的0当作初始节点添加到队列中
queue.add(new int[] {i, j});
dists[i][j] = 0;// 离最近的0的距离为0
}
else {
dists[i][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;// 先初始化为最大值
}
}
}
int[][] dirs = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] pos = queue.remove();
int dist = dists[pos[0]][pos[1]];
for (int[] dir : dirs) {
int r = pos[0] + dir[0];
int c = pos[1] + dir[1];
if (r >= 0 && c >= 0 && r < rows && c < cols) {
// dists[r][c]初始化为最大值,此处取一个最小值
if (dists[r][c] > dist + 1) {
dists[r][c] = dist + 1;
queue.add(new int[] {r, c});
}
}
}
}
return dists;
}
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/GoGleTech/article/details/135487815
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- git教程(基于vscoede)
- C++力扣题目56--合并区间 738--单调递增的数字 968--监控二叉树
- MyBatis的删除、修改、插入操作!!!
- 别再用信号放大器了,那东西就是纯智商税!高人气随身WiFi第一名,随身WiFi哪个品牌最靠谱
- 长知识,Session强制账号下线,限制账号登录!
- 数字图像处理期末速成笔记
- 磁盘管理,文件系统,挂载
- C#高级 06 文件操作
- ZYNQ程序固化
- 深入解析Python网络编程与Web开发:urllib、requests和http模块的功能、用法及在构建现代网络应用中的关键作用